The Sine Rule (Edexcel GCSE Maths) : Revision Note
Did this video help you?
Sine Rule
What is the sine rule?
The sine rule is used in non right-angled triangles
It allows us to find missing side lengths or angles
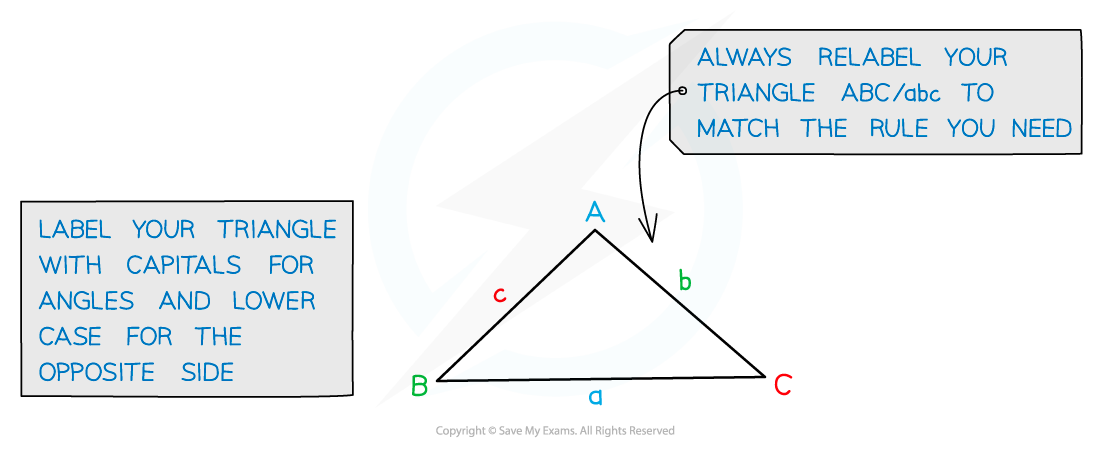
It states that for any triangle with angles A, B and C
Where
is the side opposite angle A
is the side opposite angle B
is the side opposite angle C
How do I use the sine rule to find missing lengths?
Use the sine rule
when you have opposite pairs of sides and angles in the question
a and A, or b and B, or c and C
Start by labelling your triangle with the angles and sides
Angles have upper case letters
Sides opposite the angles have the equivalent lower case letter
To find a missing length, substitute numbers into the formula
You only need to have two parts equal to each other (not all three)
Then solve to find the side you need
How do I use the sine rule to find missing angles?
To find a missing angle, it is easier to rearrange the formula first by flipping each part
The angles are now in the numerators of the fractions
Substitute the values you have into the formula and solve
You will need to use inverse sine in your calculation,
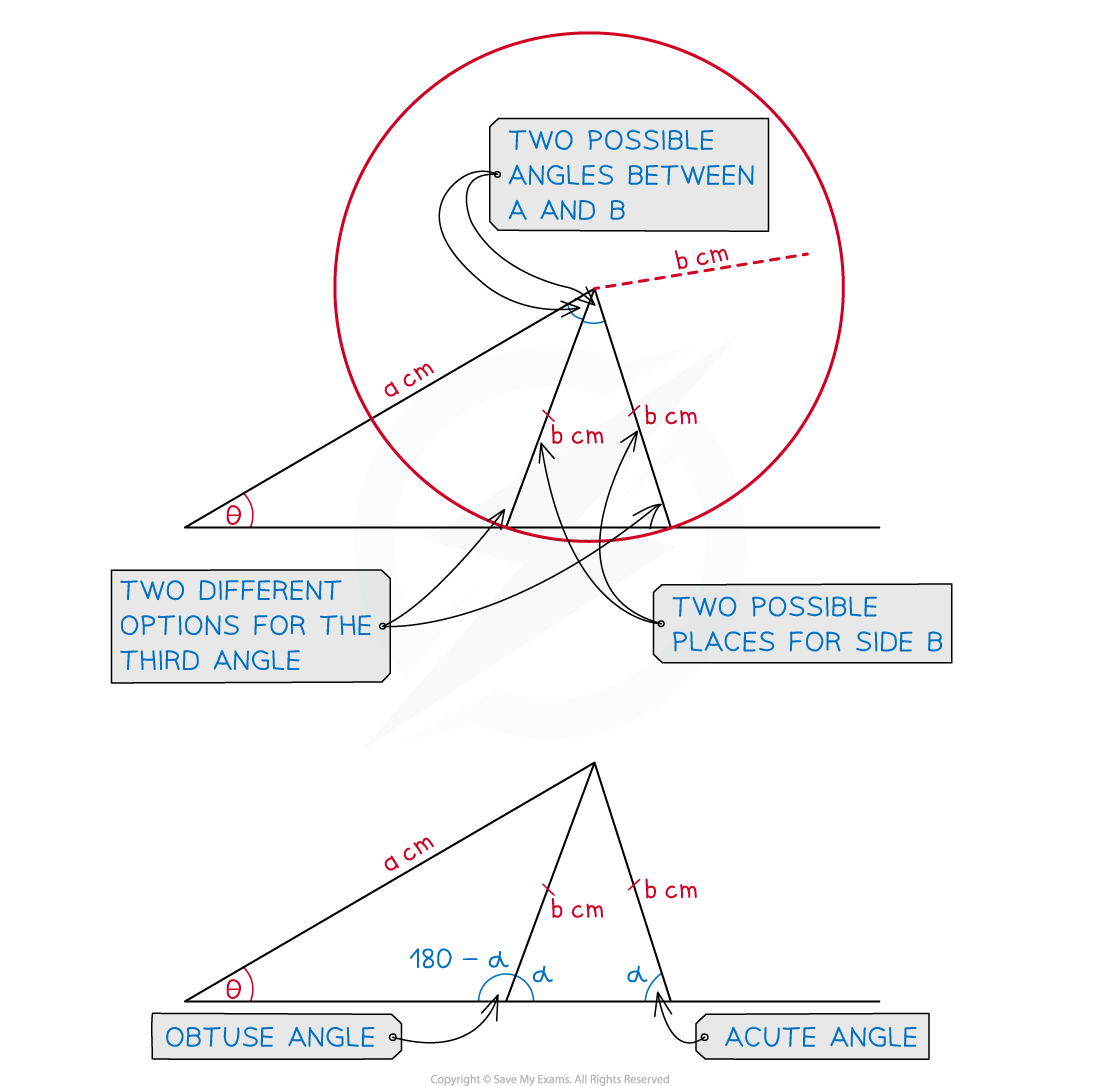
What is the ambiguous case of the sine rule?
