Lines of Symmetry (Edexcel GCSE Maths) : Revision Note
Lines of Symmetry
What is line symmetry?
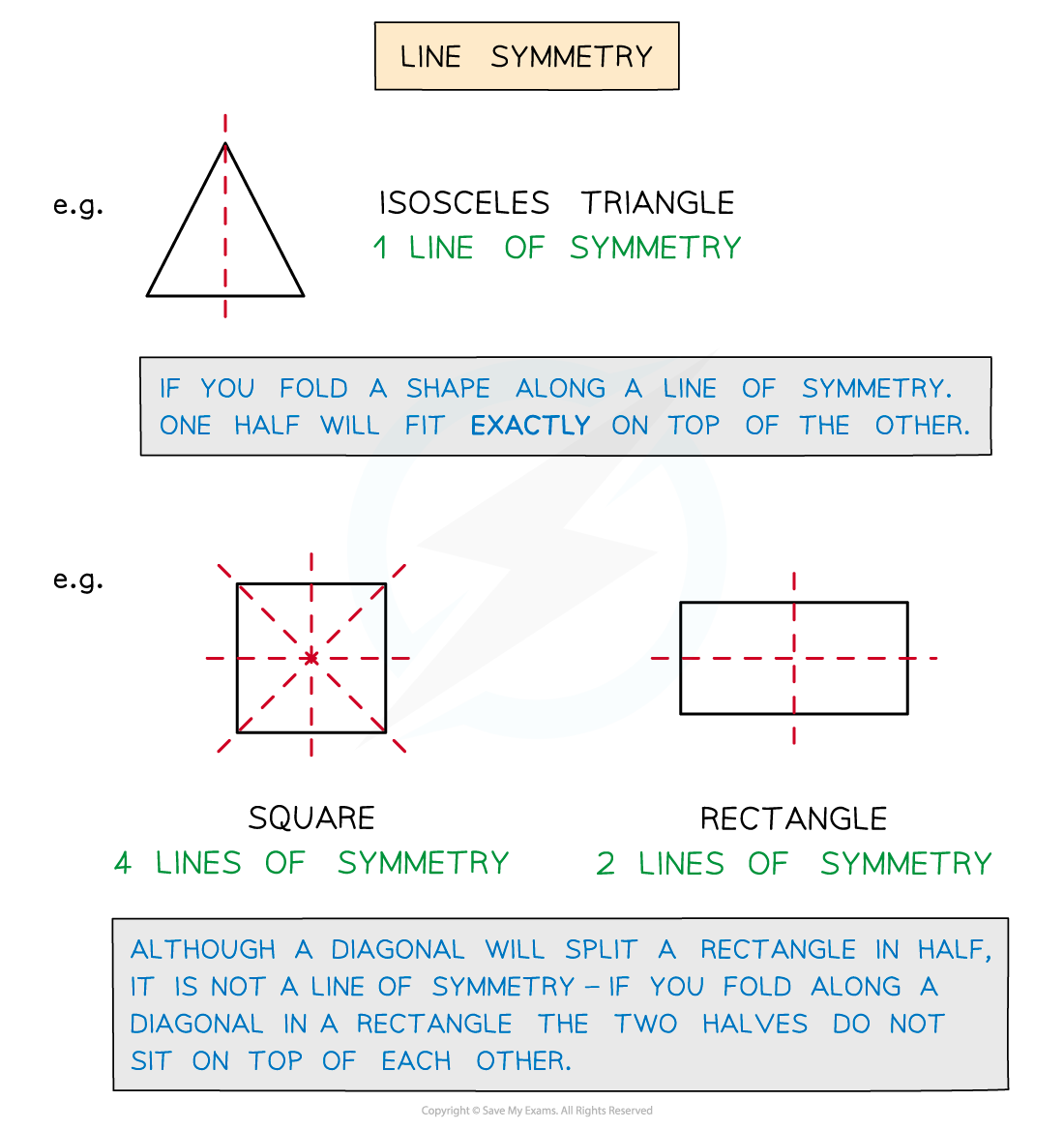
Line symmetry refers to shapes that can have mirror lines added to them
Each side of the line of symmetry is a reflection of the other side
Lines of symmetry can be thought of as a folding line too
Folding a shape along a line of symmetry results in the two parts sitting exactly on top of each other
