Resistors in Series & Parallel Circuits (WJEC GCSE Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 3420
Resistors in Series & Parallel Circuits
Adding resistors in series increases the total resistance of the circuit
This is because in a series circuit, there is only one loop and therefore one path that the electrons can take
All the electrons have to pass through all the resistors, reducing the current
Therefore total resistance is increased
Adding resistors in parallel decreases the total resistance of the circuit
This is because in a parallel circuit, there are multiple loops and therefore multiple paths that the electrons can take
These extra pathways increase the number of electrons flowing around the circuit, increasing the current
Therefore, total resistance is decreased
These rules are also true for any components (because all components have resistance)
How Adding Resistors in Series & Parallel affects Total Resistance
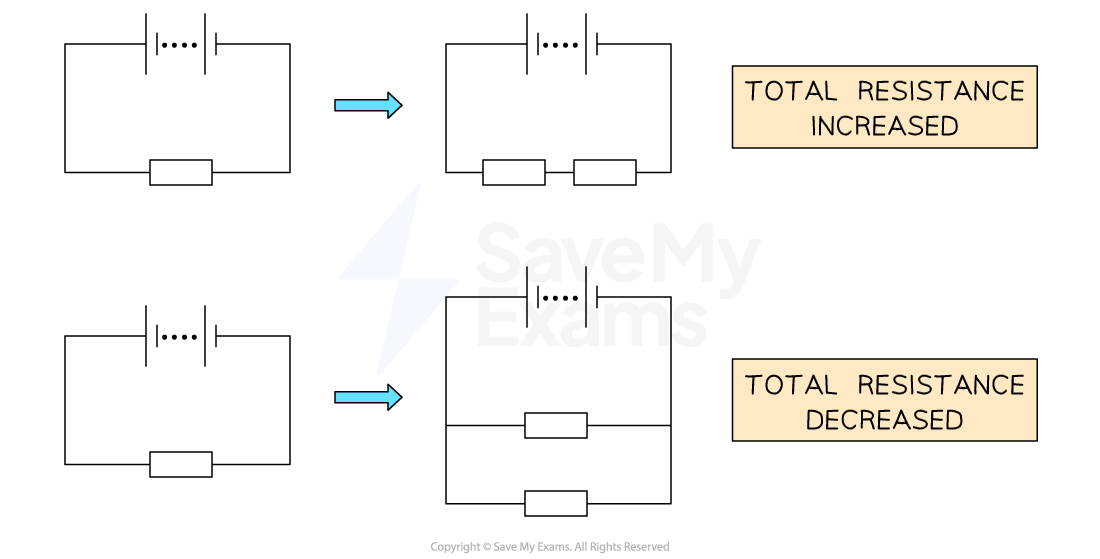
Adding resistors in series increases the total resistance of a circuit. Adding resistors in parallel decreases the total resistance of a circuit
Calculating Resistance in Series Circuits
When two or more resistors are connected in series, the total resistance is equal to the sum of their individual resistances
For two or more resistors of resistance the total resistance can be calculated using:
Where:
R is the total resistance, in ohms (Ω)
R1 is the resistance of the first resistor, in ohms (Ω)
R2 is the resistance of the second resistor, in ohms (Ω)
Increasing the number of resistors in series increases the overall resistance and decreases the current
This is because the electrons now have more resistors to pass through
Resistance and Voltage of Resistors in Series
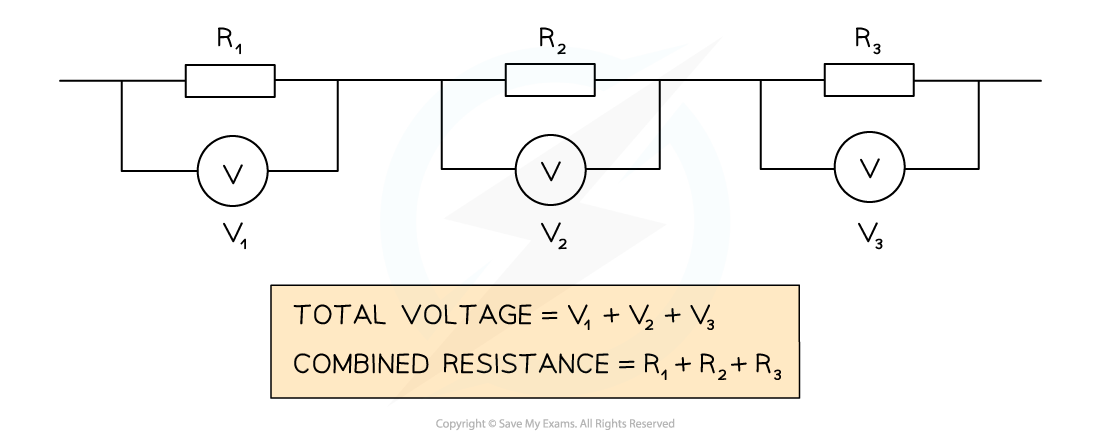
The total resistance of resistors in series is the sum of the individual resistors. The total voltage across the resistors is the sum of the voltages across each individual resistor
