Reflections of Graphs (OCR GCSE Maths): Revision Note
Exam code: J560
Reflections of Graphs
What are reflections of graphs?
Reflections of graphs are a type of transformation where the curve is reflected about one of the axes

How do I reflect graphs?
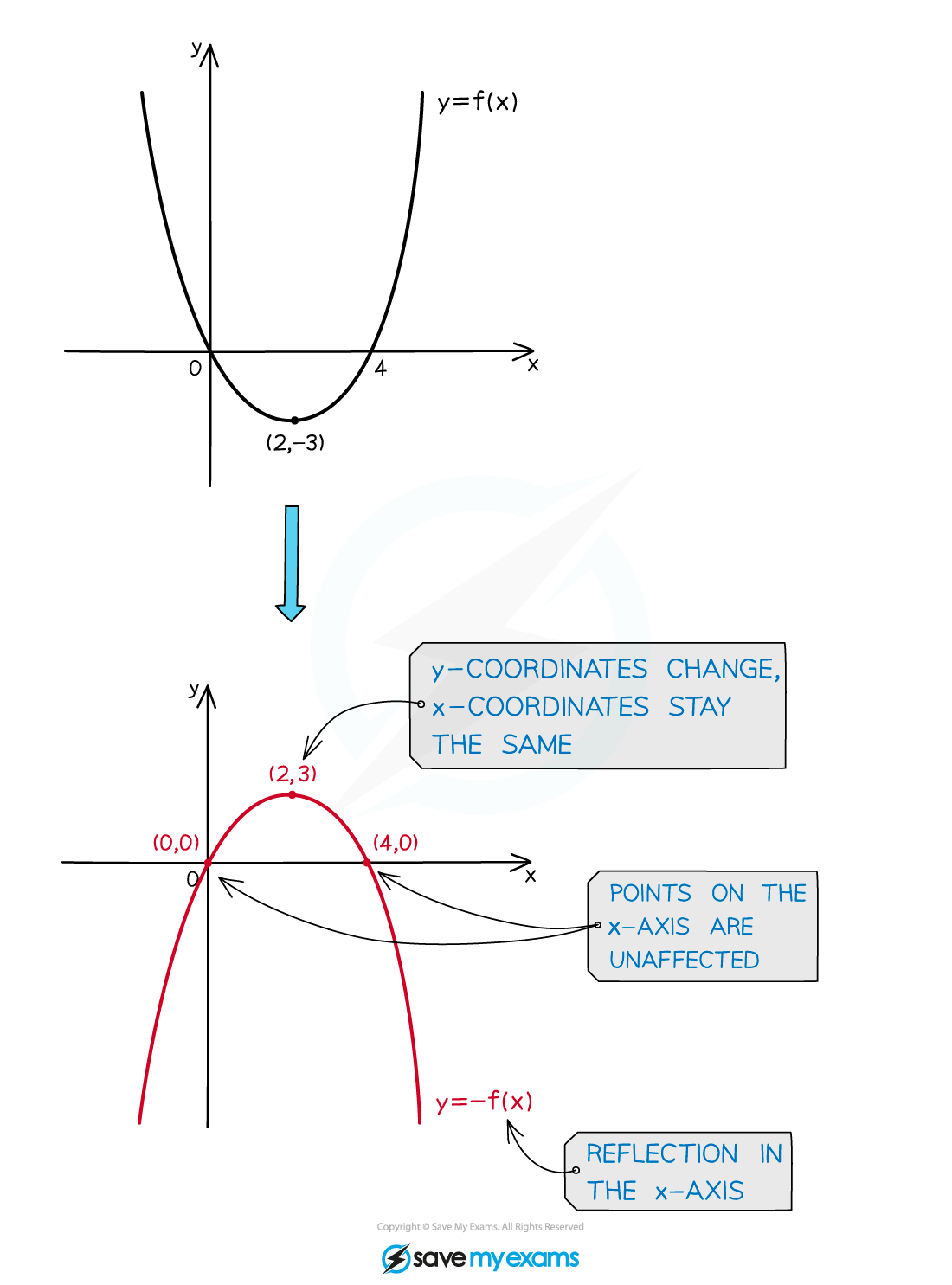
Vertical reflections: y=-f(x)
Given an original equation in x, the graph of that equation will be reflected in the x-axis by a minus sign outside the bracket
The
coordinates change sign
The
coordinates are unaffected
For example, in relation to y = x2;
y = −x2 is a reflection in the x-axis
(note that y = −x2 is the same as y = −(x2) )
Another example, in relation to y = sin(x) where x is in degrees;
