SI Units (OCR GCSE Physics A (Gateway)) : Revision Note
SI Units
There are a seemingly endless number of units in Physics
These can all be reduced to six base units from which every other unit can be derived
These seven units are referred to as the SI Base Units; this is the only system of measurement that is officially used in almost every country around the world
SI Base Quantities Table

These base units are then used to derive other common units
These units have special names, for example:
Newtons, N [kg m / s2]
Joules, J [N m]
Pascals, Pa [kg / m s2]
Common Units Table

Prefixes
Physical quantities can span a huge range of values
For example, the diameter of an atom is about 10–10 m (0.0000000001 m), whereas the width of a galaxy may be about 1021 m (1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 m)
This is a difference of 31 powers of ten
Powers of ten are numbers that can be achieved by multiplying 10 times itself
These come under two categories of units:
Multiples eg. 102, 103
Sub-multiples eg. 10-1, 10-2
Each power of ten is defined by a prefix, these are listed in the table below:
Prefixes Table
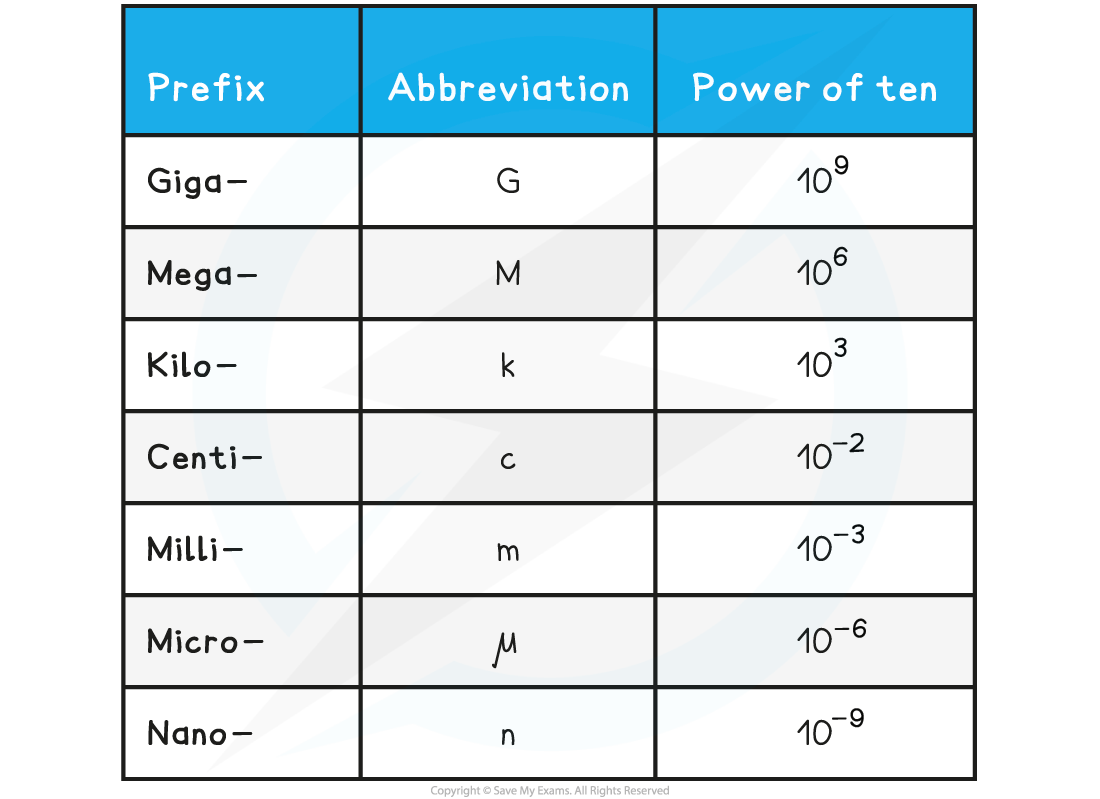
Example Conversions
12 GPa = 12 gigapascals = 12 × 109 Pa (12 000 000 000 Pa)
5 kN = 5 kilonewtons = 5 × 103 N (5000 N)
0.1 μA = 0.1 microamps = 1 × 10–7 A (0.0000001 A)
7 nC = 7 nanocoulombs = 7 × 10–9 C (0.000000007 C)
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Sometimes marks in an exam question are given for the unit, so make sure you remember which is the correct one for the quantity in your answer, e.g.. if the answer is a force, it must have the units of Newtons (N).
Prefixes are very commonly forgotten in exams too, especially on the axes of graphs! Always double check the units given and whether there are any prefixes, e.g., if points are plotted in units of kN, then every value is multiplied by a factor of 1000!

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?

