Force & Momentum (OCR GCSE Physics A (Gateway)) : Revision Note
Force & Momentum
When a force acts on an object that is moving, or able to move, the object will accelerate (or decelerate)
This causes a change in momentum
More specifically, the force is the rate of change in momentum
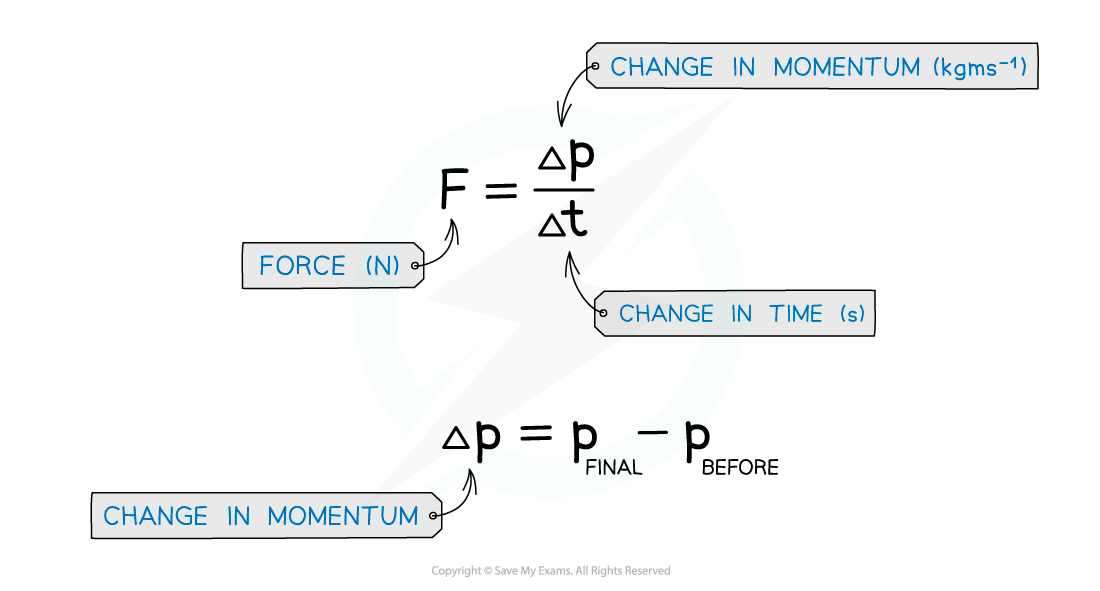
Δt is the change in time, or the time taken for the force to change
Where the change in momentum is defined as
Final momentum – Initial momentum
Δp = mv – mu
Where:
m = mass in kilograms (kg)
v = final velocity in metres per second (m/s)
u = initial velocity in metres per second (m/s)
Force and momentum are vectors so they can be either positive or negative values
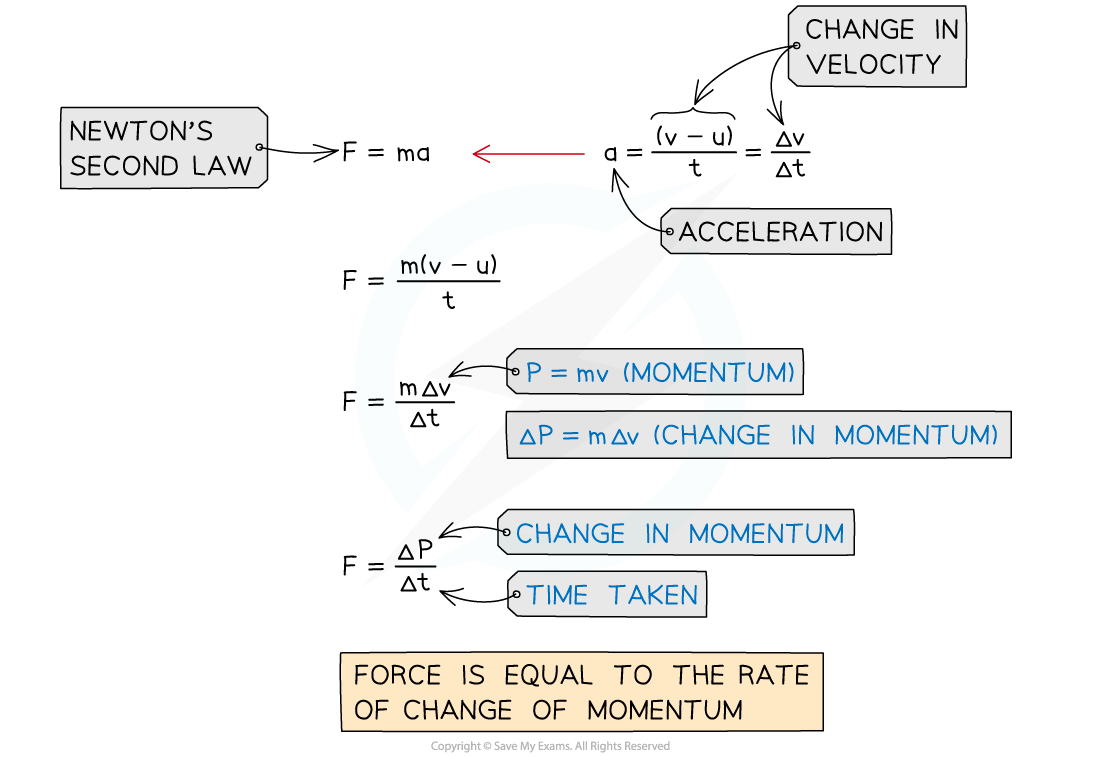
Deriving the Force & Momentum Equation