y = −sin(x) is a reflection in the x-axis
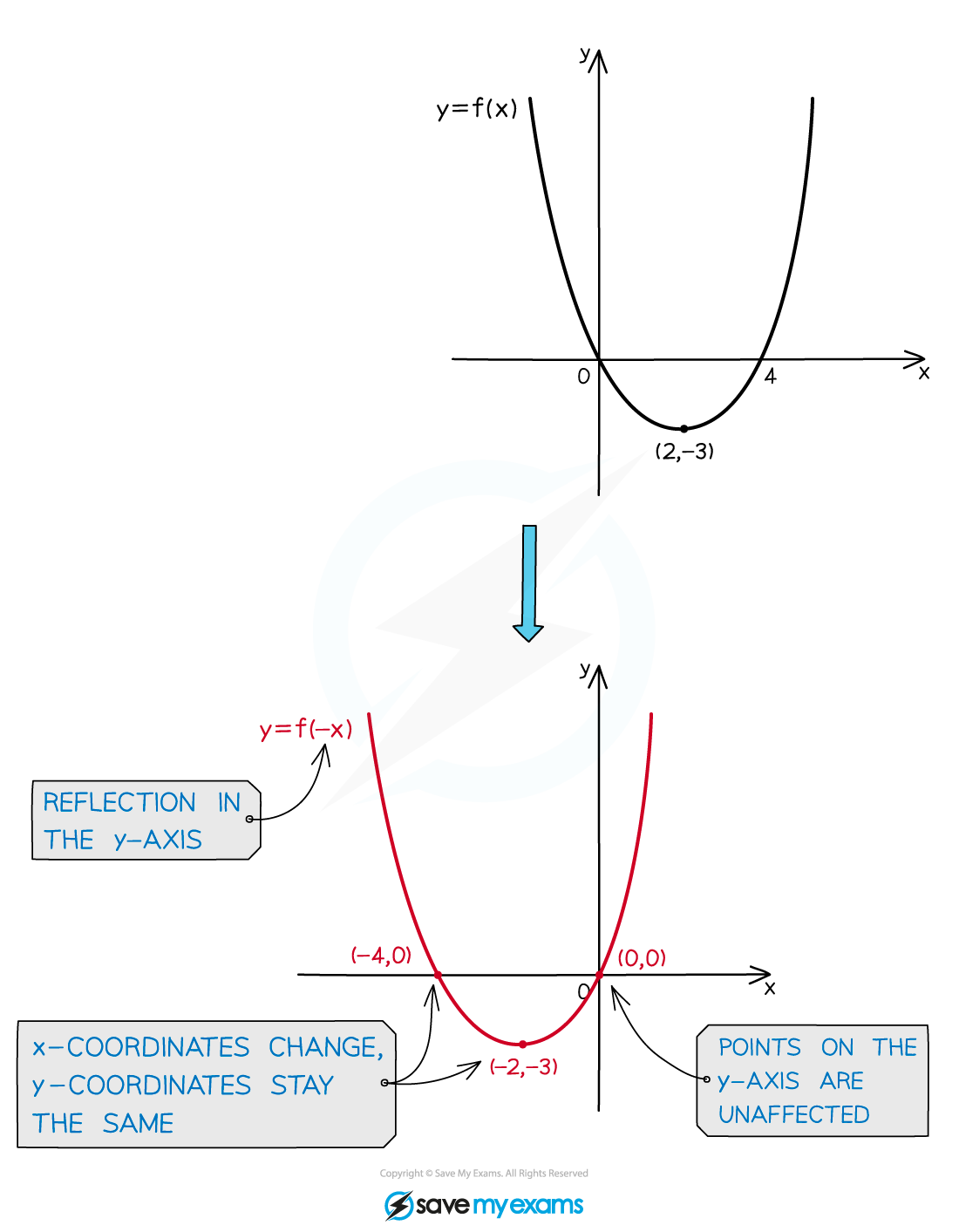
Horizontal reflections: y=f(-x)
Given an original equation in x, the graph of that equation will be reflected in the y-axis by a minus sign inside a bracket next to x
The
coordinates change sign
The
coordinates are unaffected
For example, in relation to y = x2;
y = (−x)2 is a reflection in the y-axis
Another example, in relation to y = sin(x) where x is in degrees;
y = sin(−x) is a reflection in the y-axis
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When reflecting graphs in the exam, reflect any key points on the graph first, then join them up with a smooth curve.
