The Doppler Effect (Edexcel GCSE Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 1PH0
The Doppler Effect
Usually, when an object emits waves, the wavefronts spread out symmetrically
If the wave source moves, the waves can become squashed together or stretched out
Therefore, when a wave source moves relative to an observer there will be a change in the observed frequency and wavelength
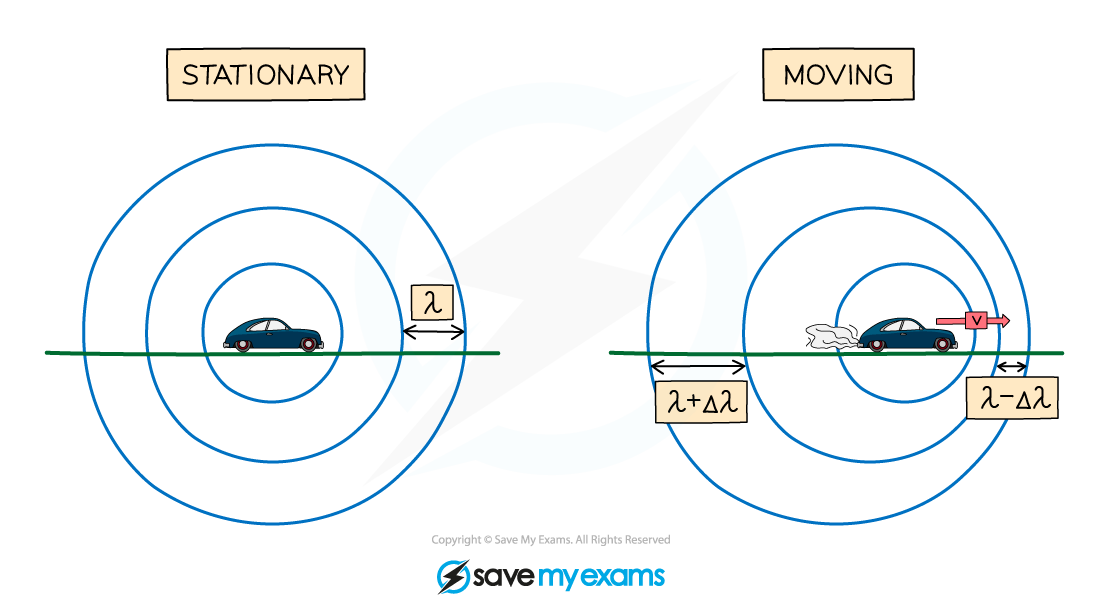
Wavefronts are even in a stationary object but are squashed in the direction of the moving wave source
A moving object will cause the wavelength, λ, (and frequency) of the waves to change:
The wavelength of the waves in front of the source decreases (λ – Δλ) and the frequency increases
The wavelength behind the source increases (λ + Δλ) and the frequency decreases
This effect is known as the Doppler effect
Note: Δλ means 'change in wavelength'
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Although you will not be expected to do any calculations with the Doppler effect, it is important you remember the relationship between wavelength and frequency (wavelength increases, frequency decreases and vice versa)

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?