Pressure & Forces (Edexcel GCSE Physics) : Revision Note
Force & Area
Pressure is defined as
The concentration of a force or the force per unit area
For example, when a drawing pin is pushed downwards:
It is pushed into the surface, rather than up towards the finger
This is because the sharp point is more concentrated (a small area) creating a larger pressure
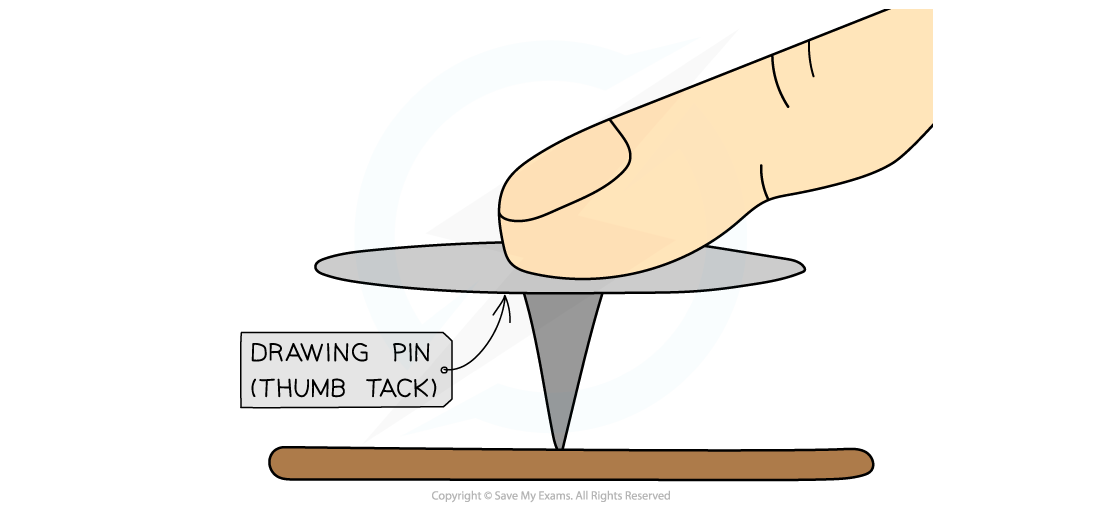
When you push a drawing pin, it goes into the surface (rather than your finger)
Example 1: Tractors
Tractors have large tyres
This spreads the weight (force) of the tractor over a large area
This reduces the pressure which prevents the heavy tractor from sinking into the mud
Example 2: Nails
Nails have sharp pointed ends with a very small area
This concentrates the force, creating a large pressure over a small area
This allows the nail to be hammered into a wall
Did this video help you?
