SOHCAHTOA (AQA GCSE Maths) : Revision Note
Did this video help you?
SOHCAHTOA
What is trigonometry?
Trigonometry is the mathematics of angles in triangles
It looks at the relationship between side lengths and angles of triangles
What are sin, cos and tan?
The three trigonometric functions sine, cosine and tangent
They come from ratios of side lengths in right-angled triangles
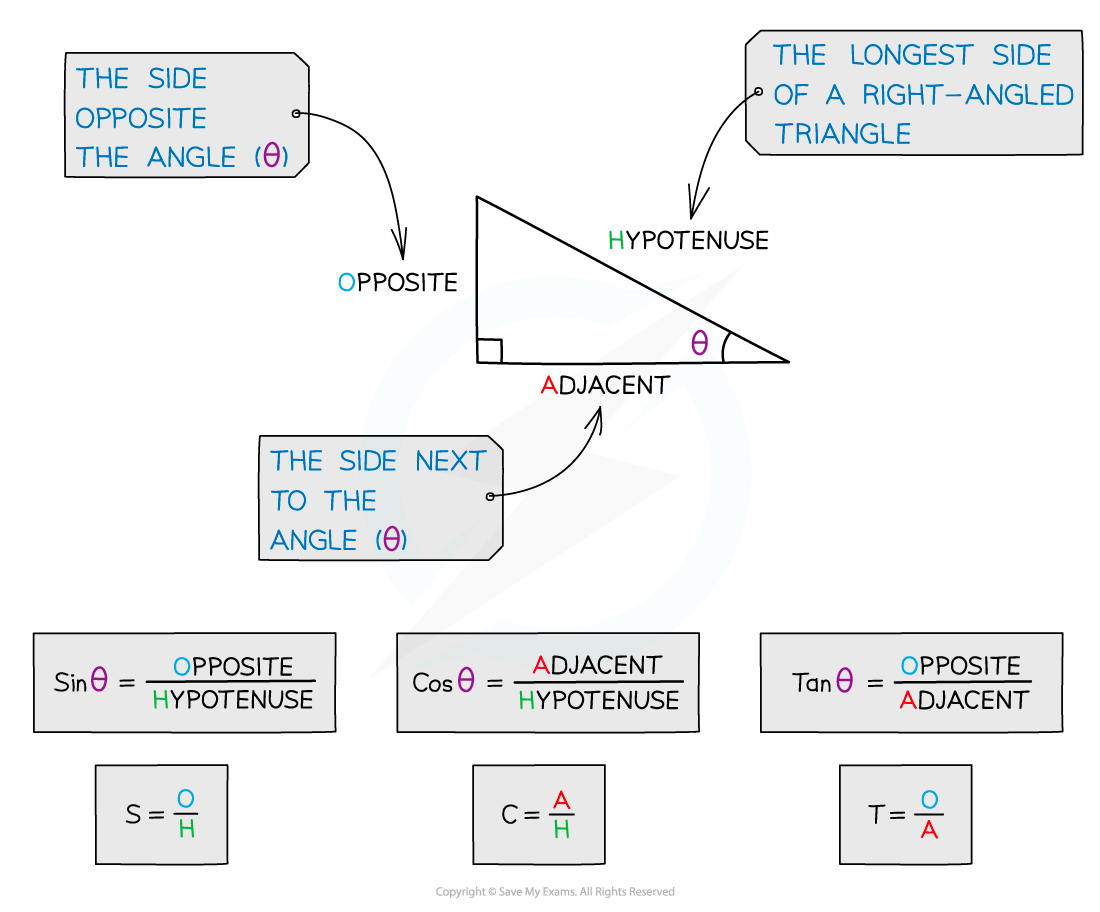
You must label the sides of a right-angled triangle in relation to a chosen angle θ
The hypotenuse, H, is the longest side in a right-angled triangle
It will always be opposite the right angle
The side opposite θ will be labelled opposite, O
The side next to θ will be labelled adjacent, A
The functions sine, cosine and tangent are the ratios of the lengths of these sides as follows
What is SOHCAHTOA?
SOHCAHTOA is a mnemonic often used to remember which ratio is which
Sin is Opposite over Hypotenuse
Cos is Adjacent over Hypotenuse
Tan is Opposite over Adjacent
H is always the same but O and A change depending on which angle is labelled as θ

