Refraction (Edexcel GCSE Physics) : Revision Note
Refraction
Refraction can occur when a wave crosses a boundary between two materials with different densities
In some cases, the wave will change direction
The ray diagram below illustrates the change of direction of a light ray at a water-air boundary:
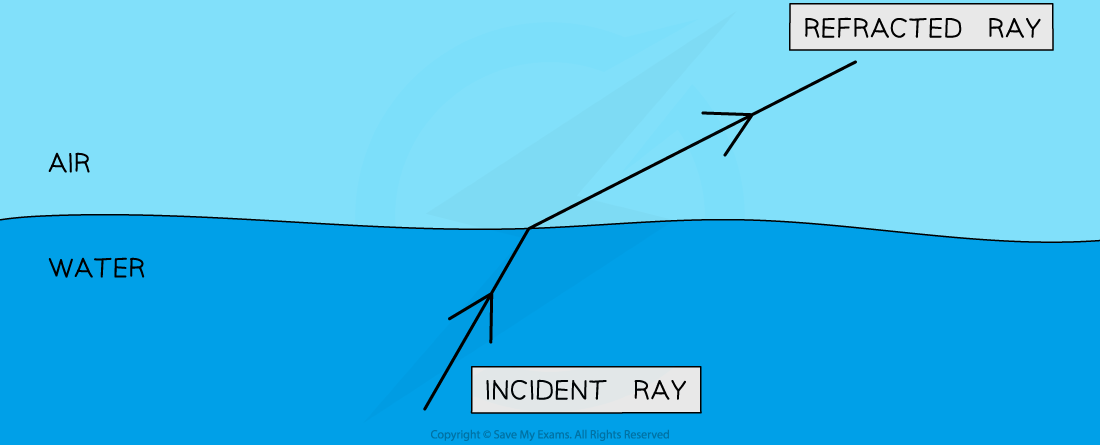
Waves can change direction when moving between materials with different densities
Refraction of light
Refraction also occurs when light passes a boundary between two different transparent media
At the boundary, the rays of light undergo a change in direction
The direction is taken as the angle from the normal
The change in direction depends on the difference in density between the two media:
From less dense to more dense (e.g air to glass), light bends towards the normal
From more dense to less dense (e.g. glass to air), light bends away from the normal
When passing along the normal (perpendicular) the light does not bend at all
Refraction of Light Through a Glass Block
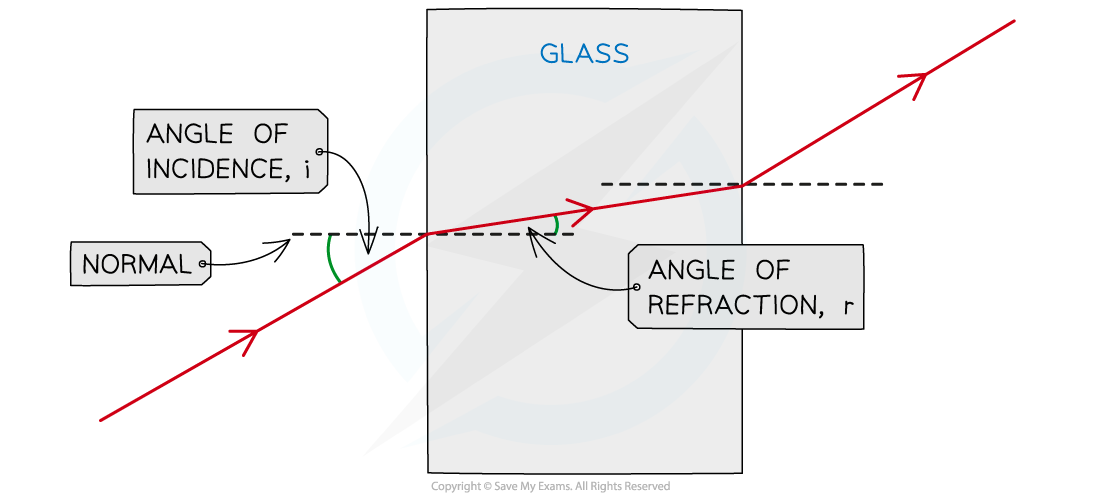
Light enters the glass where the light ray bends towards the normal. Light bends away from the normal as it exits the glass
The change in direction occurs due to the change in speed when travelling in different substances
When light passes into a denser substance the rays will slow down, hence they bend towards the normal
As with refraction of water waves, the only properties that change during refraction of light are speed and wavelength – the frequency of waves does not change
Different frequencies account for different colours of light (red has a low frequency, whilst blue has a high frequency)
When light refracts, it does not change colour (think of a pencil in a glass of water), therefore, the frequency does not change

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