Worked Example
The combined resistance R in the following series circuit is 60 Ω.What is the resistance value of R2?
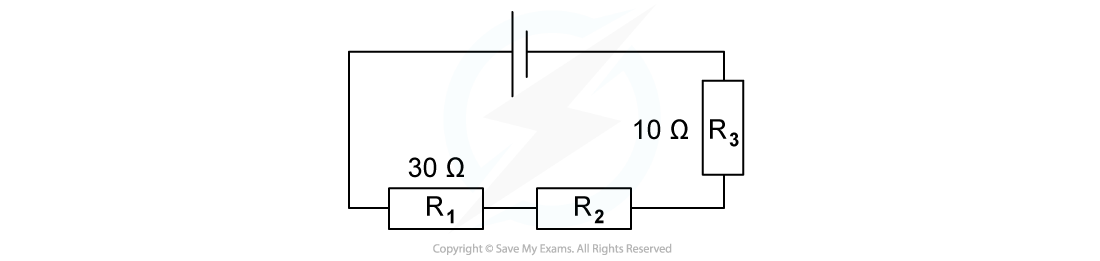
A. 100 Ω
B. 30 Ω
C. 20 Ω
D. 40 Ω
Answer: C
Step 1: Write down the equation for the combined resistance in series
R = R1 + R2 + R3
Step 2: Substitute the values for total resistance R and the other resistors
60 Ω = 30 Ω + R2 + 10 Ω
Step 3: Rearrange for R2
R2 = 60 Ω – 30 Ω – 10 Ω
R2 = 20 Ω
Calculating Resistance in Parallel Circuits
Higher Tier Only
When two or more resistors are connected in parallel, the combined resistance decreases
For two or more resistors connected in parallel, the total resistance can be found by using:
Where R is the total resistance measured in ohms (Ω)
Resistors Positioned in Parallel

When resistors are connected in parallel, the total resistance of the circuit is decreased
The advantages of resistors positioned in parallel are:
The components can be individually controlled, using their own switches
If one component stops working the others will continue to function
Worked Example
A 30 Ω resistor and a 20 Ω resistor are placed in parallel within a circuit.
Calculate the combined resistance of these resistors.
Answer:
Step 1: Write out the equation for resistors in parallel
Step 2: Substitute in the values of the resistors
Because the values are added, it doesn't matter which resistor is R1 or R2
Step 3: Calculate
You can use the fraction button on your calculator to type in the values, or you could do (1 ÷ 30) + (1 ÷ 20)
Step 4: Calculate R
To find the reciprocal you can use the reciprocal button on your calculator labelled
or
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The most common error that students make is giving an answer for and forgetting to calculate R, always double check that you have remembered to do this!

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?