Wasted Energy (Edexcel GCSE Physics) : Revision Note
Wasted Energy
Mechanical processes can become wasteful when they cause a rise in temperature
These processes often involve friction
When friction acts, it has the effect of transferring energy from the kinetic store by heating to the objects and the surroundings
This energy cannot be used in a useful way, therefore it is called wasted energy
Energy that is transferred to the surrounding is said to be dissipated (spread out) to the surroundings
Useful energy can be defined as:
An energy transfer that serves an intended purpose
Wasted energy can be defined as:
An energy transfer that is not useful for the intended purpose and is dissipated to the surroundings
Example: A Bat Hitting a Ball
The moving bat has energy in its kinetic store
Some of that energy is transferred usefully to the kinetic store of the ball
Some of that energy is transferred from the kinetic store of the bat to the thermal store of the ball mechanically due to the impact of the bat on the ball
Some of that energy is dissipated by heating to the thermal store of the bat, the ball, and the surroundings


Energy transfers taking place when a bat hits a ball
Worked Example
A student uses an electric motor to lift a load.

As the motor turns, energy is transferred to the load as the string and the pully lift it up.
a) State the useful energy transfer happening in this system.
b) State the main wasted energy transfer happening in this system.
Answer:
Part (a)
The motor turns so it is moving, therefore energy is transferred from the kinetic store of the motor
The load is lifted upwards (through a gravitational field) by the string and pulley, therefore energy is transferred usefully to the gravitational potential store of the load
Part (b)
As the motor operates, friction between the components causes heating
Therefore, energy is transferred from the kinetic store of the motor to the thermal store of the motor and dissipated to the surroundings
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Make sure you are able to identify "useful" and "wasted" energy transfers as this is commonly tested in exams!
Learn the term 'dissipated to the surroundings', because if you say the energy is simply "lost", this will not gain you the mark as it implies that energy is not conserved.
Dissipation of Energy
Energy transferred by heating and by radiation have a tendency to spread out to the surroundings
This is known as dissipation of energy
Dissipated energy is very difficult to "gather" so that it can be used again
As a result, the energy becomes less useful
Because of this, whenever a process produces unwanted heating, light or sound, the energy is dissipated and essentially wasted
Not all dissipated energy is wasted energy as the following examples show:
Example 1: A Television
The useful energy transfers occurring in a television:
Energy is transferred electrically from the mains supply and is dissipated to the surroundings by radiation as visible light, and by heating as sound waves
The wasted energy transfers occurring in a television:
Energy is transferred electrically from the mains supply to the thermal store of the television and is then dissipated to the surroundings by heating

Useful and wasted energy transfers in a television
Example 2: Heaters
The useful energy transfers occurring in a heater:
Energy is transferred electrically from the mains supply to the thermal store of the heating element and is then dissipated to the surroundings by heating
The wasted energy transfers occurring in a heater:
Energy is transferred electrically from the mains supply to the thermal store of the heating element and is then dissipated to the surroundings by radiation as visible light

Useful and wasted energy transfers in an electric heater
Reducing Energy Loss
There are many situations where energy transfers are actually unwanted:
Keeping a house warm
Keeping a hot drink hot or cold
Friction of mechanical parts

