Energy Transfers in Appliances (OCR GCSE Physics A (Gateway)) : Revision Note
Energy Transfers in Appliances
The amount of energy an appliance transfers depends on:
How long the appliance is switched on for
The power of the appliance
A 1 kW iron uses the same amount of energy in 1 hour as a 2 kW iron would use in 30 minutes
A 100 W heater uses the same amount of energy in 30 hours as a 3000 W heater does in 1 hour
Example 1: An electric heater
Energy is transferred electrically from the mains supply to the thermal store of the heating element
Some of that energy is usefully transferred to the thermal store of the surroundings by heating the air particles in the room
Some of that energy is dissipated to the thermal store of the surroundings by radiation (light)

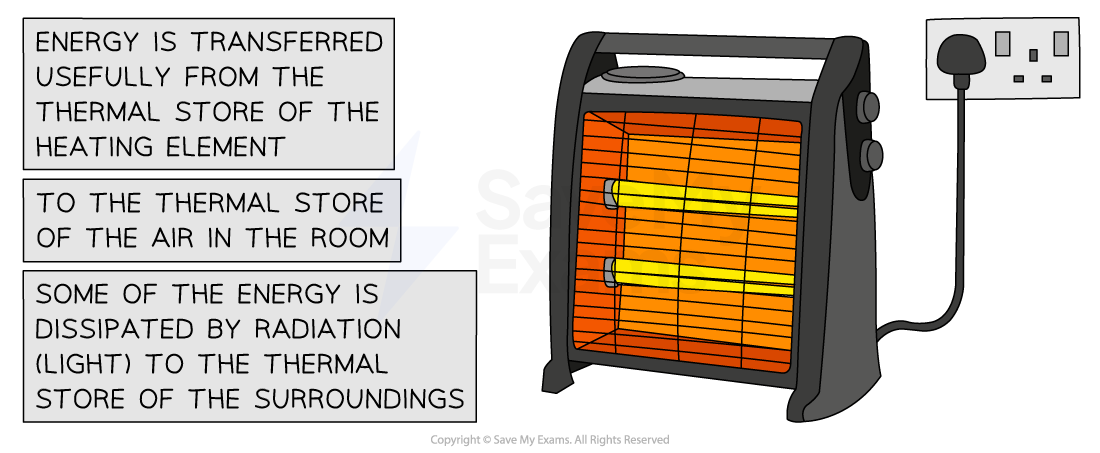
Useful and wasted energy transfers in an electric heater
Example 2: An electric kettle

Useful energy transfer
Energy is transferred by heating from the thermal store of the heating element in the kettle to the thermal store of the water
Unuseful energy transfers
Energy is transferred from the thermal store of the water to the thermal store of the kettle casing
Energy is transferred from the thermal store of the kettle casing to the thermal store of the surroundings and the temperature of the air in the room will increase slightly
Energy is transferred from the thermal store of the water to the thermal store of the surroundings as water evaporates
Example 3: An electric circuit lighting a filament bulb

Useful energy transfers
Energy is transferred from the chemical store of the bulb to the thermal store of the filament wire (the fact that the filament wire glows hot is how the light is produced)
Energy is transferred from the thermal store of the filament wire to the thermal store of the surroundings by radiation as visible light (EM radiation)
Unuseful energy transfers
Energy is transferred from the chemical store of the cell to the thermal store of the wires due to resistance
Energy is transferred from the chemical store of the cell to the thermal store of the bulb casing (the metal and glass that make up the bulb)
Energy is transferred from the thermal store of the filament wire to the thermal store of the surroundings (most of the energy transferred away from the bulb is by heating rather than as light)
Other Examples
Different domestic appliances transfer energy from cells and batteries, such as a remote control
Most household appliances transfer energy from the AC mains
This can often be to the kinetic store of an electric motor
Motors are used in:
Vacuum cleaners - to create the suction to suck in dust and dirt off carpets
Washing machines - to rotate the drum to wash clothes
Refrigerators - to compress the refrigerant chemical into a liquid to reduce the temperature
Energy is often transferred to the thermal store of devices
Such as:
Toasters - to toast bread
Kettles - to boil hot water
Radiators - hot water is pumped from the boiler so the radiator can heat up a room

Energy transfers for a washing machine and toaster

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
