Hooke's Law (AQA GCSE Physics) : Revision Note
Did this video help you?
Hooke's Law
What is Hookes' Law?
The relationship between the extension of an elastic object and the applied force is defined by Hooke's Law
Hooke's Law states that:
The extension of an elastic object is directly proportional to the force applied, up to the limit of proportionality
Directly proportional means that as the force is increased, the extension increases
If the force is doubled, then the extension will double
If the force is halved, then the extension will also halve
The limit of proportionality is the point beyond which the relationship between force and extension is no longer directly proportional
This limit varies according to the material
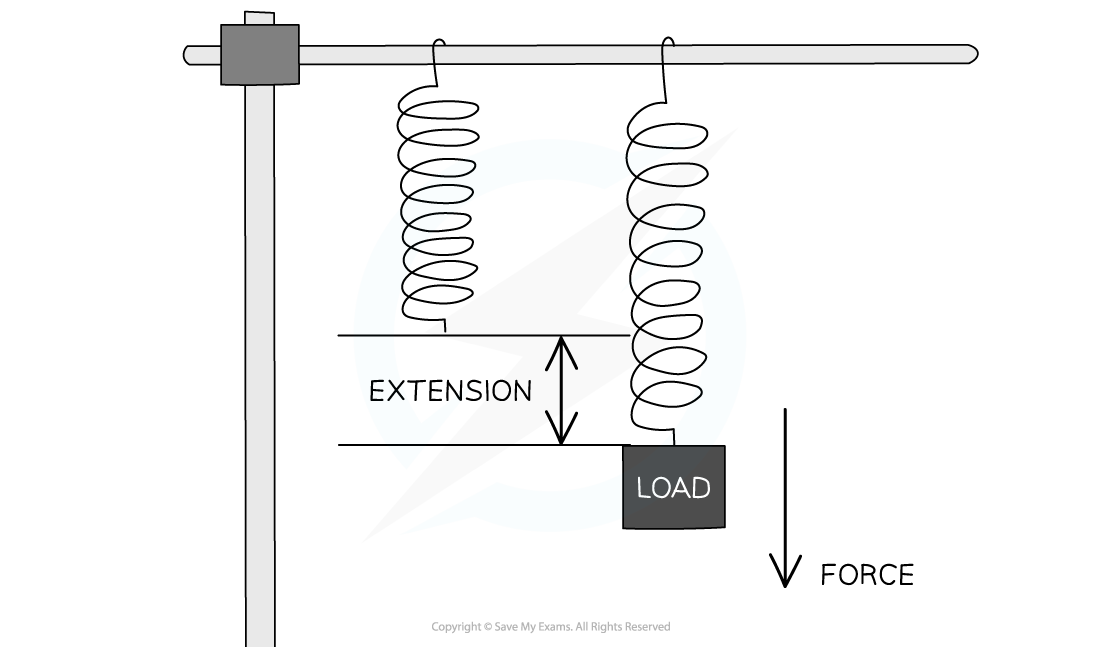
Hooke's Law states that a force applied to a spring will cause it to extend by an amount proportional to the force, this can be tested by this Hooke's Law experiment
Using Hooke's Law
Hooke's Law Equation
Hooke's Law is defined by the equation:
F = k × e
Where:
F = force in newtons (N)
k = spring constant in newtons per metres (N/m)
e = extension in metres (m)
The symbol e can represent either the extension or compression of an elastic object
The spring constant represents how stiff a spring is
The higher the spring constant, the higher the stiffness
The extension of an object can be calculated by:
final length – original length
The extension of the spring can be measured by marking the position of bottom of the unstretched spring
When the spring is stretched the final length must be measured from the bottom of the spring

Force, extension and spring constant are used to define Hooke's Law
The Hooke's Law equation can be rearranged with the help of the following equation triangle:

Worked Example
The figure below shows the forces acting on a child who is balancing on a pogo stick. The child and pogo stick are not moving.
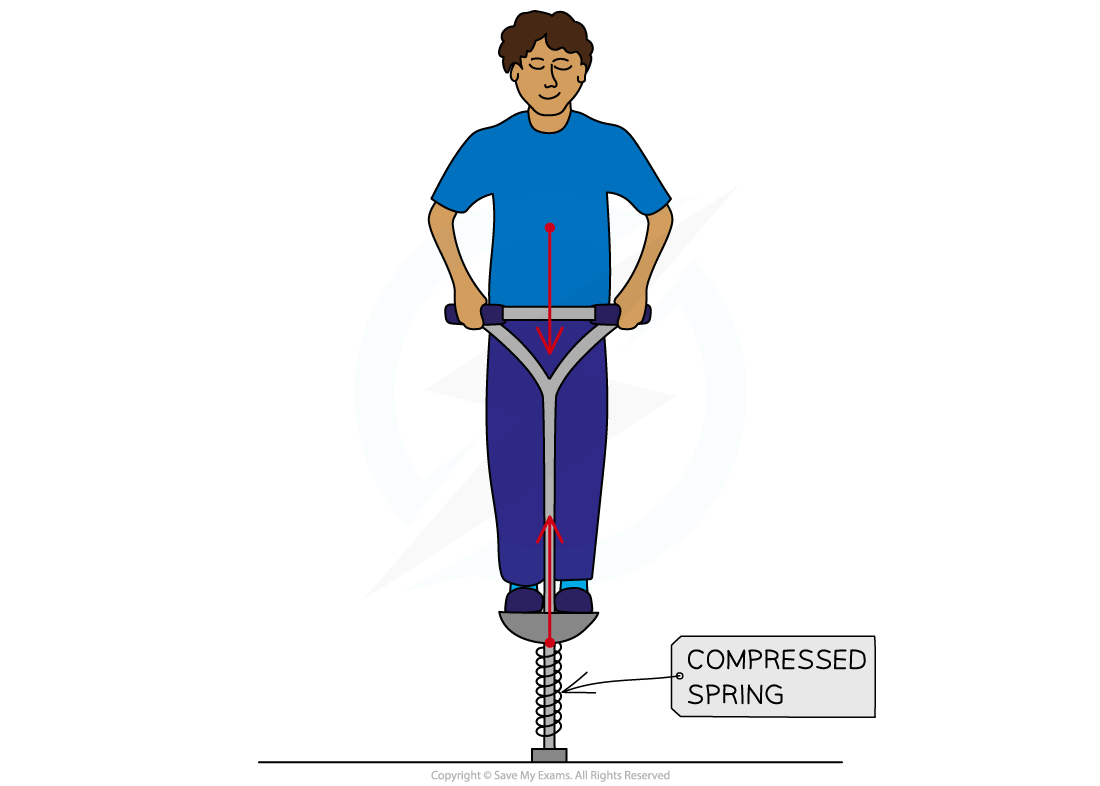
The spring constant of the spring on the pogo stick is 4900 N/m. The weight of the child causes the spring to compress elastically from a length of 40 cm to a new length of 33 cm. Calculate the weight of the child.
Answer:
Step 1: List the known quantities
Spring constant, k = 4900 N/m
Original length = 40 cm
Final length = 33 cm
Step 2: Write the relevant equation
Step 3: Calculate the compression, x
A negative extension represents a compression of 7 cm
Step 4: Convert any units
Since the spring constant is given in N/m,
must be in metres (m)
Step 5: Substitute the values into the Hooke's Law equation
The minus sign simply indicates the direction of the force, downwards in this case
The child's weight is 343 N
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Look out for unit conversions! Unless the spring constant is given in N/cm, make sure the extension is converted into metres (÷ 100) before substituting values into the Hooke's Law equation

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