Insulated mugs are used to maintain the temperature of hot or cold drinks
When an appliance is used for heating something (a kettle, a heater, a tumble drier, a central heating system etc.), the appliance requires a lot of energy
It can become expensive for a household to run such appliances
The production of electricity using fossil fuels produces greenhouse gases which contribute to global warming
The combustion of (methane) gas produces greenhouse gases which contribute to global warming
Therefore, it is often useful to explore ways of reducing unwanted energy transfers
Energy that is dissipated to the surroundings is often the main source of wasted energy transfers
If these unwanted energy transfers can be prevented, or reduced, the useful energy transfers can be made more efficient
Lubrication
Friction is a major cause of wasted energy transfers in machines
For example, the gears on a bike can become hot if the rider has been cycling for a long time
Energy is transferred wastefully from the kinetic energy store of the bike to the thermal energy store of the gears and the chain
Since the energy is originally transferred from the kinetic store of the rider to the kinetic store of the bike, this means that the person has to do more work to make the bike move
This wasted energy transfer can be reduced if the amount of friction can be reduced
This can be achieved by lubricating the parts that rub together
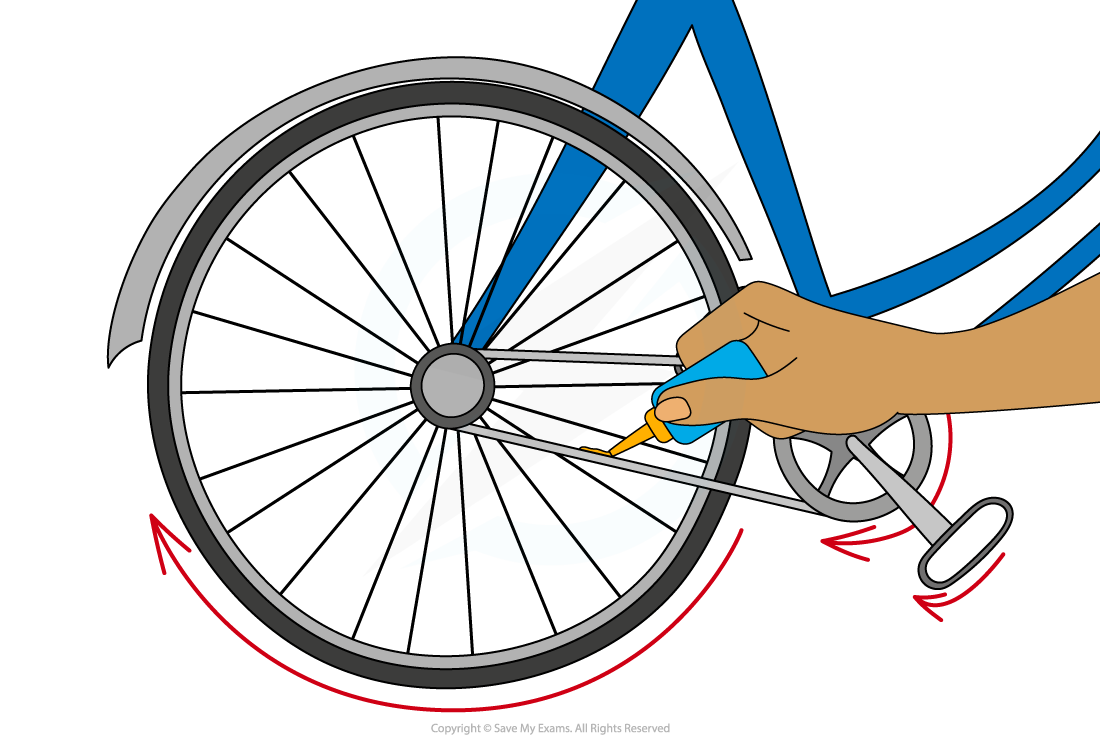
Lubrication helps reduce friction in the parts of a cycle
Insulation
Insulation reduces energy transfers from conduction
The effectiveness of an insulator is dependent upon:
The thermal conductivity of the material
The lower the conductivity, the less energy is transferred
The density of the material
The more dense the insulator, the more conduction can occur
In a denser material, the particles are closer together so they can transfer energy to one another more easily
The thickness of the material
The thicker the material, the better it will insulate
Insulating the loft of a house lowers its rate of cooling, meaning less energy is transferred to the surroundings (outside)
The insulation is often made from fibreglass (or glass fibre)
This is a reinforced plastic material composed of woven material with glass fibres laid across and held together
The air trapped between the fibres makes it a good insulator
The gaps or cavities between external walls are often filled with insulation
This is called cavity wall insulation
This is often done by drilling a hole through the external wall to reach the cavity and filling it with a special type of foam which is made from blown mineral fibre filled with gas
This lowers the conduction of heat through the walls from the inside to the outside

Less energy is transferred by conduction if the cavity is insulated

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
