Applications of the Generator Effect (Edexcel GCSE Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 1PH0
Applications of the Generator Effect
Higher Tier Only
The generator effect can be used to:
Generate a.c in an alternator
Generate d.c in a dynamo
Alternator
A simple alternator is a type of generator that produces an alternating current using electromagnetism

An alternator is a rotating coil in a magnetic field with commutator rings
A rectangular coil is forced to spin in a uniform magnetic field
The coil is connected to a circuit containing a centre-reading meter by metal brushes that press on two metal slip rings (or commutator rings)
The slip rings and brushes provide a continuous connection between the coil and the meter
When the coil turns in one direction:
The pointer on the meter deflects first one way, then the opposite way, and then back again
This is because the coil cuts through the magnetic field lines and a potential difference, and therefore current, is induced in the coil
The pointer deflects in both directions because the current in the circuit repeatedly changes direction as the coil spins
This is because the induced potential difference in the coil repeatedly changes its direction
This continues on as long as the coil keeps turning in the same direction
The induced potential difference and the current alternate because they repeatedly change direction

A.C output from an alternator - the current is both in the positive and negative region of the graph
Dynamos
A dynamo is a direct-current generator
A simple dynamo is the same as an alternator except that the dynamo has a split-ring commutator instead of two separate slip rings

A dynamo is a rotating coil in a magnetic field connected to a split ring commutator
As the coil rotates, it cuts through the field lines
This induces a potential difference between the end of the coil
The split ring commutator changes the connections between the coil and the brushes every half turn in order to keep the current leaving the dynamo in the same direction
This happens each time the coil is perpendicular to the magnetic field lines
Therefore, the induced potential difference does not reverse its direction as it does in the alternator
Instead, it varies from zero to a maximum value twice each cycle of rotation, and never changes polarity (positive to negative)
This means the current is always positive (or always negative)

D.C output from a dynamo - the current is only in the positive region of the graph
Bicycle Dynamo
A bicycle dynamo is used to supply electricity to bicycle lights whilst in motion
It consists of a rotating magnet placed inside (or next to) a coil
The magnet is rotated by its connection to the bicycle inside the coil
This is sometimes called the friction wheel and the axle / spindle
The magnetic field lines cut through the sides of the coil
This induces a potential difference in the coil
Since the magnetic field is constantly changing direction as it rotates, so does the output potential difference
This means the output current is also changing direction
Therefore, a bicycle dynamo, unlike a normal dynamo, produces alternating current (a.c)
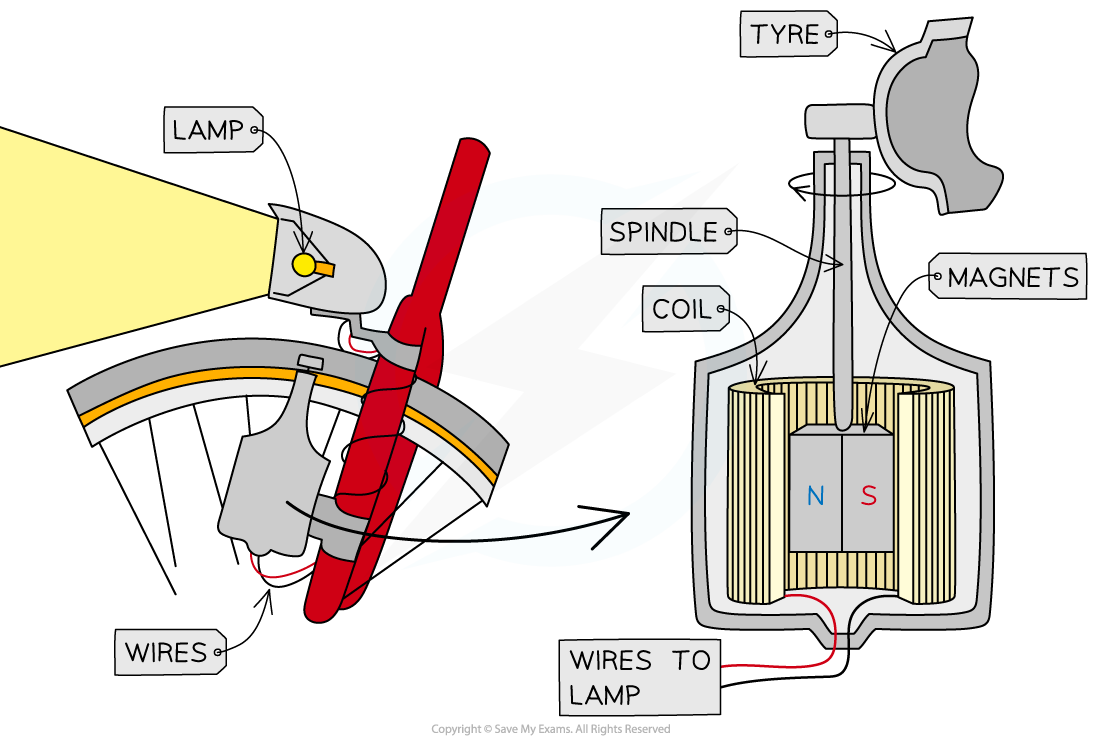
A bicycle dynamo consists of a magnet rotating in a coil due to the motion of the wheels
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Motors and generators look very similar (as do microphones and loudspeakers), but they do very different things. When tackling a question on either of them, make sure you are writing about the right one! You might be expected to give the above explanations - make sure that you understand their subtle differences!

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?