Galactic Red-shift (Edexcel GCSE Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 1PH0
Did this video help you?
Galactic Red-shift
The Doppler effect affects all types of waves, including light
Light emitted from stars and galaxies will be at a certain wavelength in the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum
If an object moves away from an observer the wavelength of light increases
This is known as redshift as the light moves towards the red end of the spectrum
If an object moves towards an observer the wavelength of light decreases
This is known as blueshift as the light moves towards the blue end of the spectrum

Light from a star that is moving towards an observer will be blue shifted and light from a star moving away from an observer will be red shifted
An increase in wavelength is a decrease in frequency and vice versa
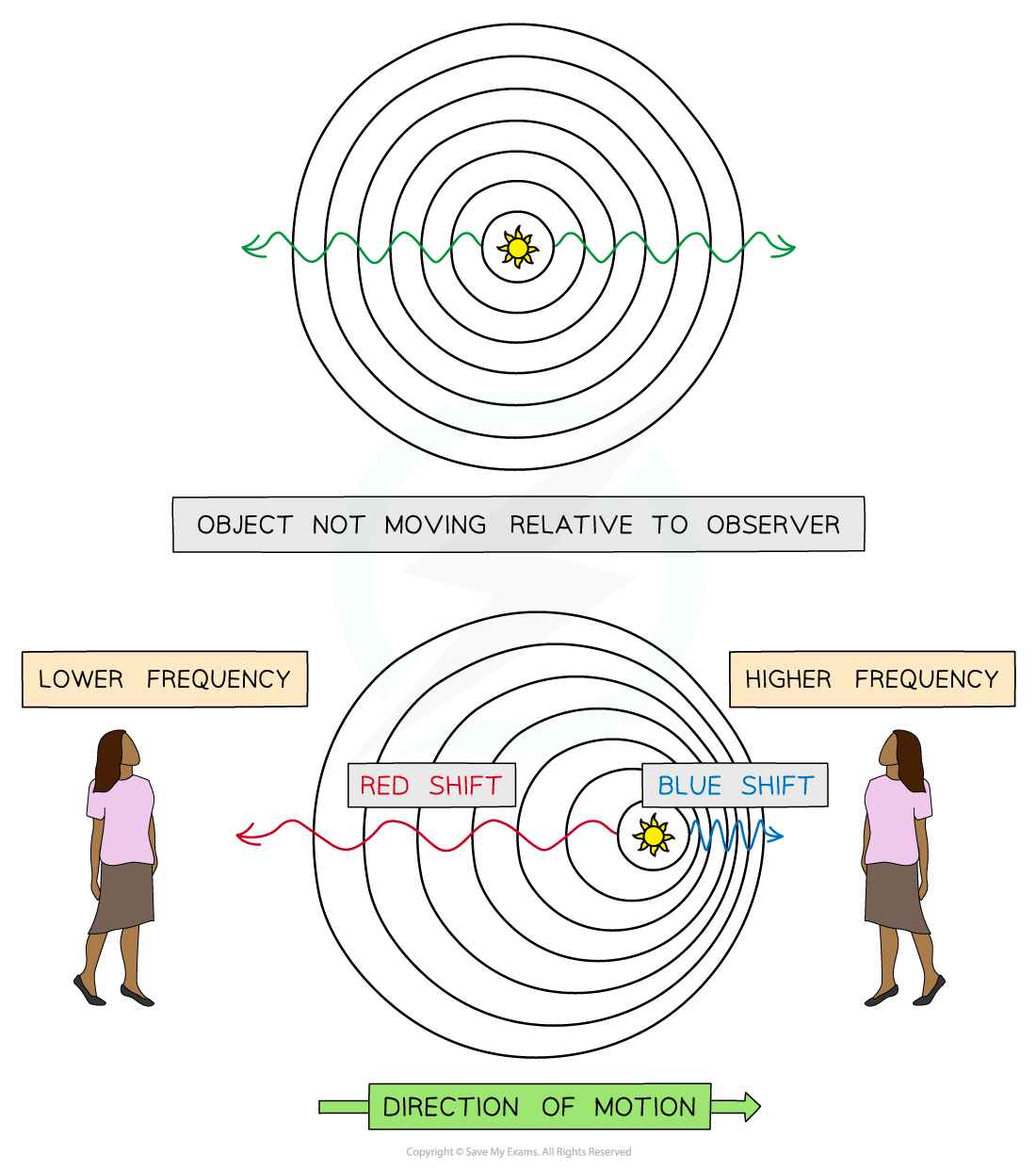
The observer in front observes a blue shift, the observer behind observes a redshift
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You need to know that in the visible light spectrum red light has the longest wavelength and the smallest frequency compared to blue light which has a shorter wavelength and higher frequency

