Speed (AQA GCSE Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 8463
Speed
The speed of an object is the distance it travels every second
Speed is a scalar quantity
This is because it only contains a magnitude (without a direction)
The average speed of an object is given by the equation:

Distance is measured in metres, m
Time is measured in seconds, s
Speed is therefore measured in metres per second, m/s
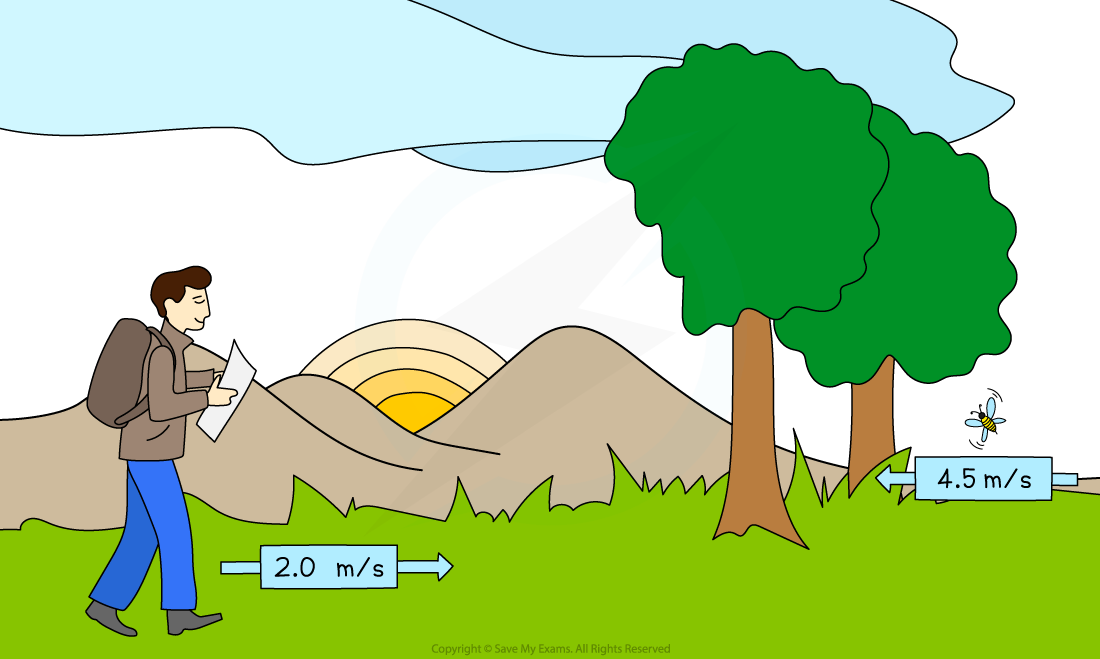
A hiker might have an average speed of 2.0 m/s, whereas a particularly excited bumble bee can have average speeds of up to 4.5 m/s
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remember that average speed is the mean speed of the moving object.Its speed at a specific moment could be higher or lower - so because the speed changes you need to consider the total distance and time taken.
Non-Uniform Motion
The speed of an object is rarely constant
Hikers change their pace continuously as they walk
Bumblebees buzz around in all directions with varying speed
Cars are constantly speeding up and slowing down throughout a journey
Non-uniform motion refers to motion that is changing
Changing motion can mean the object is changing its speed, direction or both

Race drivers know all about non-uniform motion, especially slowing down for corners and speeding up on the straight sections of track
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The term 'non-uniform motion' sounds much scarier than it actually is. Uniform means constant, or the same. So non-uniform just means not constant or changing. Non-uniform motion really just means changing motion. The speed of the object changes throughout its journey.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?