Upthrust (Edexcel GCSE Physics) : Revision Note
Upthrust
Higher Tier Only
Upthrust is a force that pushes upwards on an object submerged in a fluid i.e. liquids and gases
It is always in the opposite direction to the object's weight
This is why boats, and objects that are less dense than water, float
The size of the upthrust depends on the density of the fluid as well as the volume of fluid that is displaced (which is equal to the volume of the object)
The denser the liquid, the greater the upthrust it will exert on an object
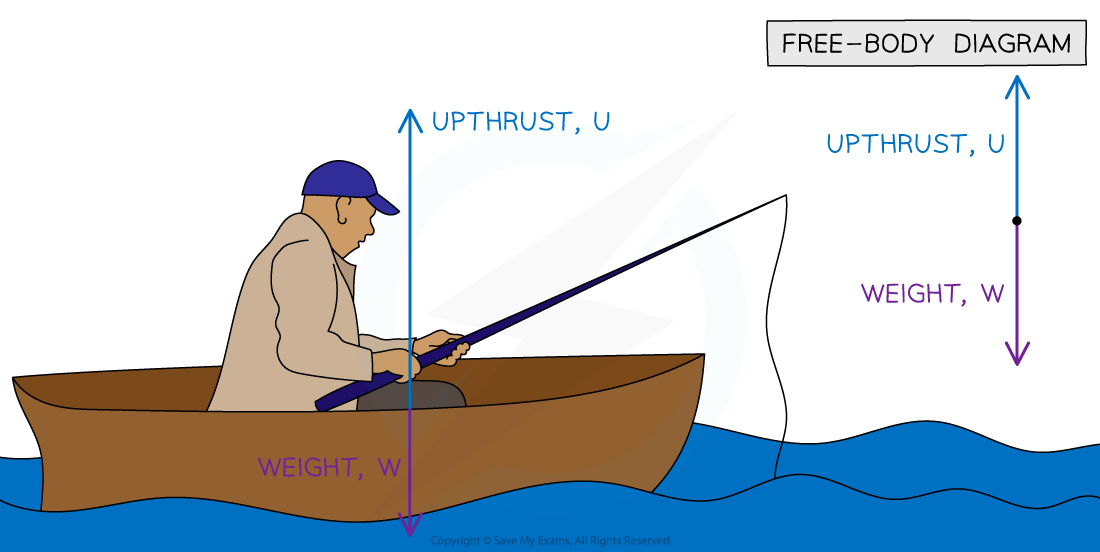
Upthrust is in the opposite direction to the weight of the boat and the fisherman
Upthrust is due to the difference in pressure between the top and the bottom of the submerged object
A partially (or totally) submerged object experiences a greater pressure on the bottom surface than on the top surface
This is because the pressure p is proportional to the depth h of the object
The difference in pressure creates a resultant force upwards (upthrust)
