Newton’s Second Law (OCR GCSE Physics A (Gateway)) : Revision Note
Newton's Second Law
Newton's second law of motion states:
The acceleration of an object is proportional to the resultant force acting on it and inversely proportional to the object's mass
Newton's second law explains the following important principles:
An object will accelerate (change its velocity) in response to a resultant force
The bigger this resultant force, the larger the acceleration
For a given force, the greater the object's mass, the smaller the acceleration experienced
The image below shows some examples of Newton's second law in action:
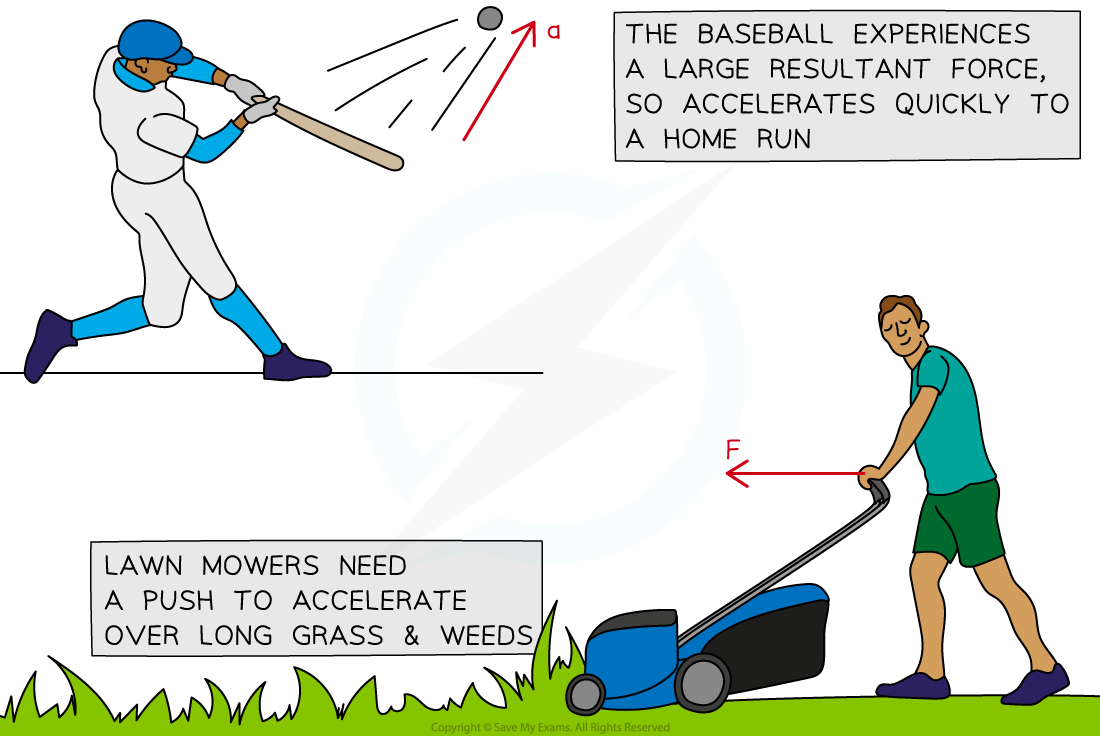
Objects like baseballs and lawnmowers accelerate when a resultant force is applied on them. The size of the acceleration is proportional to the size of the resultant force
Calculating Force & Acceleration
Newton's second law can be expressed as an equation:
F = ma
Where:
F = resultant force on the object in Newtons (N)
m = mass of the object in kilograms (kg)
a = acceleration of the object in metres per second squared (m/s2)
This equation can be rearranged with the help of a formula triangle:
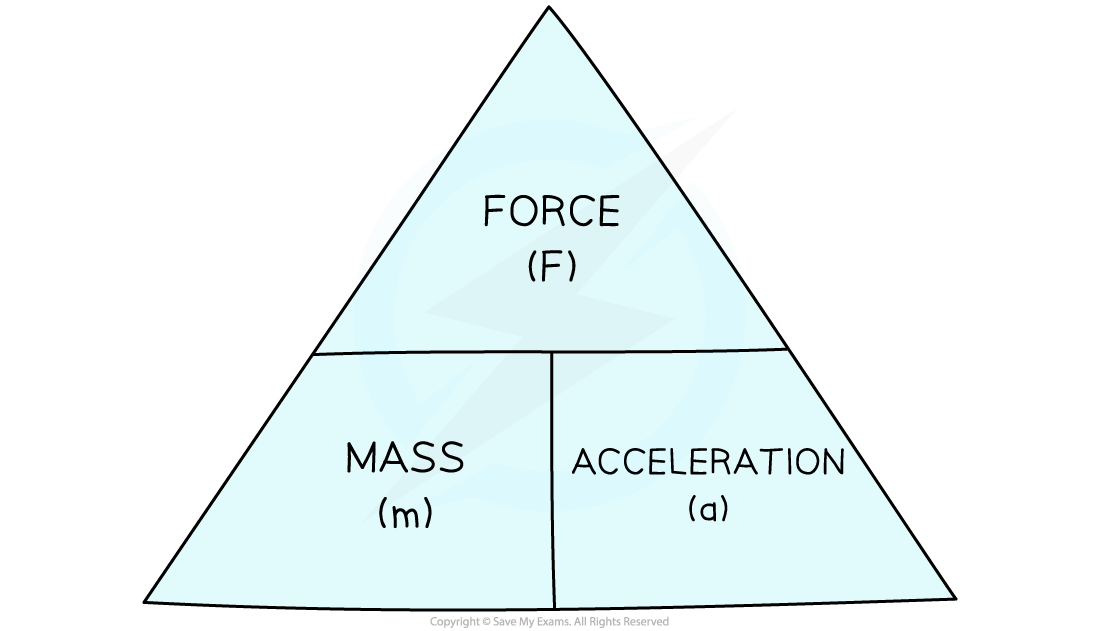
Force, mass, acceleration formula triangle
Worked Example
A car salesman says that his best car has a mass of 900 kg and can accelerate from 0 to 27 m/s in 3 seconds. Calculate:
a) The acceleration of the car in the first 3 seconds.
b) The force required to produce this acceleration.
Answer:
Part (a)
Step 1: List the known quantities
Initial velocity = 0 m/s
Final velocity = 27 m/s
Time, t = 3 s
Step 2: Calculate the change in velocity
change in velocity = Δv = final velocity − initial velocity
Δv = 27 − 0 = 27 m/s
Step 3: State the equation for acceleration
Step 4: Calculate the acceleration
a = 27 ÷ 3 = 9 m/s2
Part (b)
Step 1: List the known quantities
Mass of the car, m = 900 kg
Acceleration, a = 9 m/s2
Step 2: Identify which law of motion to apply
The question involves quantities of force, mass and acceleration, so Newton's second law is required:
F = ma
Step 3: Calculate the force required to accelerate the car
F = 900 × 9 = 8100 N
Worked Example
Three shopping trolleys, A, B and C, are being pushed using the same force. This force causes each trolley to accelerate.

Which trolley will have the smallest acceleration? Explain your answer.
Answer:
Step 1: Identify which law of motion to apply
The question involves quantities of force and acceleration, and the image shows trolleys of different masses, so Newton's second law is required:
F = ma
Step 2: Re-arrange the equation to make acceleration the subject
Step 3: Explain the inverse proportionality between acceleration and mass
Acceleration is inversely proportional to mass
This means for the same amount of force, a large mass will experience a small acceleration
Therefore, trolley C will have the smallest acceleration because it has the largest mass

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?