The force and momentum equation can be derived from Newton's Second law and the definition of acceleration
Worked Example
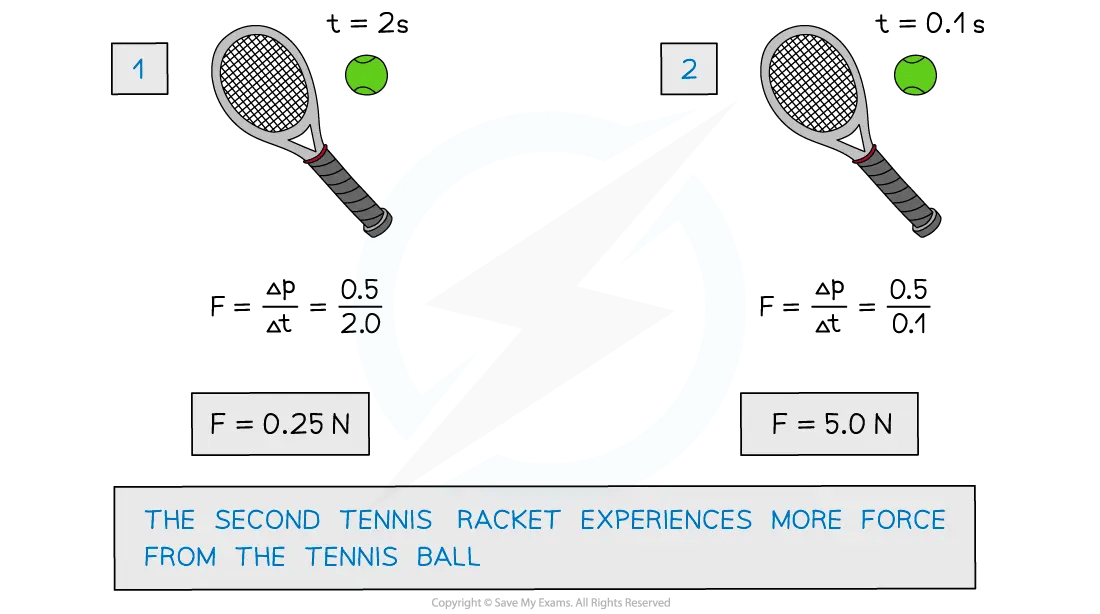
A tennis ball hits a racket with a change in momentum of 0.5 kg m/s. For the different contact times, which tennis racket experiences more force from the tennis ball?
Answer:
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Maths Tip: Remember ‘rate of change’ describes how one variable changes with respect to anotherIn maths, how fast something changes with time is represented as dividing by Δt (e.g. acceleration is the rate of change in velocity)More specifically, Δt is used for finite and quantifiable changes such as the difference in time between two events


You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?