Upthrust is why objects appear to weigh less when immersed in a liquid
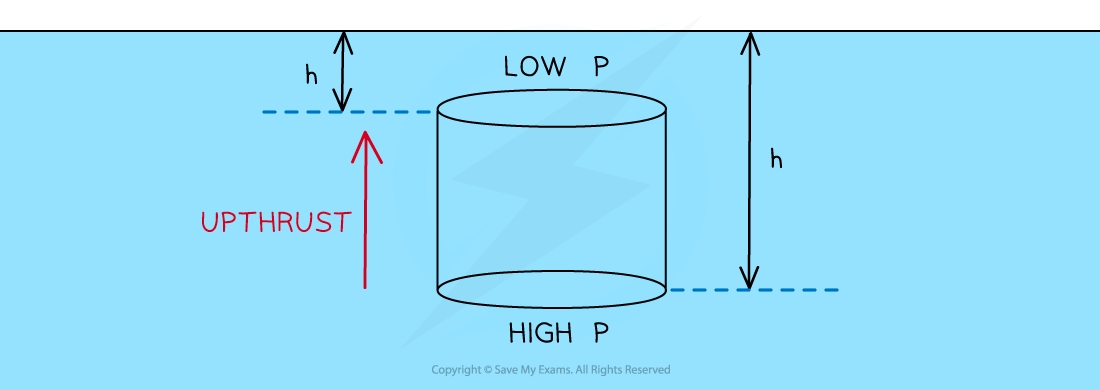
Upthrust is due to the different pressure at the top and bottom of this cylinder
Upthrust & Displacement
Higher Tier Only
The amount of upthrust on an object depends on the weight of the fluid that the object displaces
Upthrust is equal to the weight of fluid displaced
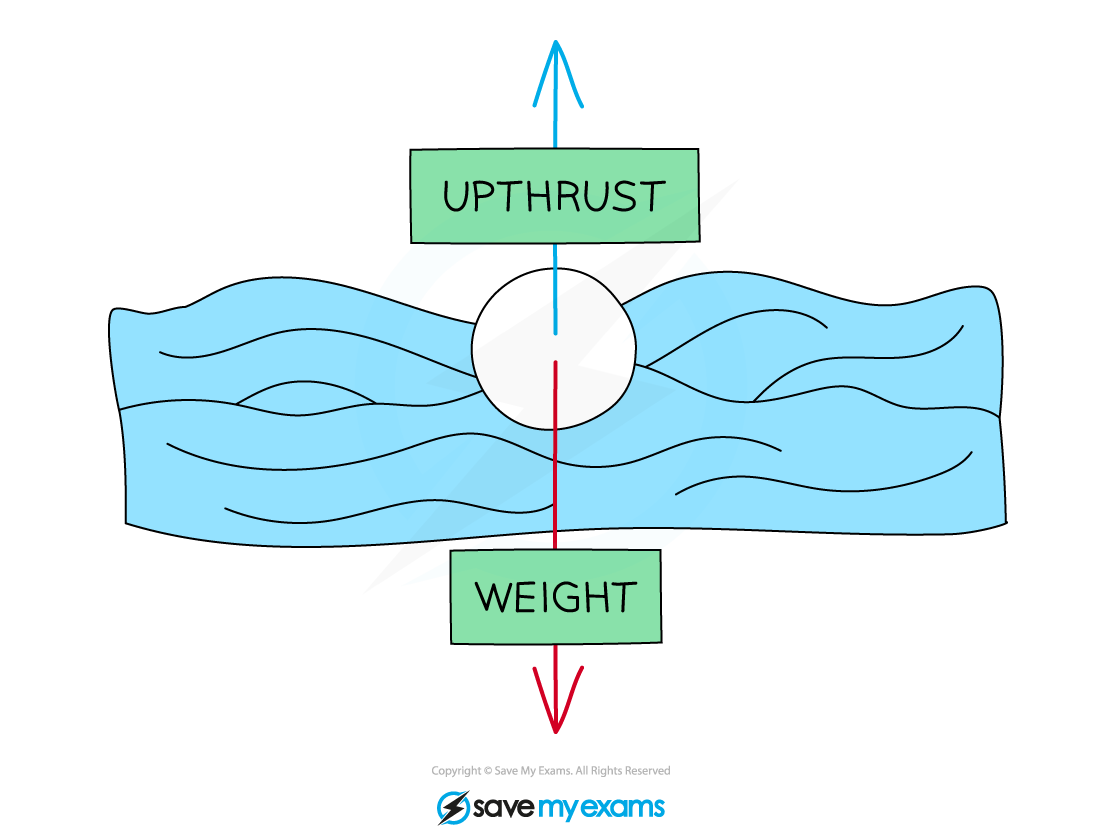
Liquids exert an upwards force (upthrust) on objects immersed in them equal to the weight of the fluid displaced
Upthrust can be found by:
Calculating the volume of the object that is immersed in the fluid
Then using this volume to calculate the weight of the liquid that would occupy that volume
Worked Example
A cube of length 40 cm is partially submerged up to 20 cm in water.
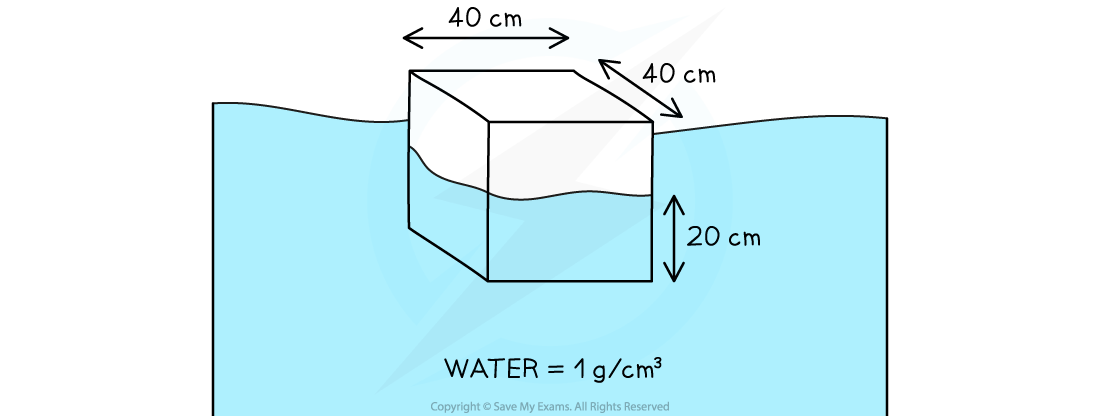
Water has a density of 1 g/cm3. Take gravitational field strength to be 10 N/kg. Calculate the upthrust on the cube.
