Transverse & Longitudinal Waves (AQA GCSE Physics) : Revision Note
Transverse Waves
Waves are repeated vibrations that transfer energy
Energy is transferred by parts of the wave knocking nearby parts
This is similar to the effect of people knocking into one another in a crowd, or a "Mexican Wave" at football matches
Waves can exist as one of two types:
Transverse
Longitudinal
Transverse Waves
Transverse waves are defined as:
Waves where the points along its length vibrate at 90 degrees to the direction of energy transfer
For a transverse wave:
The energy transfer is perpendicular to wave motion
They transfer energy, but not the particles of the medium
They can move in solids and on the surfaces of liquids but not inside liquids or gases
Some transverse waves (electromagnetic waves) can move in solids, liquids and gases and in a vacuum
The point on the wave that is:
The highest above the rest position is called the peak, or crest
The lowest below the rest position is called the trough

Transverse waves can be seen in a rope when it is moved quickly up and down
Examples of transverse waves are:
Ripples on the surface of water
Vibrations in a guitar string
S-waves (a type of seismic wave)
Electromagnetic waves (such as radio, light, X-rays etc)
Representing Transverse Waves
Transverse waves are drawn as a single continuous line, usually with a central line showing the undisturbed position
The curves are drawn so that they are perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer
These represent the peaks and troughs

Transverse waves are represented as a continuous solid line
Did this video help you?
Longitudinal Waves
Longitudinal waves are defined as:
Waves where the points along its length vibrate parallel to the direction of energy transfer
For a longitudinal wave:
The energy transfer is in the same direction as the wave motion
They transfer energy, but not the particles of the medium
They can move in solids, liquids and gases
They can not move in a vacuum (since there are no particles)
The key features of a longitudinal wave are where the points are:
Close together, called compressions
Spaced apart, called rarefactions

Longitudinal waves can be seen in a slinky spring when it is moved quickly backwards and forwards
Examples of longitudinal waves are:
Sound waves
P-waves (a type of seismic wave)
Pressure waves caused by repeated movements in a liquid or gas
Representing Longitudinal Waves
Longitudinal waves are usually drawn as several lines to show that the wave is moving parallel to the direction of energy transfer
Drawing the lines closer together represents the compressions
Drawing the lines further apart represents the rarefactions