To help you to remember what happens to the wavelength and the frequency of an object as it moves further away, it is useful to think about how the sound of a motorbike would change as it travels away from you. As the motorbike travels away from you the pitch of the sound will become lower. This means the frequency of the sound is decreasing. If the frequency has decreased, the wavelength must also have increased.
The Expanding Universe
Galactic redshift provides evidence for the Big Bang Theory and the expansion of the universe
The diagram below shows the light coming to the Earth from a close object, such as the Sun, and the light coming to the Earth from a distant galaxy
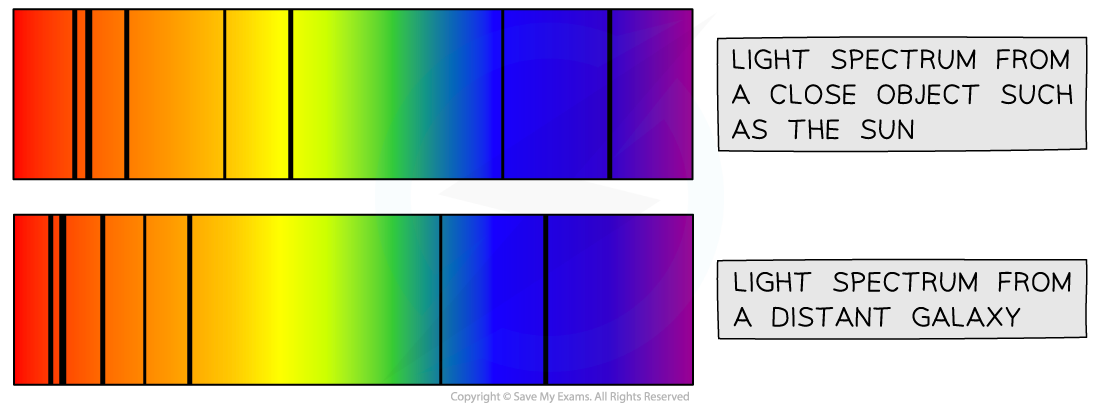
Comparing the light spectrum produced from the Sun and a distant galaxy
Red-shift provides evidence that the Universe is expanding because:
Red-shift is observed when the spectral lines from the distant galaxy move closer to the red end of the spectrum
This is because light waves are stretched by the expansion of the universe so the wavelength increases (or frequency decreases)
This indicates that the galaxies are moving away from us
Light spectrums produced from distant galaxies are red-shifted more than nearby galaxies
This shows that the greater the distance to the galaxy, the greater the redshift
This means that the further away a galaxy is, the faster it is moving away from the Earth
These observations imply that the universe is expanding and therefore support the Big Bang Theory
Red-shift & the Origin of the Universe
Both the Big Bang and Steady State theories of the origin of the Universe account for the red-shift of galaxies
The fact that light from distant galaxies is redshifted shows that the galaxies are:
Moving away from the Earth
Moving away from each other
This is a predicted consequence of the universe expanding from some initial point (as implied in the Big Bang Theory):
Suppose the galaxies were originally all grouped together and then started to spread out at different speeds
The galaxies that are moving fastest would move the furthest – the distance they move would be proportional to their speed - exactly the sort of relationship shown in the following graph

Graph showing the greater the distance to a galaxy, the greater the redshift
The Steady State Theory, however, does also account for the redshift of galaxies
It suggested that as galaxies moved apart, new ones were created in the space in between, resulting in a universe that remains the same over time
This means that more distant galaxies are still seen to have a greater redshift
However, the Steady State Theory does not support the evidence from the Cosmic Microwave Background radiation, and hence is no longer a supported theory

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?