Area & Circumference of Circles (AQA GCSE Maths) : Revision Note
Did this video help you?
Area & Circumference
Why are circles different to other 2D shapes?
Circles are a shape that is made up of all the points on a 2D plane that are equidistant from a single point
Equidistant means the same distance
The circumference of a circle is its perimeter
π (pi) is the number (3.14159 …) that links a circle’s diameter to its circumference
You may be asked to give an area answer to a certain number of decimal places or significant figures
Alternatively you may be asked to give the exact value – or “give your answer in terms of π” – so this topic could crop up on the non-calculator paper!Diameter (d) is twice the radius (r)
How do I work with circles?
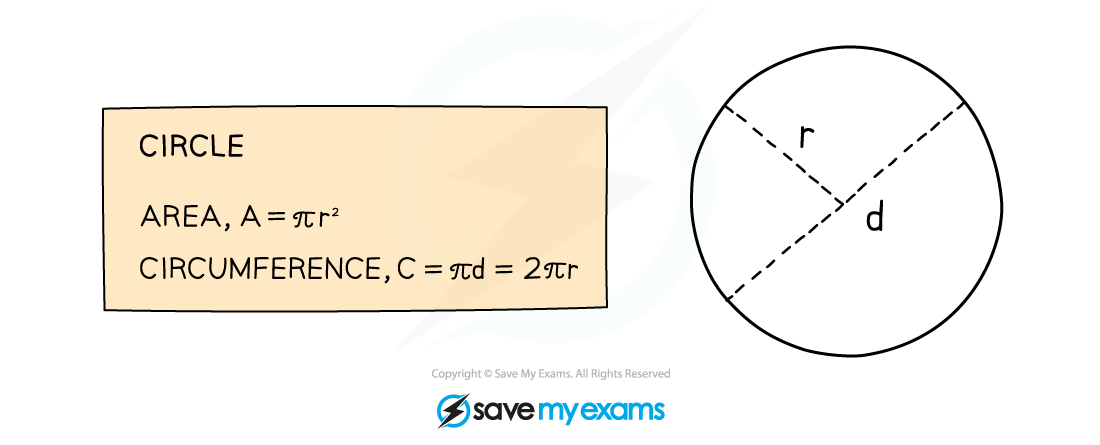
You must know the formulae for the area and circumference of a circle
There are two versions for the circumference and it is important not to get the radius and diameter confused
Remember that d = 2r
But you may prefer to remember the formulae by having different letters involved
Working with circle formulae is just like working with any other formula:
WRITE DOWN – what you know (what you want to know)
Pick correct FORMULA
SUBSTITUTE and SOLVE
Examiner Tips and Tricks
If you’re under pressure and can’t remember which formula is which, remember that area is always measured in square units (cm2, m2 etc.) so the formula with r2 in it is the one for area
The circumference is just a length, so its units will be the same as for length (cm, m, etc)
Worked Example
Find the area and perimeter of the semicircle shown in the diagram.
Give your answers in terms of .

The area of a semicircle is half the area of the full circle with the same diameter, so begin by finding the area of the full circle.
Find the radius by dividing the diameter by 2.
Substitute this into the formula for the area of a circle .
Leave your answer in terms of . (This just means do not multiply by
).
Find the area of the semicircle by dividing the full area by 2.
Area = 32π cm2
The perimeter of the semicircle is made up of both the arc of the circle (half of the circumference) and the diameter of the semicircle.
Find the full length of the circumference of the circle using the formula (or
).
Substitute the radius = 8 cm into the formula.
Again, leave your answer in terms of .
Find the length of the arc (the curved part of the perimeter of the semicircle) by dividing the full area by 2.
Find the full perimeter by adding this to the length of the diameter of the circle.
Perimeter = 8π + 16 cm

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?