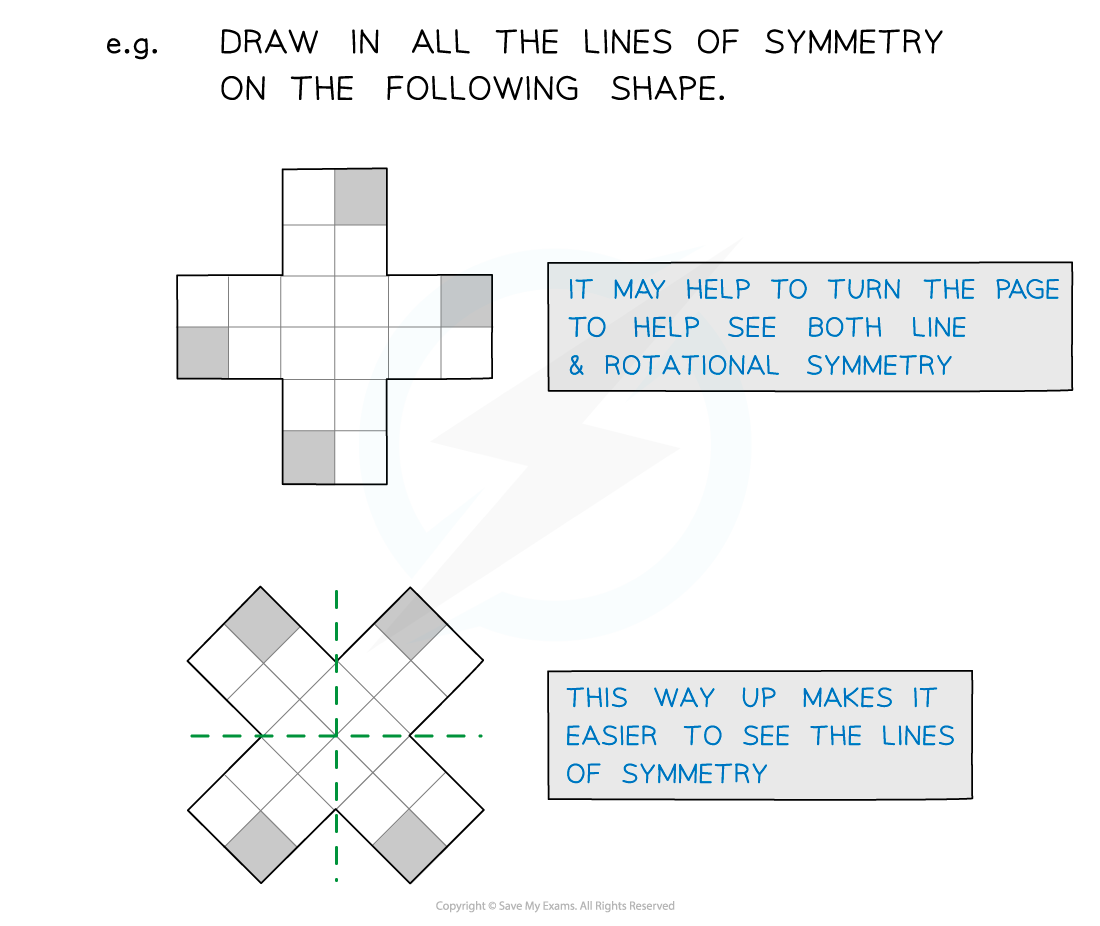
It can help to look at shapes from different angles; turn the page to do this
Some questions will provide a portion of a shape and a line of symmetry, and you need to fill in the remaining half of the shape
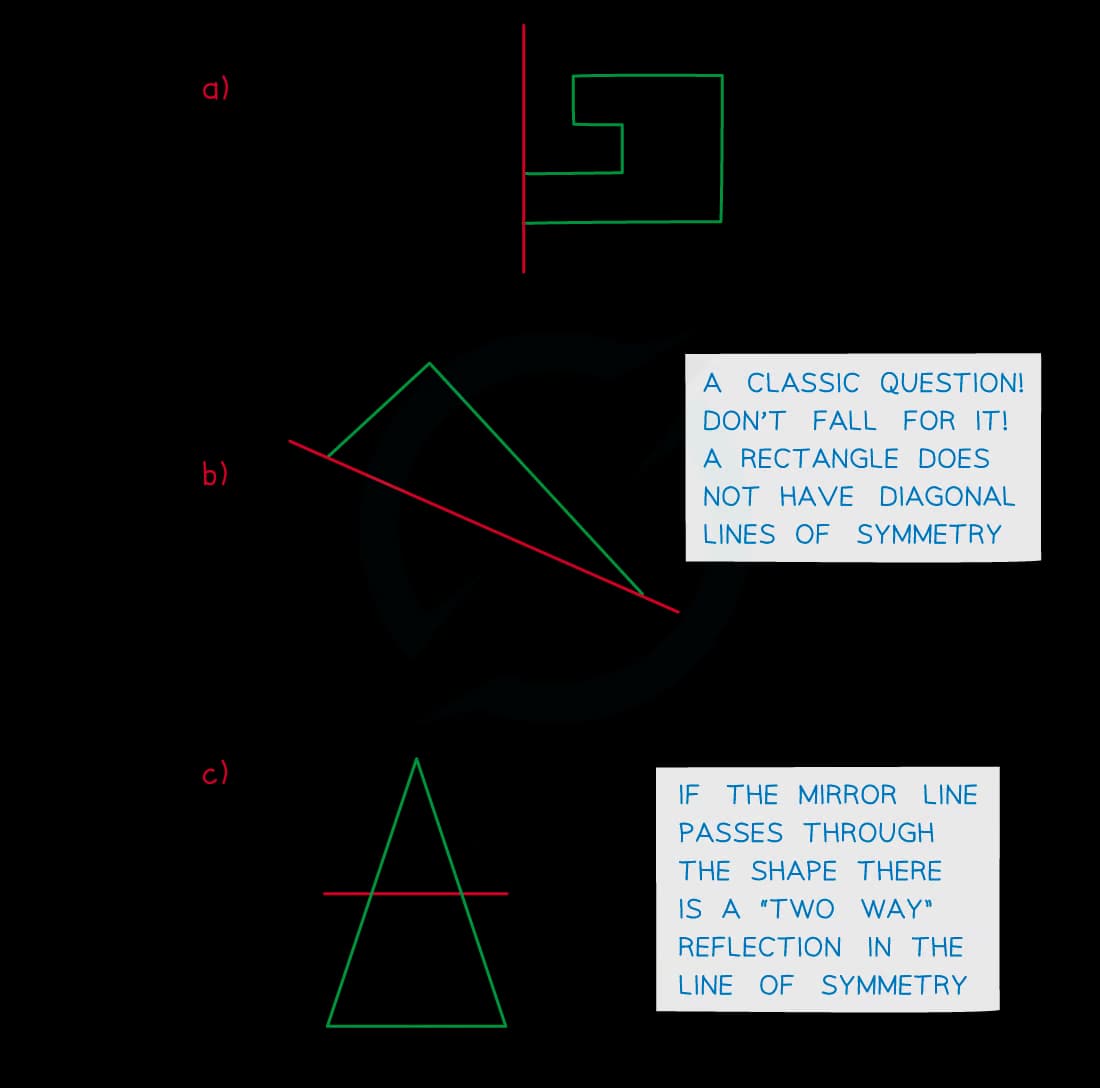
Be careful with diagonal lines of symmetry
Use tracing paper to trace the shape and then flip along the line of symmetry
“Two-way” reflections (like part c below) occur if the line of symmetry passes through the shape


Examiner Tips and Tricks
It can help to add the lines of symmetry to a diagram if one is given in a question
You should be provided with tracing paper in the exam, use this to help you
You can request it if you are not given it at the start
Worked Example
Consider the shape below.
