Electric Charge (AQA GCSE Physics) : Revision Note
Did this video help you?
Electric Forces Between Charges
The charge of a particle is either:
Positive
Negative
Neutral (no charge)
Electrons are negatively charged particles, whilst protons are positive and neutrons are neutral
This is why in a neutral atom, the number of electrons is equal to the number of protons
This is so the equal (but opposite) charges cancel out to make the overall charge of the atom zero
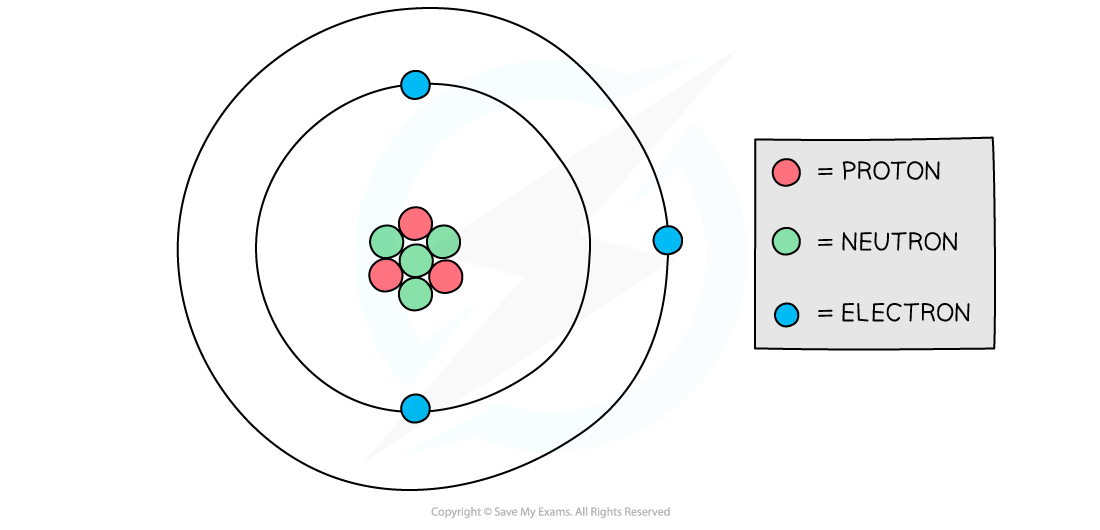
The number of negative electrons in an atom balances the number of positive protons
Therefore, an object becomes negatively charged when it gains electrons and positively charged when it loses electrons
When two charged particles or objects are close together, they also exert a force on each other
This force could be:
Attractive (the objects get closer together)
Repulsive (the objects move further apart)
Whether two objects attract or repel depends on their charge
If the charges are the opposite, they will attract
If the charges are the same, they will repel

Opposite charges attract, like charges repel
Attraction or Repulsion Summary Table

Attraction and repulsion between two charged objects are examples of a non-contact force
This is a force that acts on an object without being physically in contact with it
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remember the saying: “Opposites attract”
Materials only become positively charged because of the loss of electrons, rather than the 'gain' of any positive charge, which is a common misconception.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
