Length of a Line (Edexcel GCSE Maths) : Revision Note
Length of a Line
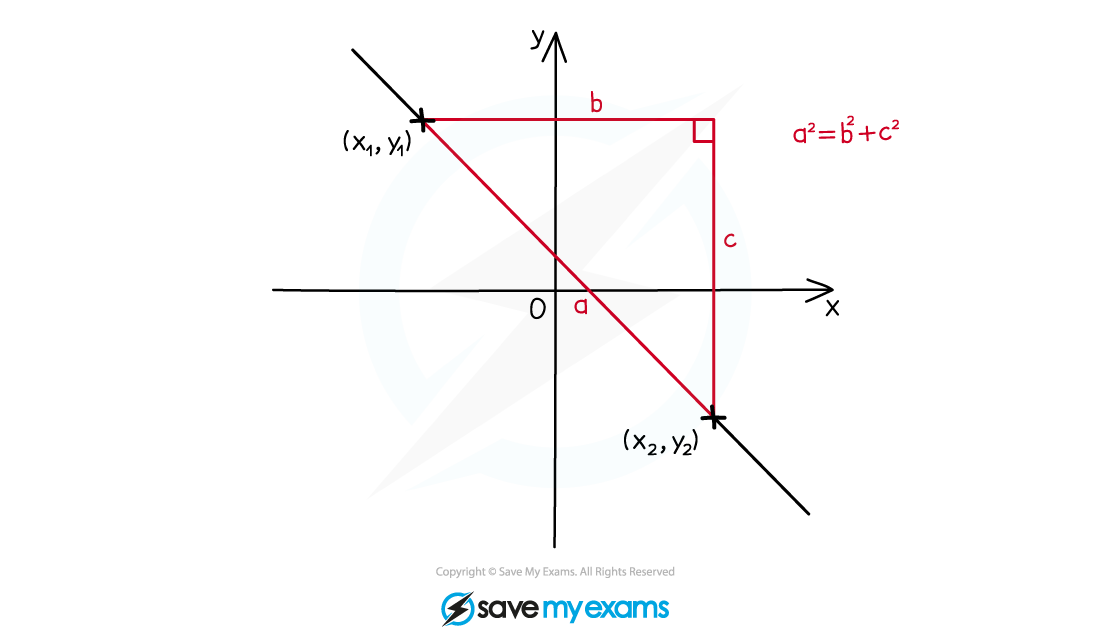
How do I calculate the length of a line?
The distance between two points with coordinates
and
can be found using the formula
This formula uses Pythagoras’ theorem
It is applied to the difference in the
-coordinates and the difference in the
-coordinates
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Be extra careful when negative coordinates are involved
It can help to put negative numbers in brackets to make your working clearer
E.g.
Worked Example
Point A has coordinates (3, -4) and point B has coordinates (-5, 2).
Calculate the distance of the line segment AB.
Using the formula for the distance between two points,
Substitute in the two given coordinates
Be careful with the negative numbers and
Simplify
10 units

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?