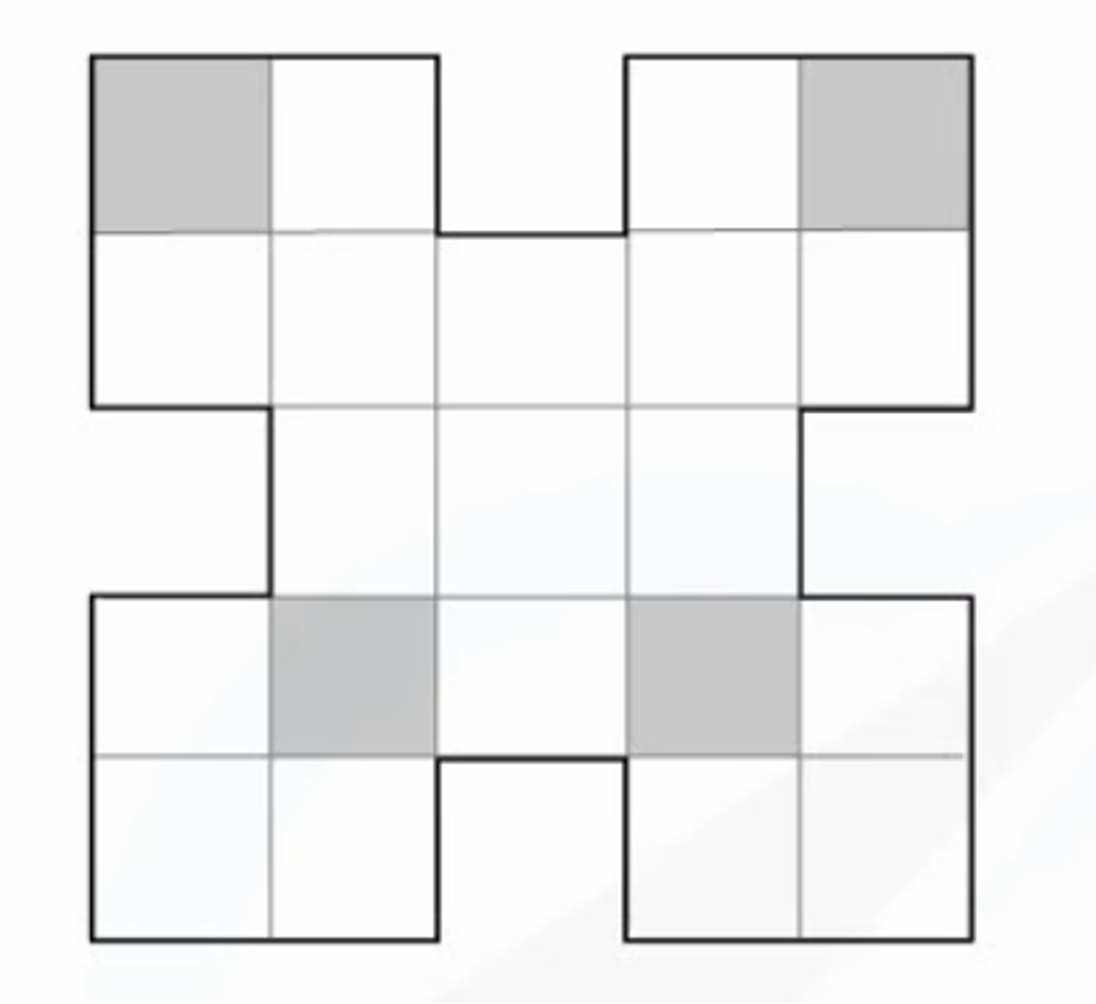
(a) Write down the number of lines of symmetry.
