Quadratic Graphs (Edexcel GCSE Maths) : Revision Note
Quadratic Graphs
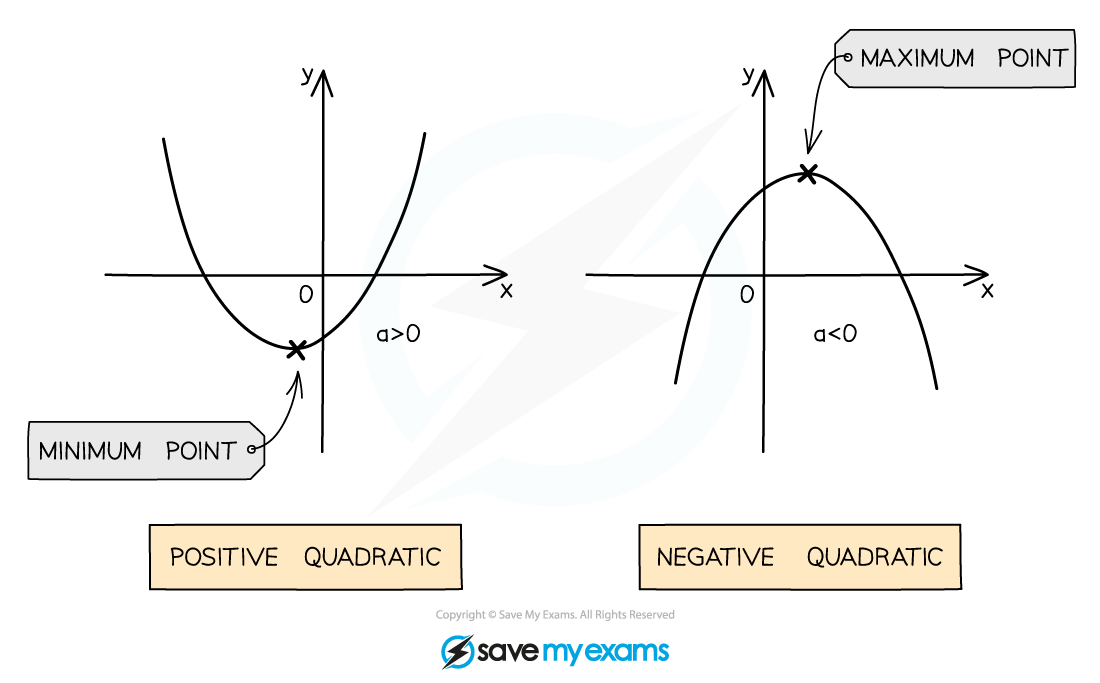
What are the key features of a quadratic graph?
The point where the graph turns is called the vertex
Positive quadratics have a minimum point
The bottom of the u-shape
Negative quadratics have a maximum point
The top of the n-shape
Quadratic graphs always have a vertical line of symmetry down the middle
The equation of the vertical line of symmetry is x = k
k is the x-coordinate of the minimum or maximum point
Quadratic graphs do not have to cross the x-axis
If they do, two x-intercepts are created, called roots
If the curve just touches the x-axis, only 1 root is created
Roots are symmetric about the vertical line of symmetry
Quadratic graphs always have one y-intercept
Worked Example
The graph of the equation is shown below.

(a) Write down the coordinates of the roots of the equation.
The roots of the equation are the x-intercepts of the graph
The graph crosses at x = 2 and x = 3
The roots of the graph are at (0, 2) and (0, 3)
(b) Write down the equation of the line of symmetry.
The line of symmetry is a vertical line that occurs halfway between the x-intercepts
Find the x-value that is halfway between the roots
The x-intercepts are x = 2 and x = 3
Halfway between is x = 2.5
Write down the equation of the line of symmetry
x = 2.5

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?