Longitudinal waves are represented as sets of lines with rarefactions and compressions
Transverse v Longitudinal Waves
Their different motions can be shown on ropes (transverse) and springs (longitudinal)
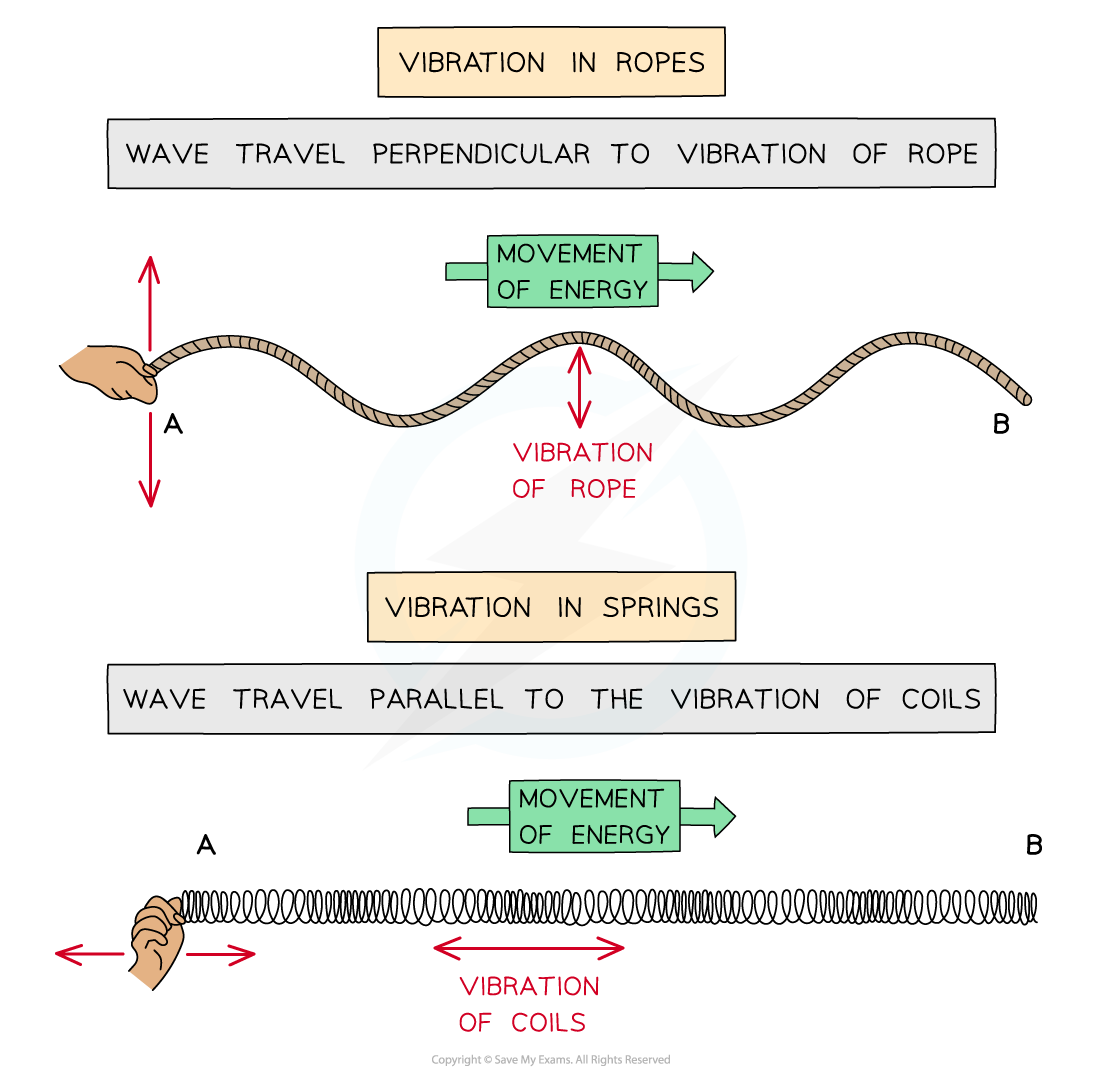
Waves can be shown through vibrations in ropes or springs
The different properties of transverse and longitudinal waves are shown in the table:
Transverse Waves v Longitudinal Waves Table

Wavefronts
Both transverse and longitudinal waves can be represented as wavefronts
This is where the waves are viewed from above
For a transverse wave:
One line represents either a peak or a trough
For a longitudinal wave:
One line represents either a compression or a rarefaction
The arrow shows the direction the wave is moving and is sometimes called a ray
The space between the lines represents the wavelength
When the lines are close together, this is a wave with a short wavelength
When the lines are far apart, this is a wave with a long wavelength

Worked Example
Both transverse and longitudinal waves can travel through water. The diagram below shows a toy duck bobbing up and down on top of the surface of some water.

Explain how the toy duck demonstrates that waves do not transfer matter.
Answer:
Step 1: Identify the type of wave
The type of wave on the surface of a body of water is a transverse wave
This is because the duck is moving perpendicular to the direction of the wave
Step 2: Describe the motion of the toy duck
The plastic duck moves up and down but does not travel with the wave
Step 3: Explain how this motion demonstrates that waves do not transfer matter
Both transverse and longitudinal waves transfer energy, but not the particles of the medium
This means when a wave travels between two points, no matter actually travels with it, the points on the wave just vibrate back and forth about fixed positions
Objects floating on the water simply bob up and down when waves pass under them, demonstrating that there is no movement of matter in the direction of the wave, only energy
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Exam questions may ask you to describe waves and this is most easily done by drawing a diagram of the wave and then describing the parts of the wave - a good, clearly labelled diagram can earn you full marks!
Make sure you know the difference between the wave front diagram and the longitudinal wave diagram, do not confuse the two!

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