The only line of symmetry is shown below
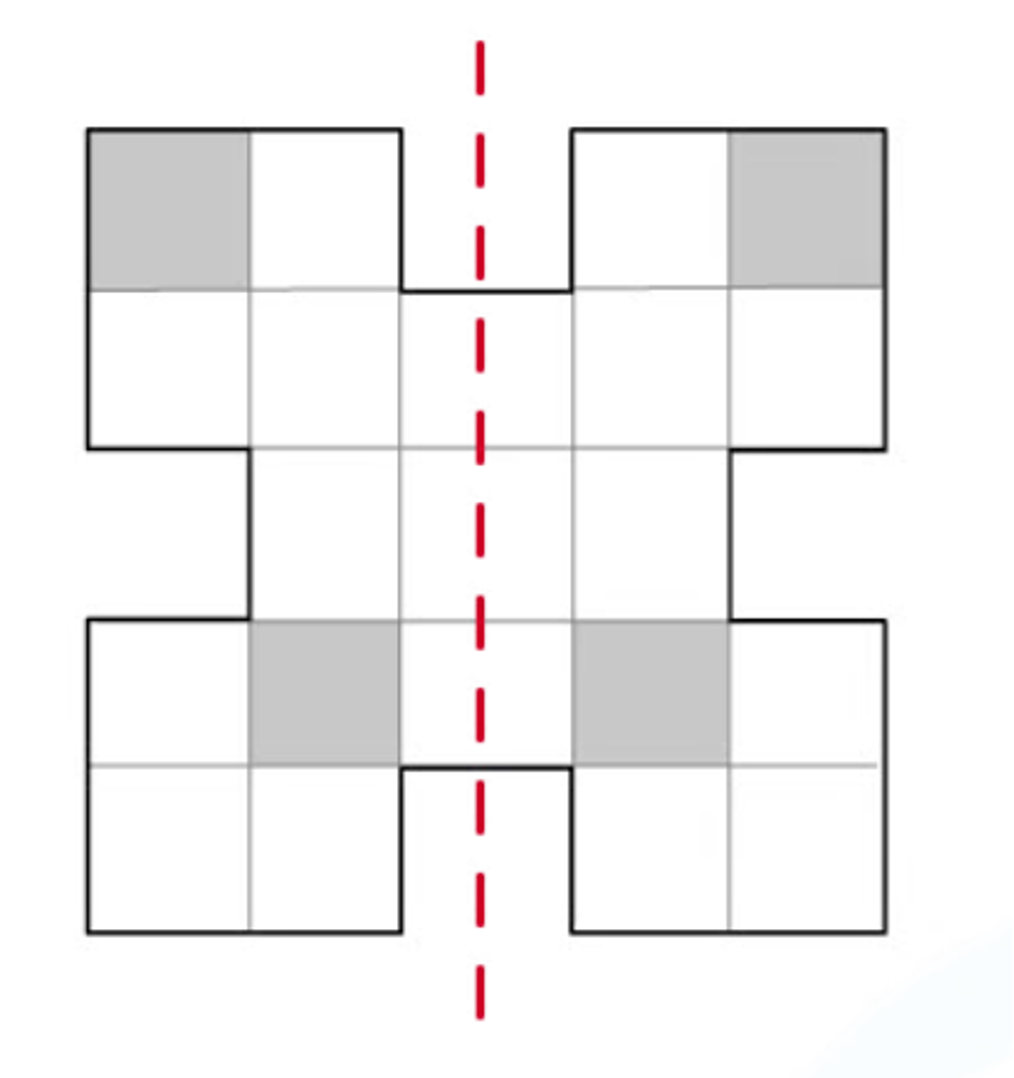
There is 1 line of symmetry.
