Momentum (AQA GCSE Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 8463
Did this video help you?
Calculating Momentum
A moving object has momentum which is defined by the equation:
p = mv
Where:
p = momentum in kilogram metre per second (kg m/s)
m = mass in kilograms (kg)
v = velocity in metres per second (m/s)
This means that an object at rest (i.e v = 0) has no momentum
Momentum keeps an object moving in the same direction, making it difficult to change the direction of an object with a large momentum
Since velocity is a vector this means that the momentum of an object also depends on its direction of travel
This means that momentum can be either positive or negative
If an object travelling to the right has positive momentum, an object travelling in the opposite direction (to the left) will have negative momentum
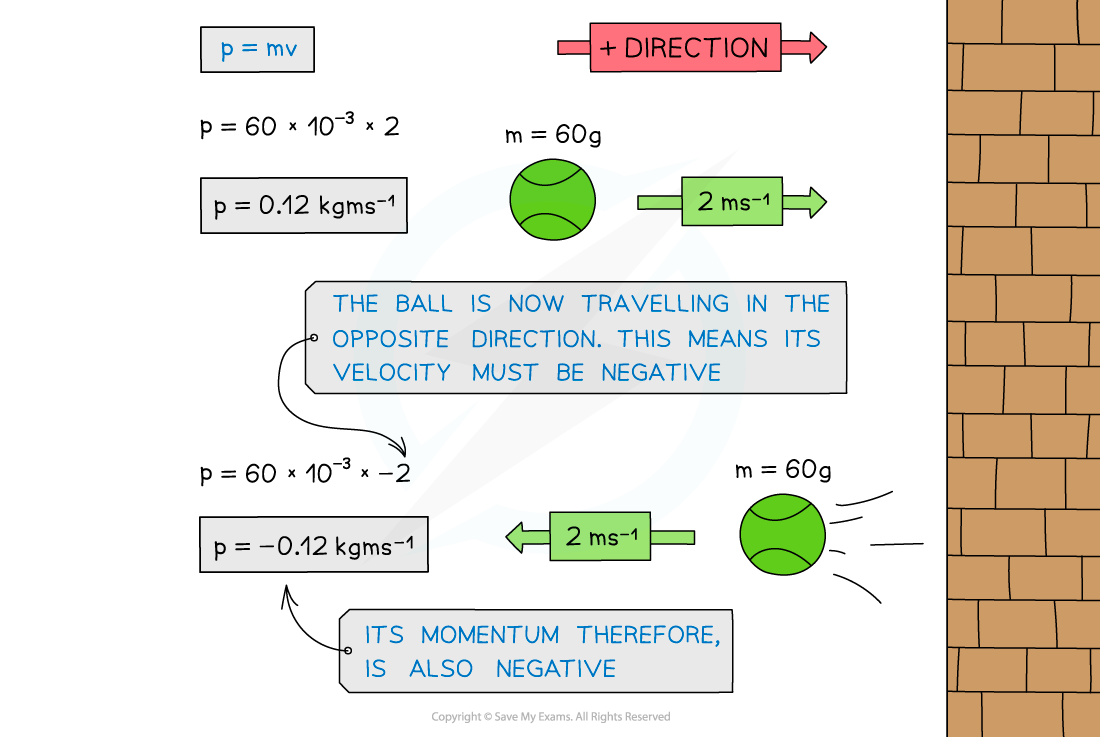
The tennis ball's momentum is negative when it moves in the opposite direction to which it initially was travelling in
Therefore, the momentum of an object will change if:
The object accelerates (speeds up) or decelerates (slows down)
Changes direction
Its mass changes
Worked Example
Which object has the most momentum?
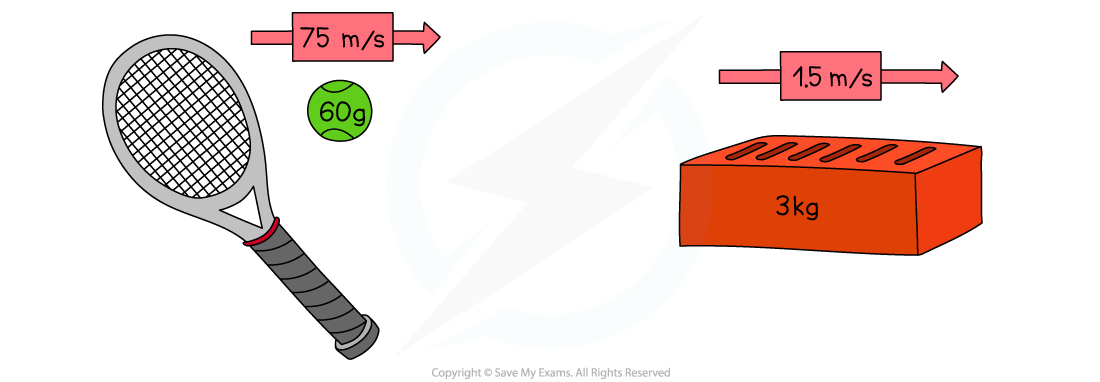
Answer:

Both the tennis ball and the brick have the same momentum
Even though the brick is much heavier than the ball, the ball is travelling much faster than the brick
This means that on impact, they would both exert a similar force (depending on the time it takes for each to come to rest)
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remember the units of momentum as kg m/s which is the product of the units of mass (kg) and velocity (m/s).Which direction is taken as positive is completely up to you in the exam. In general, the right and upwards are taken as positive, and down or to the left as negative.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?