Calculating Pressure
The pressure at the surface of a fluid can be calculated using the equation:
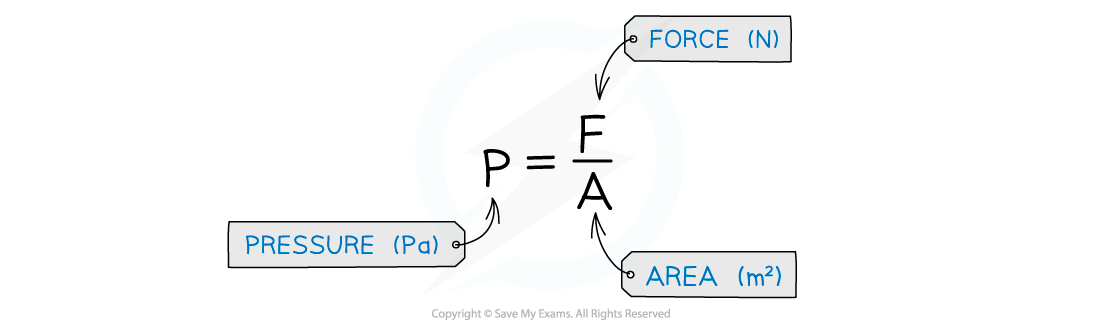
Pressure is measured in the units Pascals (Pa)
The area should always be the cross-sectional area of the object
This means the area where the force is at right angles to it
This equation can be rearranged with the help of a formula triangle:
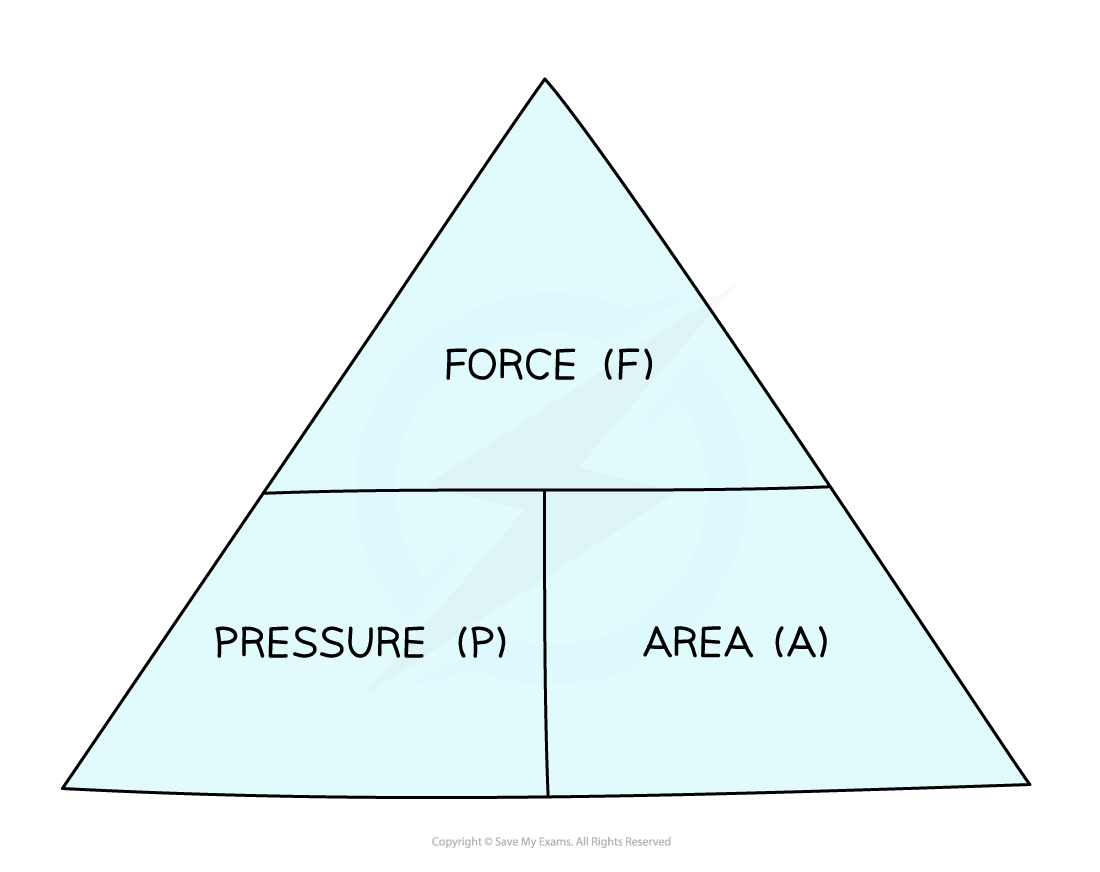
Force, pressure, area formula triangle
This equation tells us that:
If a force is spread over a large area it will result in a small pressure
If it is spread over a small area it will result in a large pressure
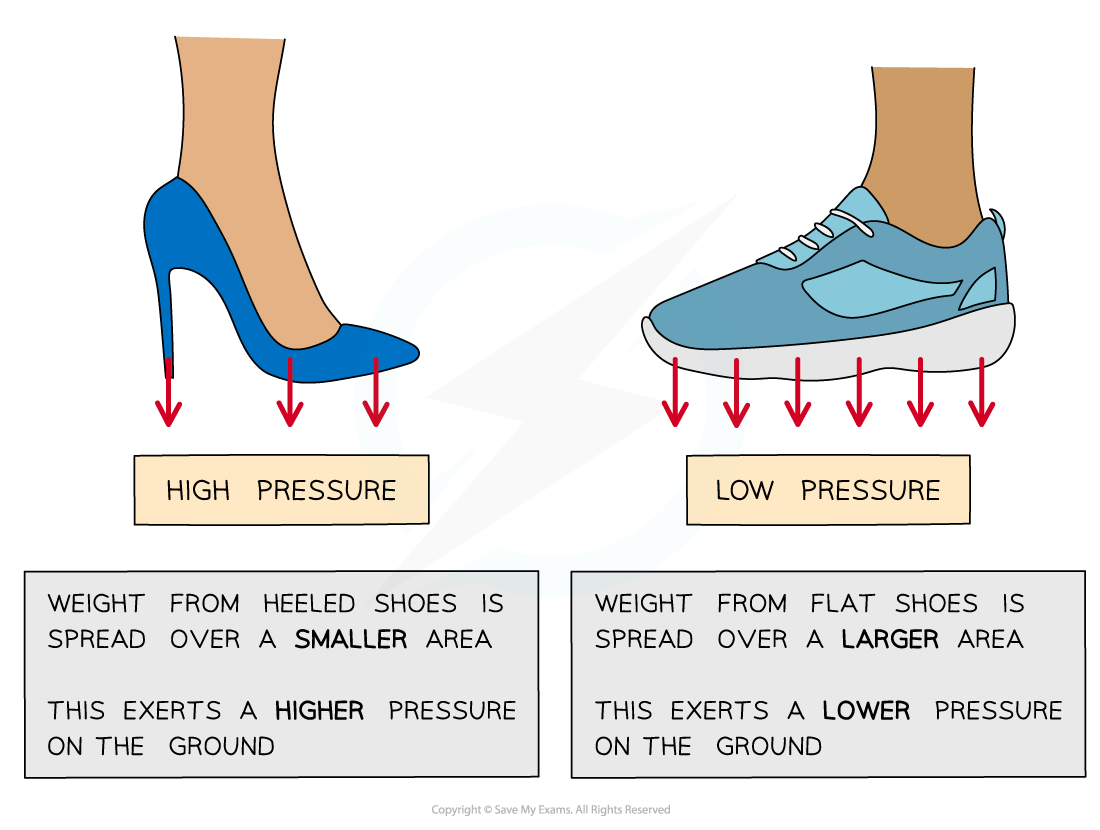
High heels produce a higher pressure on the ground because of their smaller area, compared to flat shoes
Worked Example
The diagram below shows the parts of the lifting machine used to move the platform up and down.