Answer:
Step 1: Calculate the volume of the cube submerged in the water
Volume, V = 40 cm × 40 cm × 20 cm = 32 000 cm3
Step 2: Write down the equation for density, mass and volume
mass = density × volume
m = ρV
Step 3: Calculate the mass of displaced water
Since water has a density of 1 g/cm3, the mass of displaced water will be:
m = 1 g/cm3 × 32 000 cm3 = 32 000 g = 32 kg
Step 4: Write down the equation for weight
Weight = mass × gravitational field strength
W = mg
Step 5: Calculate the weight of displaced water
W = mg = 32 kg × 10 N/kg = 320 N
Step 6: State the value of upthrust
The upthrust on an object is equal to the weight of fluid displaced
Hence the upthrust on the object will be 320 N
Factors Affecting Upthrust
Higher Tier Only
Whether an object sinks or floats depends on the upthrust:
If the upthrust on an object is equal to (or greater than) the object’s weight, then the object will float
If the upthrust is smaller than the weight then the object will sink
The outcome also depends on the object's density:
If it has a density less than the density of the fluid it is immersed in, the object will float
If it has a density more than the density of the fluid it is immersed in, the object will sink
This is because if the density of the object is greater than the density of the fluid, the object can never displace enough fluid to create an upthrust that will hold its weight up (and therefore sinks)
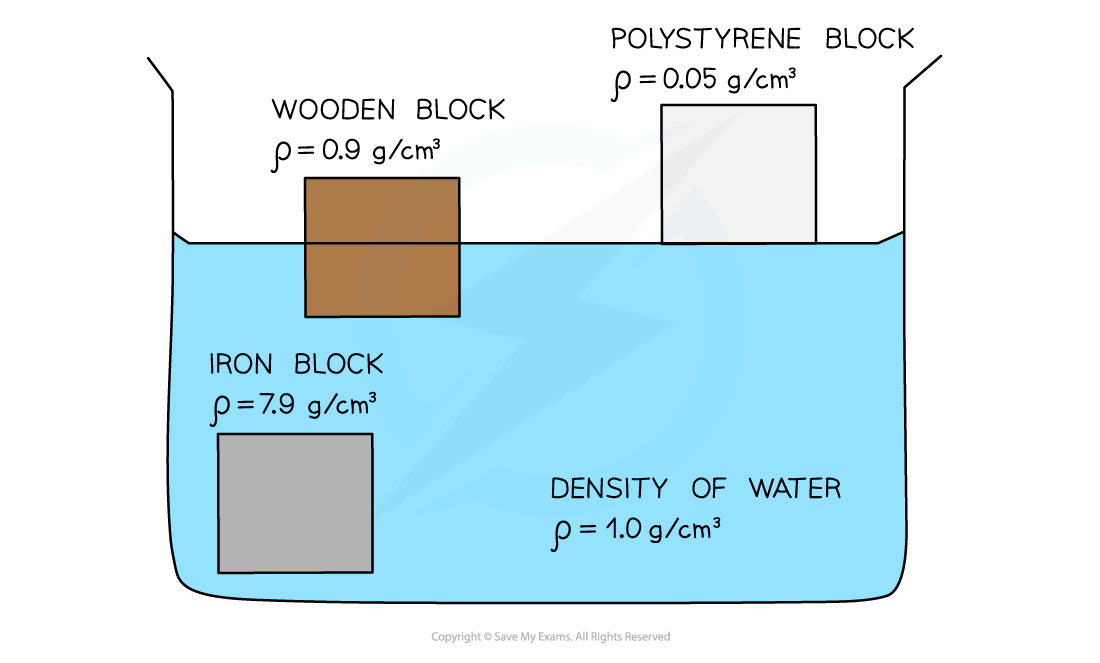
Objects which are less dense than water will float and which are more dense will sink
A polystyrene block will float in water
This is because polystyrene has a density of 0.05 g/cm3 which is much less than the density of water (1.0 g/cm3)
A wooden block will be partially submerged but will still float
This is because the density of a wooden block (0.9 g/cm3) is slightly less than the density of water
An iron block will sink
This is because iron has a density (7.9 g/cm3) that is much higher than water

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
