The Cosine Rule (Edexcel GCSE Maths) : Revision Note
Did this video help you?
Cosine Rule
What is the cosine rule?
The cosine rule is used in non right-angled triangles
It allows us to find missing side lengths or angles
It states that for any triangle
Where
is the side opposite angle A
and
are the other two sides
and
are either side of angle A
A is the angle between them
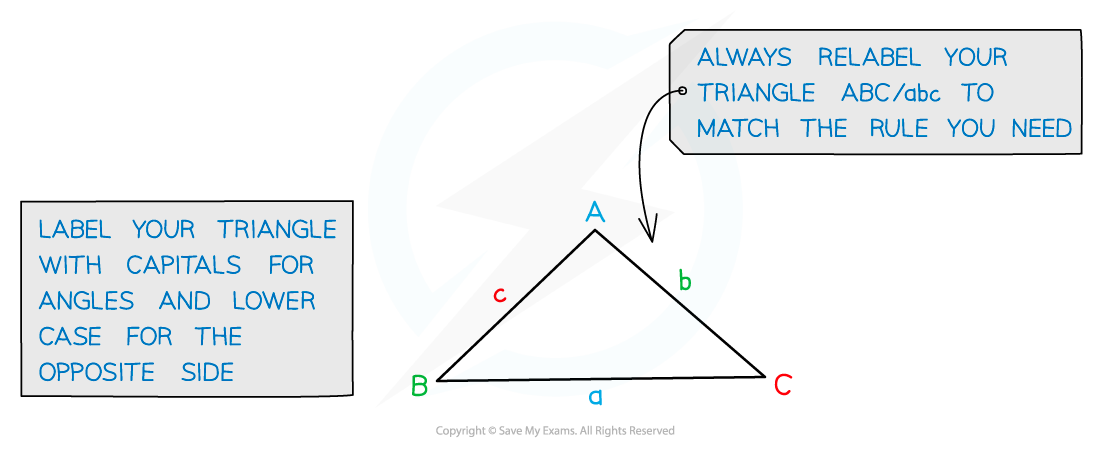
How do I use the cosine rule to find a missing length?
Use the cosine rule for lengths
when you have two sides and the angle between them
and you want to find the opposite side, a
Start by labelling your triangle with the angles and sides
Angles have upper case letters
Sides opposite the angles have the equivalent lower case letter
Substitute values into
Make a the subject (don't forget to square root)
How do I use the cosine rule to find a missing angle?
Use the cosine rule for angles
when you have all three sides
and you want to find an angle
It helps to rearrange the formula as follows, by adding
to both sides then making
the subject
Use the formula
to find the unknown angle A
Remember, A is the angle between sides b and c
(you may need to relabel the triangle)
You will need to use inverse cosine at the end,
Unlike the sine rule, there is no ambiguous case of the cosine rule
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You are given the cosine rule in the form
on the formula sheet
Getting an error on your calculator when finding an angle may mean you have rearranged the formula incorrectly
Worked Example
The following diagram shows triangle , where
,
and
.
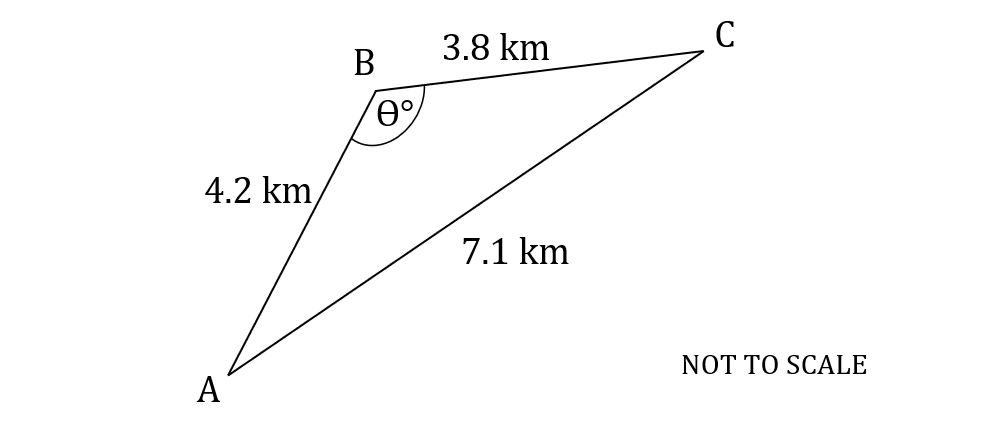
Calculate the value of angle .
The side opposite the angle is 7.1, so
The sides 4.2 and 3.8 are and
(in either order)
Use the cosine rule in the rearranged form
(to 1 d.p.)

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?

