Static Electricity (OCR GCSE Physics A (Gateway)) : Revision Note
Electric Forces Between Charges
The charge of a particle is either:
Positive
Negative
Neutral (no charge)
Electrons are negatively charged particles, whilst protons are positive and neutrons are neutral
This is why in a neutral atom, the number of electrons is equal to the number of protons
This is so the equal (but opposite) charges cancel out to make the overall charge of the atom zero
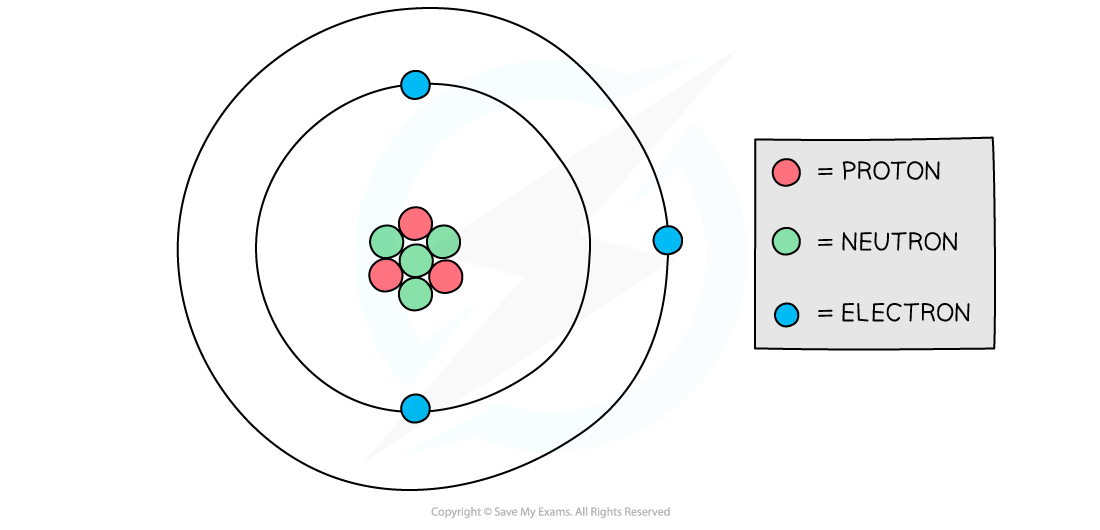
The number of negative electrons in an atom balances the number of positive protons
Therefore, an object becomes negatively charged when it gains electrons and positively charged when it loses electrons
When two charged particles or objects are close together, they also exert a force on each other
This force could be:
Attractive (the objects get closer together)
Repulsive (the objects move further apart)
Whether two objects attract or repel depends on their charge
If the charges are the opposite, they will attract
If the charges are the same, they will repel

Opposite charges attract, like charges repel
Attraction or Repulsion Summary Table

Attraction and repulsion between two charged objects are examples of a non-contact force
This is a force that acts on an object without being physically in contact with it
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remember the saying: “Opposites attract”. Materials only become positively charged because of the loss of electrons, rather than the 'gain' of any positive charge, which is a common misconception.
Static Electricity
Common electrostatic phenomena include:
Shocks from everyday objects
Lightning
A charged balloon sticking to a wall
Charged comb picking up small pieces of paper
Shocks From Everyday Objects
The build-up of electrostatic charge can be quite dangerous and can cause sparking (also known as an electric shock)
A static electric spark occurs when:
Two objects are charged by friction
They become oppositely charged
The large surplus of electrons causes electrons to 'jump' across to an object that is neutral
Since a current is the flow of electrons, this causes a small current to flow between the objects, called a spark
An example of sparking is the small electric shock felt from touching a door handle, or another person, after walking on a vinyl floor or nylon carpet with rubber shoes or socks
Sparks can become quite dangerous and can cause a fire by igniting flammable gases and liquids, such as petrol


Examples of sparking from touching a door handle or another person
Lightning
In a storm, clouds move over each other
This causes them to become charged when electrons are transferred between them
Since the ground is neutral, the negative charges from the cloud jump to meet the positive charges on the ground creating a giant spark (a current from a transfer of charge)
This phenomenon is known as lightning

Lightning is caused by the build-up of charge in clouds
Sticking a Balloon to the Wall
Rubbing a balloon on a woollen jumper transfers electrons onto the balloon by friction
The balloon is now negatively charged whilst the jumper is left positively charged
The wall is still neutral, however, when the balloon is placed near the wall, the positive charges in the wall are brought to the surface because they are attracted to the negative charge of the balloon
Since opposite charges attract, the balloon sticks to the wall from only the electrostatic attraction
Charged Comb Picking up Paper
Static electricity can be observed when running a plastic comb through hair then placing the comb near small pieces of paper
The pieces of paper can be observed to jump up and stick to the comb
The comb becomes charged by friction from the hair so it is left with a negative charge as the electrons are transferred to it
This also means the hair strands become positively charged and they begin to repel each other
Pieces of paper are neutral but as the comb comes close to them, the positive charges are brought to the surface of the paper and are attracted to the negative charges on the comb
Therefore, the papers 'stick' to the comb through static electricity

A negatively charged comb can attract small pieces of paper
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Answers to exam questions in this topic are mainly looking for the words 'friction' and the transfer of 'electrons'. Avoid saying the transfer of 'charge' since this is too vague and will not get you full marks.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?

