Fields & Static (AQA GCSE Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 8463
Fields & Static
Objects with static charge create an electric field in the space around them
If other charges enter the field then they will experience an electric force, attracting or repelling them from the object
Therefore, an electric field can be defined as:
A region in which a charged object will experience an electric force
Electric fields are represented by electric field lines that are always in the direction of positive to negative
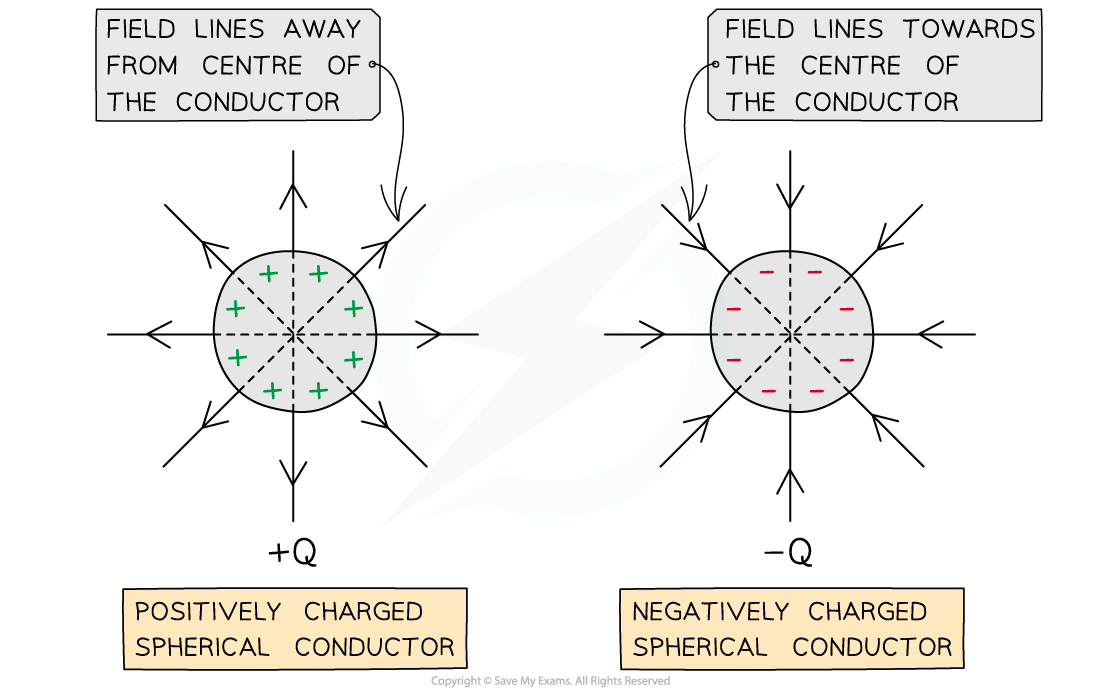
The electric field lines for a charged, isolated sphere, such as a spherical conductor:
Point away from the centre of a positive sphere
Point towards the centre of a negative sphere
A uniform electric field, such as that between two parallel plates, are straight parallel lines from positive to negative:

Electric field lines between two parallel plates
The electric field pattern between two oppositely charged spheres (or point charges) is slightly different and looks like:

Electric field pattern for two opposite charges
The electric field helps to explain the non-contact force between charged objects since the electric field cannot be seen, but can be detected by another charged object that moves within that field due to the electric force
This is a non-contact force because the charged objects do not touch for the force to be exerted
If an electric field becomes strong enough, the charges are forced through insulators such as air, creating a spark
This is what happens for example, when a charged person touches a conductor
The charged particles will travel towards areas with the opposite charge

Positive and negative charges will travel towards the opposite charge, creating a spark
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remember when drawing field lines to always include their direction with arrows pointing in the correct direction. If the field lines are straight, always use a ruler or a straight edge to draw them
All non-contact forces occur because of the presence of a field. Magnetism is a great example because you can feel the force of attraction and repulsion when you bring two magnets close to one another, and because (with the help of some iron filings) you are able to see the field pattern. Electric fields work in the same way as magnetic fields. When you have a charged object, there is an electric field around it. If you place another charged object in that field, it experiences a force. Like charges will repel and opposite charges will attract.
The more links you make between topics as you study and revise this course, the deeper your understanding will grow across all topics. Mind maps are a great visual way to organise concepts that can be linked together.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?