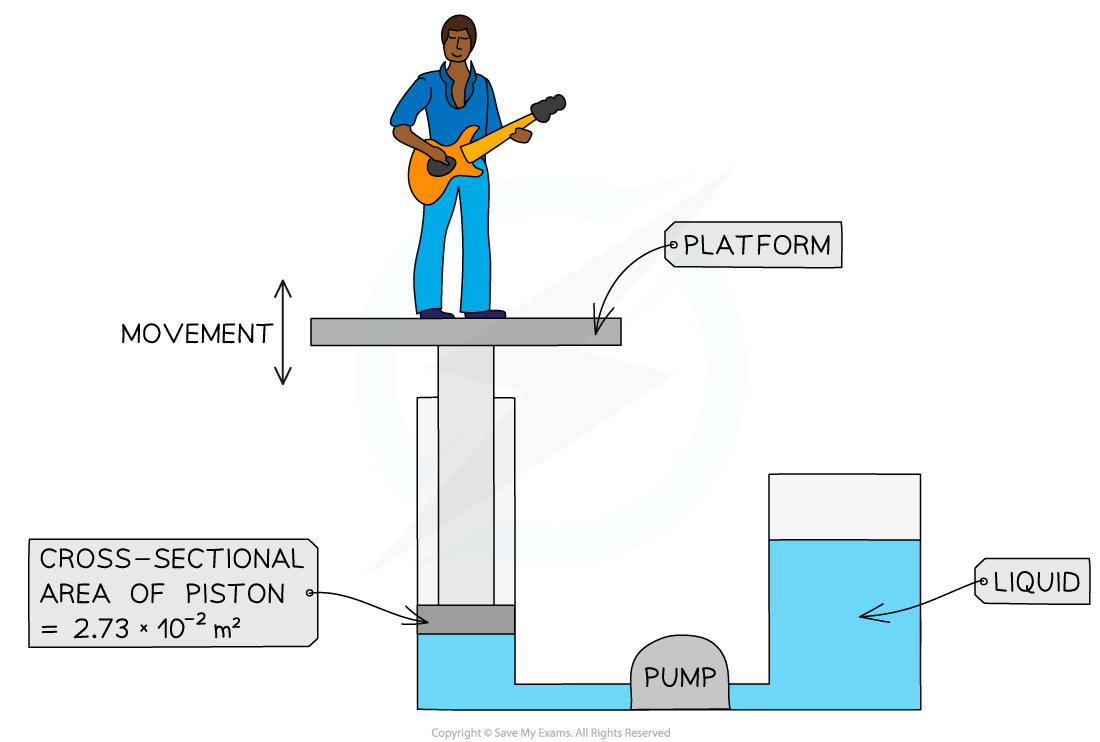
The pump creates pressure in the liquid of 5.28 × 105 Pa to move the platform upwards. Calculate the force that the liquid applies to the piston.
Answer:
Step 1: List the known quantities
Cross-sectional area = 2.73 × 10-2 m2
Pressure = 5.28 × 105 Pa
Step 2: Write down the relevant equation

Step 3: Rearrange for the force, F
F = p × A
Step 4: Substitute the values into the equation
F = (5.28 × 105) × (2.73 × 10-2) = 14 414.4
Step 5: Round to the appropriate number of significant figures and quote the correct unit
F = 14 400 N = 14.4 kN (3 s.f)
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Look out for the units for the force! Large pressures produce large forces - this is sometimes in kN! (1 kN = 1000 N)

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?