How does a reflection affect the equation of the graph?
When a graph is reflected, you can change its equation algebraically
There is no need to sketch the graph
Reflecting in the
-axis puts a
in front of the whole equation
For example,
becomes
This simplifies to
Reflecting in the
-axis replaces any
with
in the equation
For example,
becomes
This simplifies to
Worked Example
The graph of is shown on the graph below.
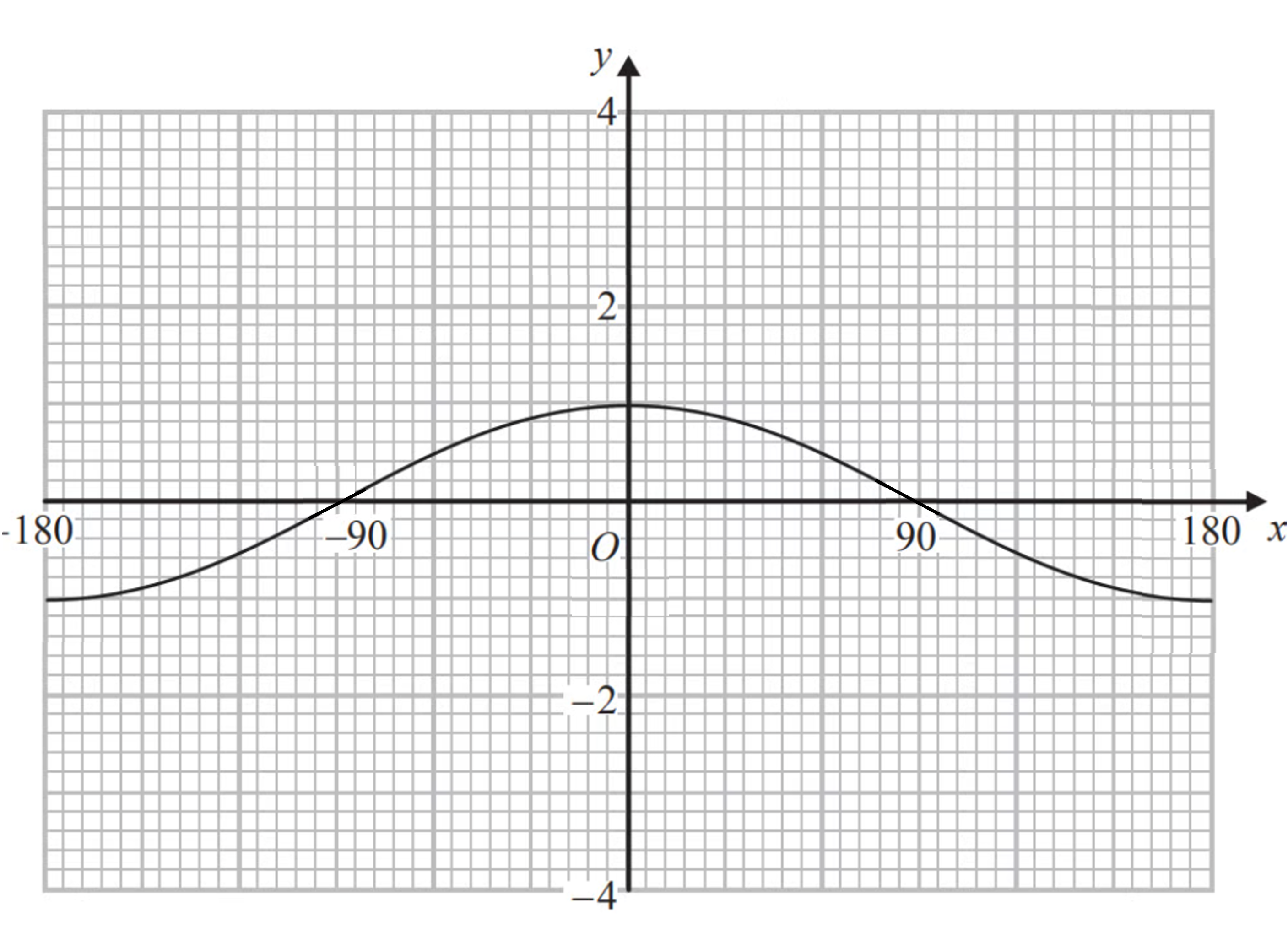
(a) On the same graph sketch .