Given information about a triangle, there may be two different ways to draw it
In the diagram below, the lengths of two sides are given, a and b
A base angle is also given,
, but no angle near b is given
It turns out that there are two possible ways to arrange b to complete the triangle!
Both triangles have the correct values of a, b and
To other base angle could either be obtuse or acute
The sine rule only gives the acute answer on your calculator
You need to check the diagram to see if the angle you need is actually obtuse
If it is, use this rule: obtuse angle = 180 - acute angle
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The sine rule is given in the formula booklet.
Worked Example
The following diagram shows triangle ABC.
,
and angle
.
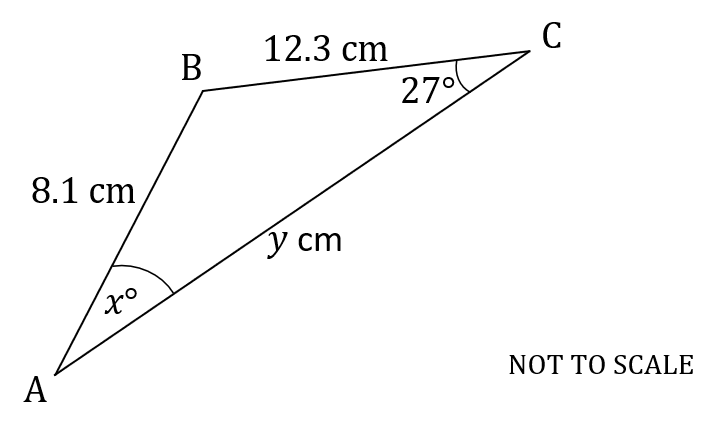
(a) Calculate the value of .
Label the sides of the diagram

x is an angle so use the sine rule with the angles on top
In practice, you only need to equate two of these three parts
(to 1 d.p)
(b) Calculate the value of .
To find y you need to know the angle opposite (angle ABC)
You know 27 and x from above, so subtract these from 180
y is a length so use the sin rule with the sides on the top
cm (to 3 s.f.)

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?

