Free Body Diagrams (OCR GCSE Physics A (Gateway)): Revision Note
Exam code: J249
Examples of Forces
Higher Tier Only
When forces act on an isolated body or system they can be represented as vectors
These vectors can be added together to work out resultant forces to determine the motion of the body or system
For example:
The forces acting on a body in freefall are weight (downwards) and drag (upwards). This body will reach terminal velocity when these two forces are balanced
The forces acting on an aircraft are thrust (forwards) drag (backwards) lift (upwards) and weight (downwards). The engine can control the amount of thrust, and the tilt of the wings can control the lift
Free Body Diagrams
Higher Tier Only
Free body diagrams are useful for modelling the forces that are acting on an object
Each force is represented as a vector arrow, where each arrow:
Is scaled to the magnitude of the force it represents
Points in the direction that the force acts
Is labelled with the name of the force it represents
Free body diagrams can be used:
To identify which forces act in which plane
To resolve the net force in a particular direction

Free body diagrams can be used to show the various forces acting on objects
Worked Example
Draw free-body diagrams for the following scenarios:
a) A picture frame hanging from a nail
b) A box sliding down a slope
c) A man fishing in a stationary boat
d) A car accelerating along a road
Answer:
Part (a)

The size of the arrows should be such that adding the three forces (head-to-tail) would make a closed triangle as they are in equilibrium
Part (b)

There are three forces acting on the box
The normal contact force, R, acts perpendicular to the slope
Friction, F, acts parallel to the slope and in the opposite direction to the direction of motion
Weight, W, acts down towards the Earth
Part (c)
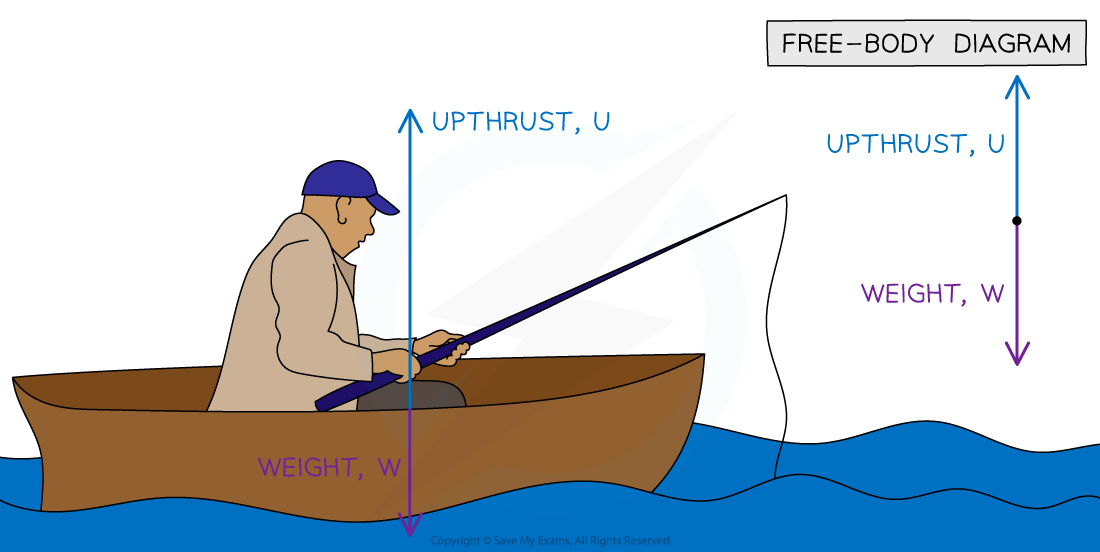
As the boat is not moving, the size of both arrows must be the same
Part (d)

As the car is accelerating, the size of the thrust must be larger than the size of the friction force
As in part (c), the upwards and downwards forces must be equal

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
