Specific Heat Capacity (AQA GCSE Physics) : Revision Note
Specific Heat Capacity Equation
If the temperature of the system increases, the increase in temperature of this system depends on:
The mass of the substance heated
The type of material
The energy input to the system
Energy is transferred to the thermal store of the substance
The amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of a given mass by a given amount can be calculated using the equation:
ΔE = mcΔθ
Where:
ΔE = change in energy, in joules (J)
m = mass, in kilograms (kg)
c = specific heat capacity, in joules per kilogram per degree Celsius (J/kg °C)
Δθ = change in temperature, in degrees Celsius (°C)
The specific heat capacity, c of a substance is defined as:
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of the substance by 1 °C
Different substances have different specific heat capacities
If a substance has a low specific heat capacity, it heats up and cools down quickly
It takes less energy to change its temperature
If a substance has a high specific heat capacity, it heats up and cools down slowly
It takes more energy to change its temperature
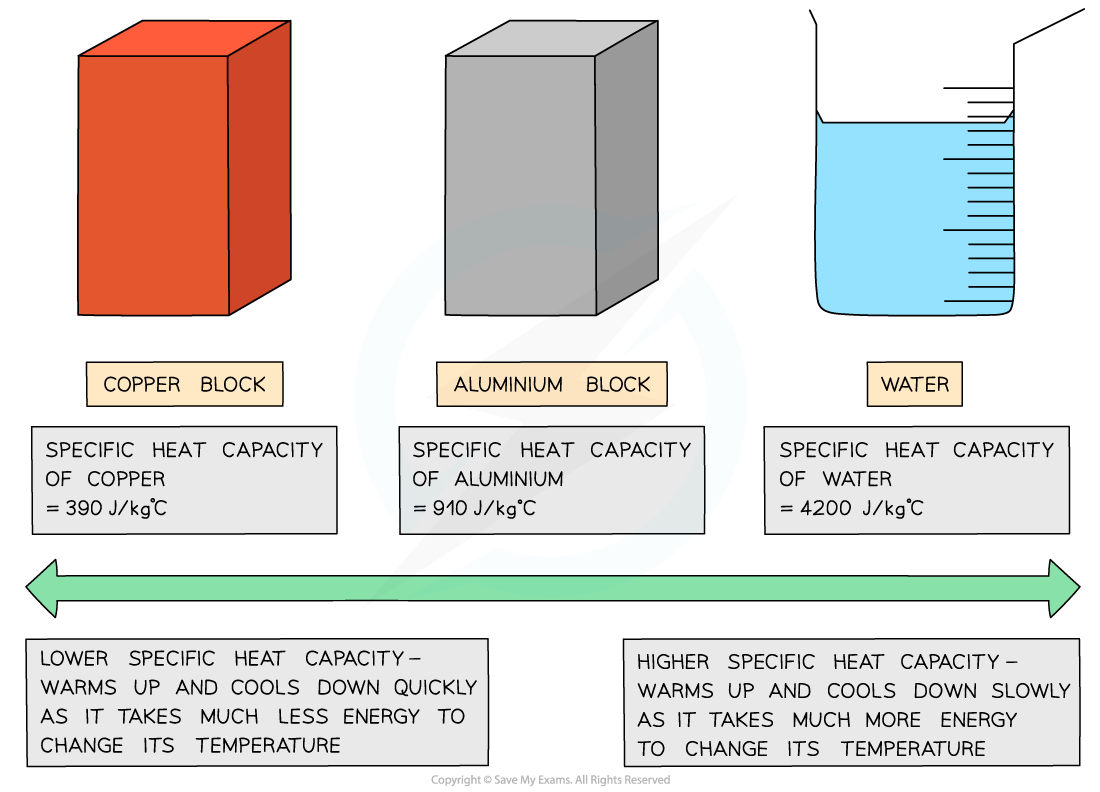
Low v high specific heat capacity
Specific heat capacity is mainly used for liquids and solids
The specific heat capacity of different substances determines how useful they would be for a specific purpose eg. choosing the best material for kitchen appliances
Good electrical conductors, such as copper and lead, are excellent conductors of heat due to their low specific heat capacity
On the other hand, water has a very high specific heat capacity, making it ideal for heating homes as the water remains hot in a radiator for a long time
The specific heat capacity of some substances are given in the table below as examples:
Table of values of specific heat capacity for various substances

Worked Example
Water of mass 0.48 kg is increased in temperature by 0.7 °C. The specific heat capacity of water is 4200 J / kg °C. Calculate the amount of energy transferred to the water.
Answer:
Step 1: Write down the known quantities
Mass, m = 0.48 kg
Change in temperature, Δθ = 0.7 °C
Specific heat capacity, c = 4200 J / kg °C
Step 2: Write down the relevant equation
ΔE = mcΔθ
Step 3: Calculate the energy transferred by substituting in the values
ΔE = (0.48) × (4200) × (0.7) = 1411.2
Step 4: Round the answer to 2 significant figures
ΔE = 1400 J
Examiner Tips and Tricks
This equation will be given on your equation sheet, so don't worry if you cannot remember it, but it is important that you understand how to use it. You will always be given the specific heat capacity of a substance, so you do not need to memorise any values.
You will have studied the Required Practical Specific Heat Capacity in Unit 1, Energy. In this lesson, you tend to look more at the theory, although in school you may have repeated the practical investigation (it is a common practical for exam questions). Remember that you may need to use the equations and
to calculate the amount of energy transferred to the substance, particularly if an exam question gives you a table of data. Students often struggle with calculations involving specific heat capacity as they often involve multiple steps and two different equations.
Other common exam questions on specific heat capacity include describing a method, suggesting improvements on a method given, or plotting a graph. So make sure you know the theory (including the maths) and the investigation really well.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