How can I use SOHCAHTOA to find missing lengths?
STEP 1
Label the sides of the triangle as H, O and ASTEP 2
Identify which trigonometric ratio to use: sin, cos or tanWrite down the letter of the length you are given
Write down the letter of the length you want to find
Find the two letters in SOHCAHTOA to identify which ratio to use
If you have A and H then use cos
STEP 3
Substitute the values into the relevant trigonometric formulaRemember to put brackets around the angle
or
STEP 4
Rearrange and solve for the unknown letterYou will either need to multiply or divide
leads to
leads to
STEP 5
Type the expression into your calculatorThe question might ask you to round your answer
If not then round to three significant figures
How can I use SOHCAHTOA to find missing angles?
STEP 1
Label the sides of the triangle as H, O and ASTEP 2
Identify which trigonometric ratio to use: sin, cos or tanWrite down the letters of the lengths you are given
Find the two letters in SOHCAHTOA to identify which ratio to use
If you have O and A then use tan
STEP 3
Substitute the values into the relevant trigonometric formulaThe angle will be unknown
STEP 4
Substitute the fraction into the inverse trigonometric functionYou normally need to press SHIFT on your calculator first
leads to
STEP 5
Type the expression into your calculatorThe question might ask you to round your answer
If not then round to one decimal place
How do I find the shortest distance from a point to a line?
The shortest distance from any point to a line will always be the perpendicular distance
Form a right-angled triangle and then use SOHCAHTOA to find the relevant distance
Examiner Tips and Tricks
SOHCAHTOA (like Pythagoras) can only be used in right-angled triangles
Ensure your calculator is set to measure angles in degrees
You should see the letter D or the word Deg at the top of your screen
Worked Example
Find the length of the side cm in the following triangle.
Give your answer to 3 significant figures.

First label the triangle

We know A and we want to know O - that's TOA or
Multiply both sides by 9
Enter on your calculator
Round to 3 significant figures
Worked Example
Find the value of the angle ° in the following triangle.
Give your answer to 1 decimal place.
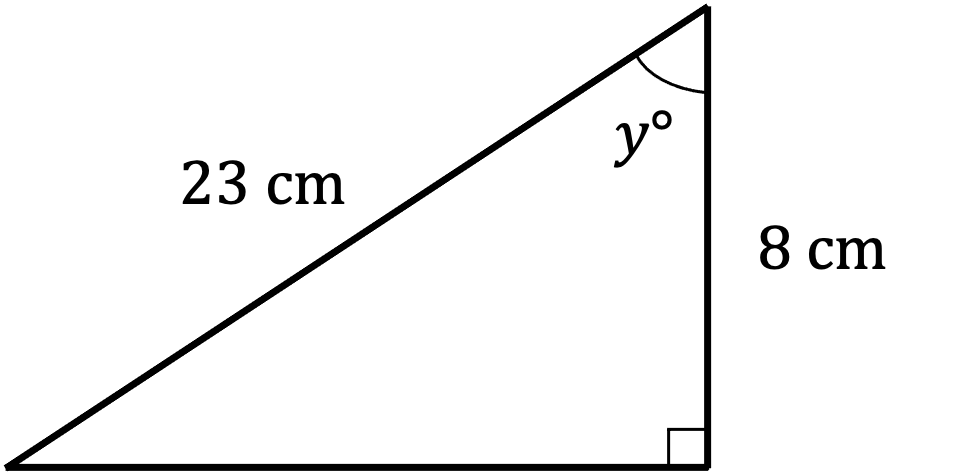
First label the triangle

We know A and H - that's CAH or
Use inverse cos to find
Enter on your calculator
Round to 1 decimal place

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?