y = −cos(x) is a reflection in the x-axis
Reflect key points first- x-intercepts, maximums and minimums as shown below
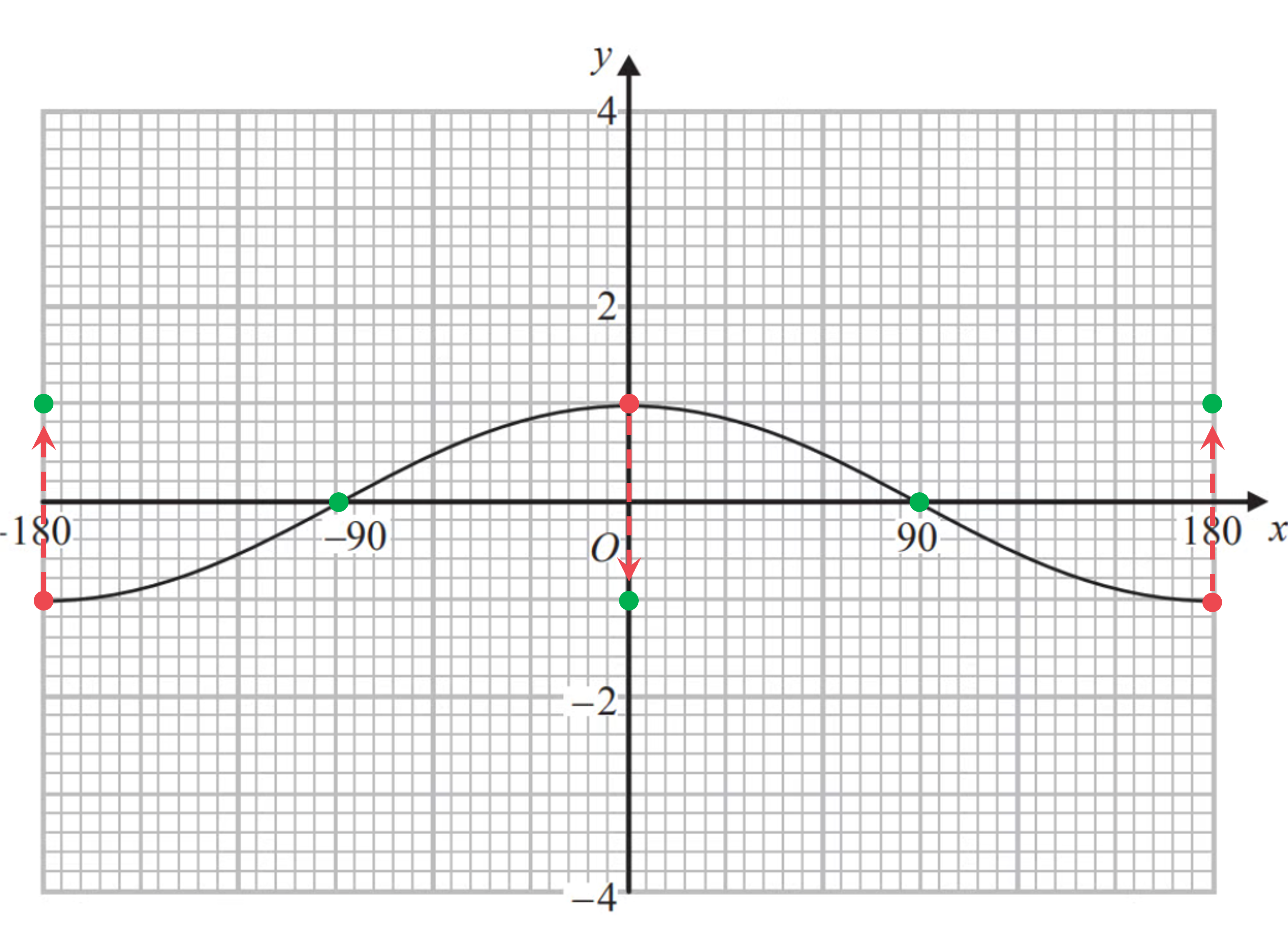
(Notice that points on the x-axis don't change during a reflection in the x-axis. They are invariant)
Now join your new points with a curved line. The new curve should go through the key points shown in the answer below
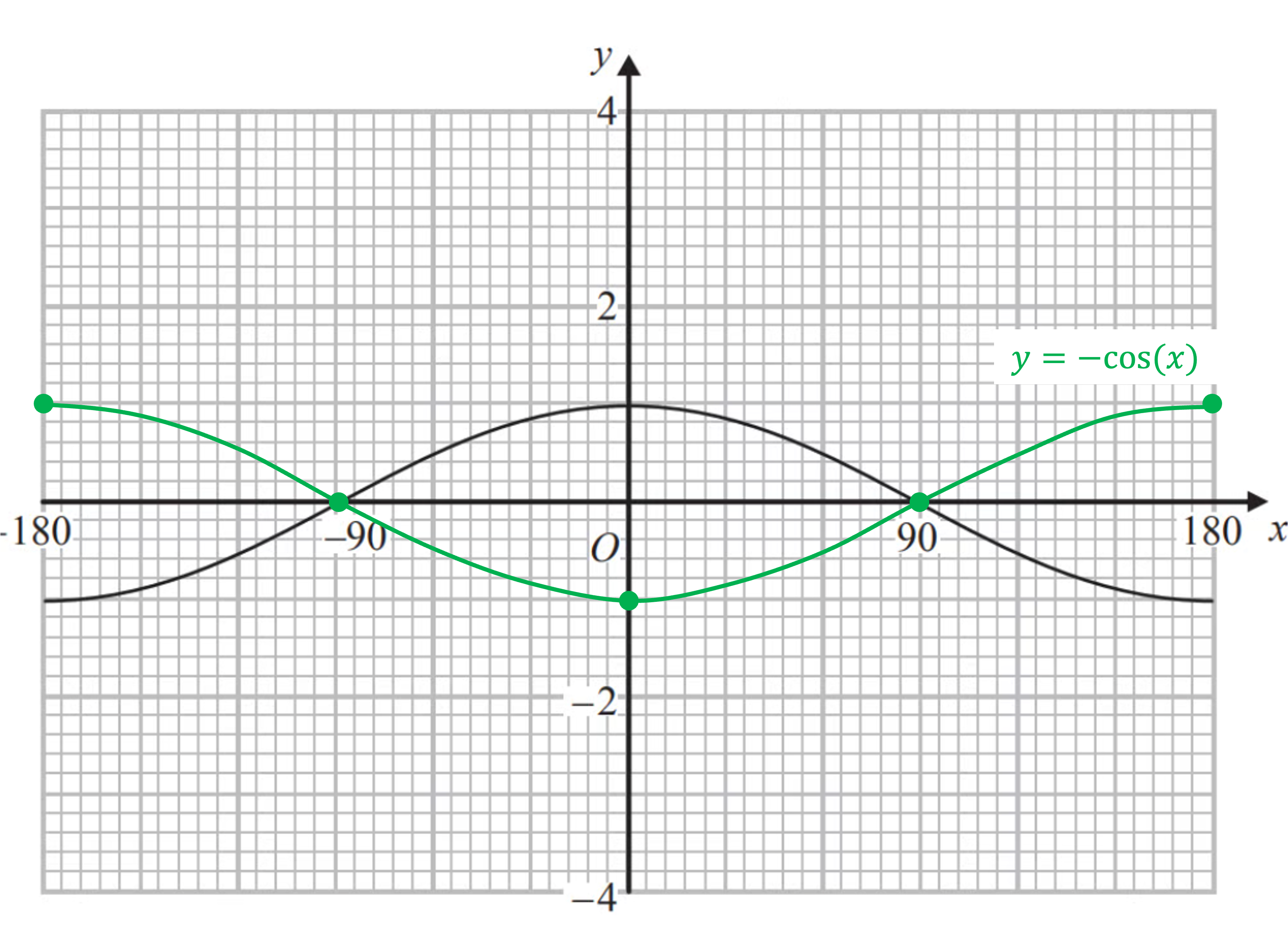
(b) Comment on the graph of in relation to the graph of
.
y = cos(−x) is a reflection in the y-axis. If we reflect y=cos(x) in the y-axis it maps exactly onto itself
They are the same graph
Worked Example
The graph of is reflected in the x-axis and translated 3 units to the left.
Write down an equation of the translated graph.
"Reflected in the x-axis" leads to
And "translated 3 units left" leads to

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?