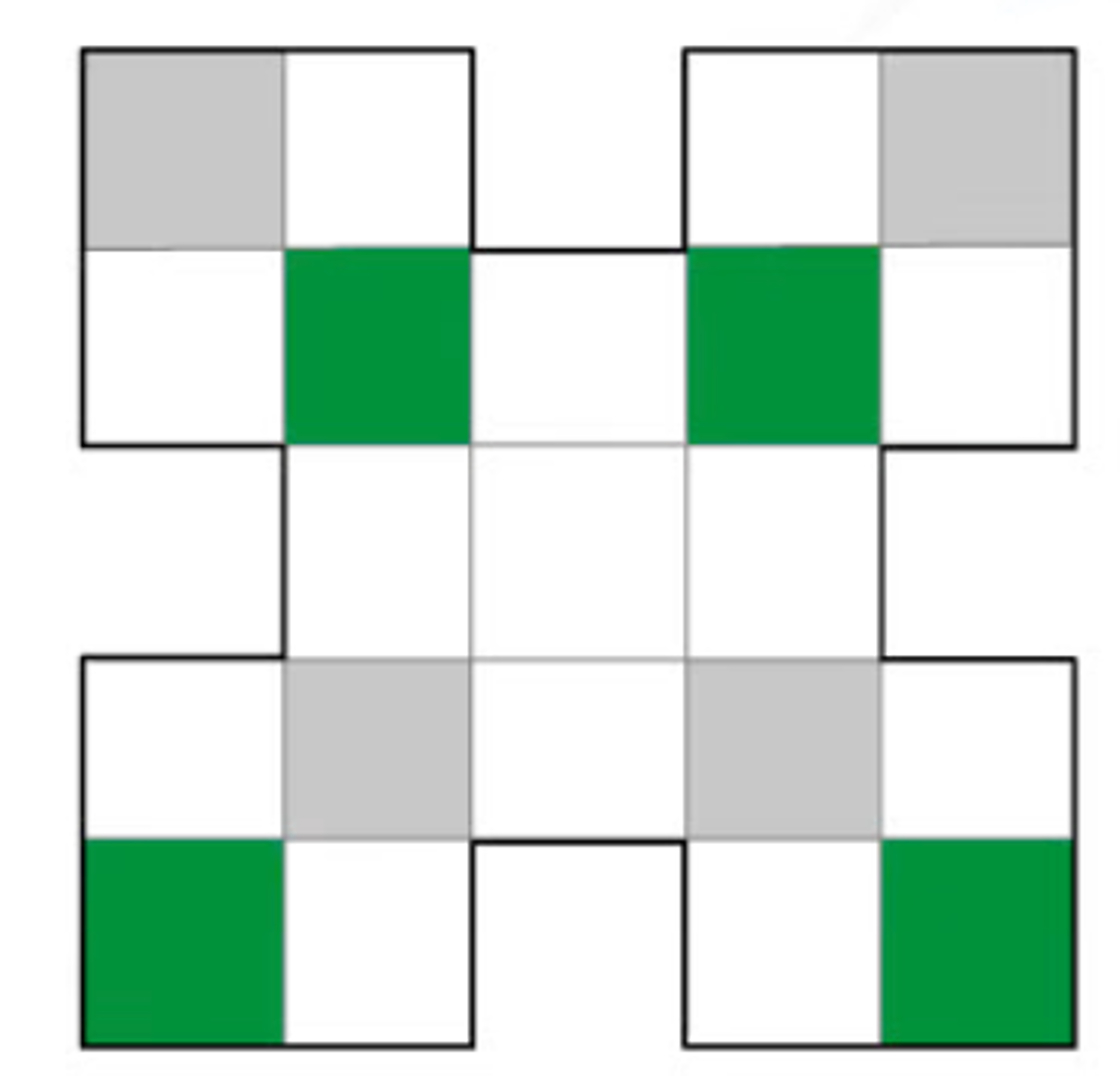
(b) Shade exactly 4 more squares so that the shape has 4 lines of symmetry.
The shape below has a horizontal, a vertical, and 2 diagonal lines of symmetry

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?

