Reflections of Graphs (Edexcel GCSE Maths) : Revision Note
Did this video help you?
Reflections of Graphs
What are reflections of graphs?
Reflections of graphs are a type of transformation where the curve is reflected about one of the axes

How do I reflect graphs?
Let
be the equation of the original graph
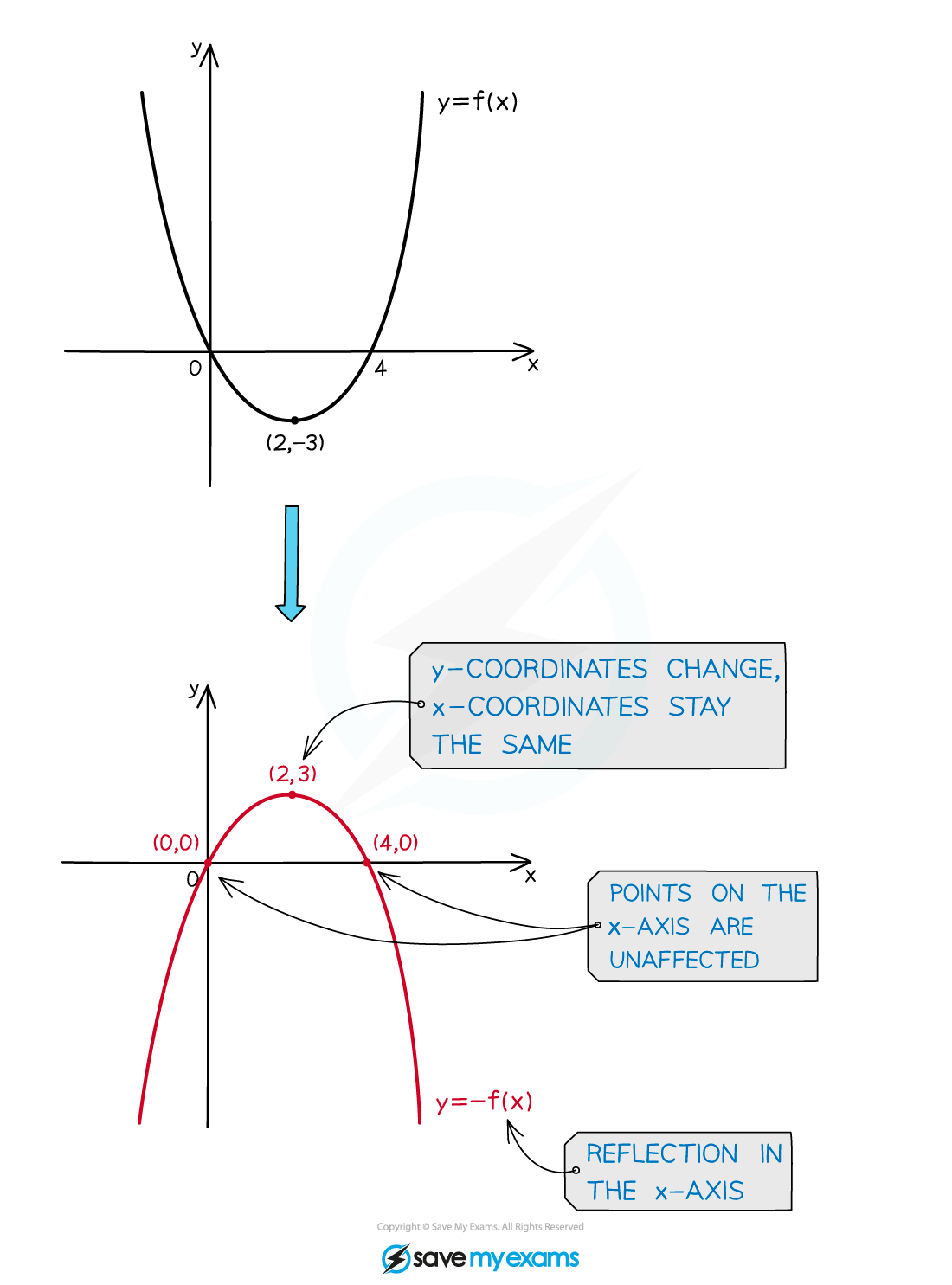
Vertical reflections: y=-f(x)
is a reflection in the
-axis
The
coordinates change sign
The
coordinates are unaffected
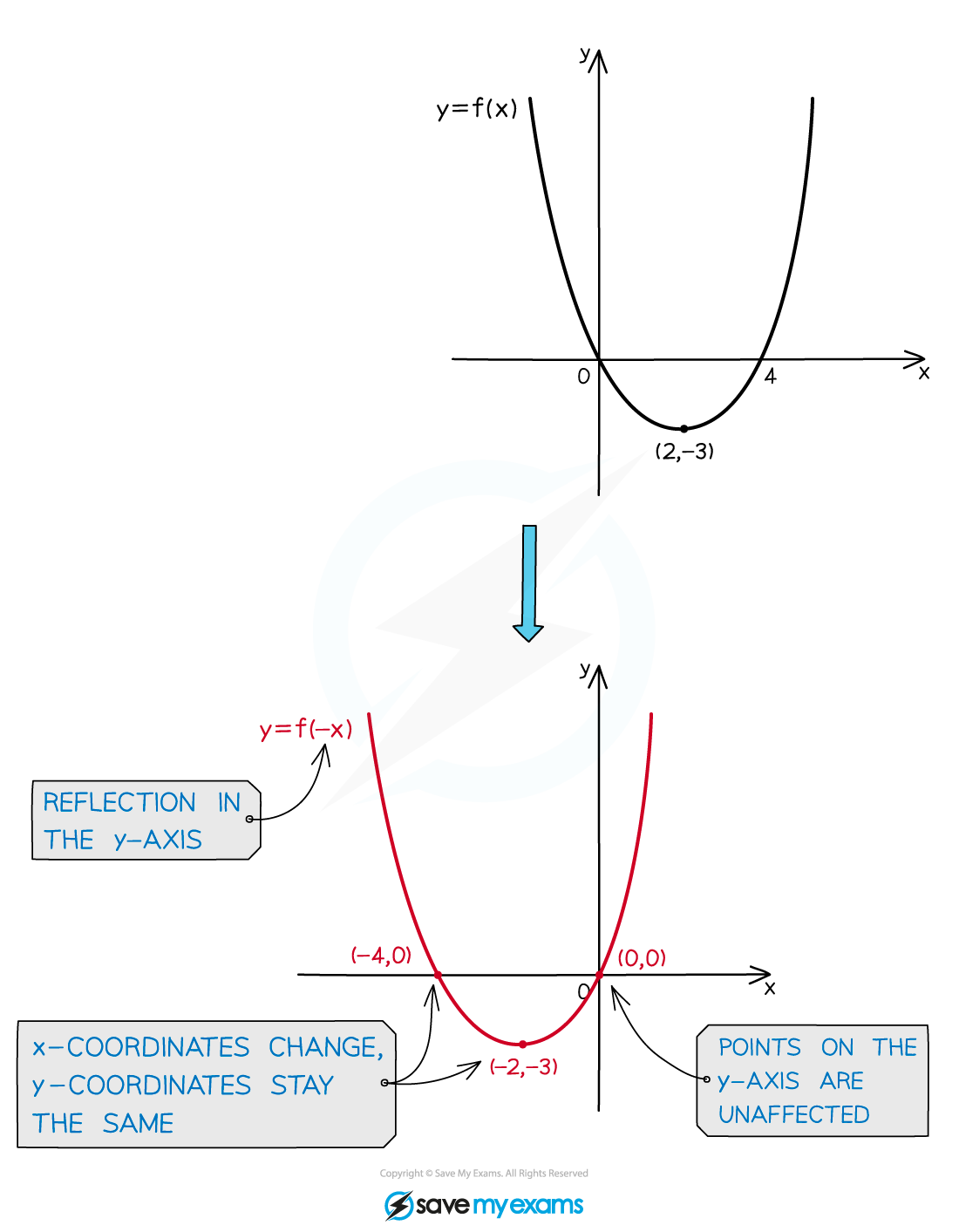
Horizontal reflections: y=f(-x)
is a reflection in the
-axis
The
coordinates change sign
The
coordinates are unaffected
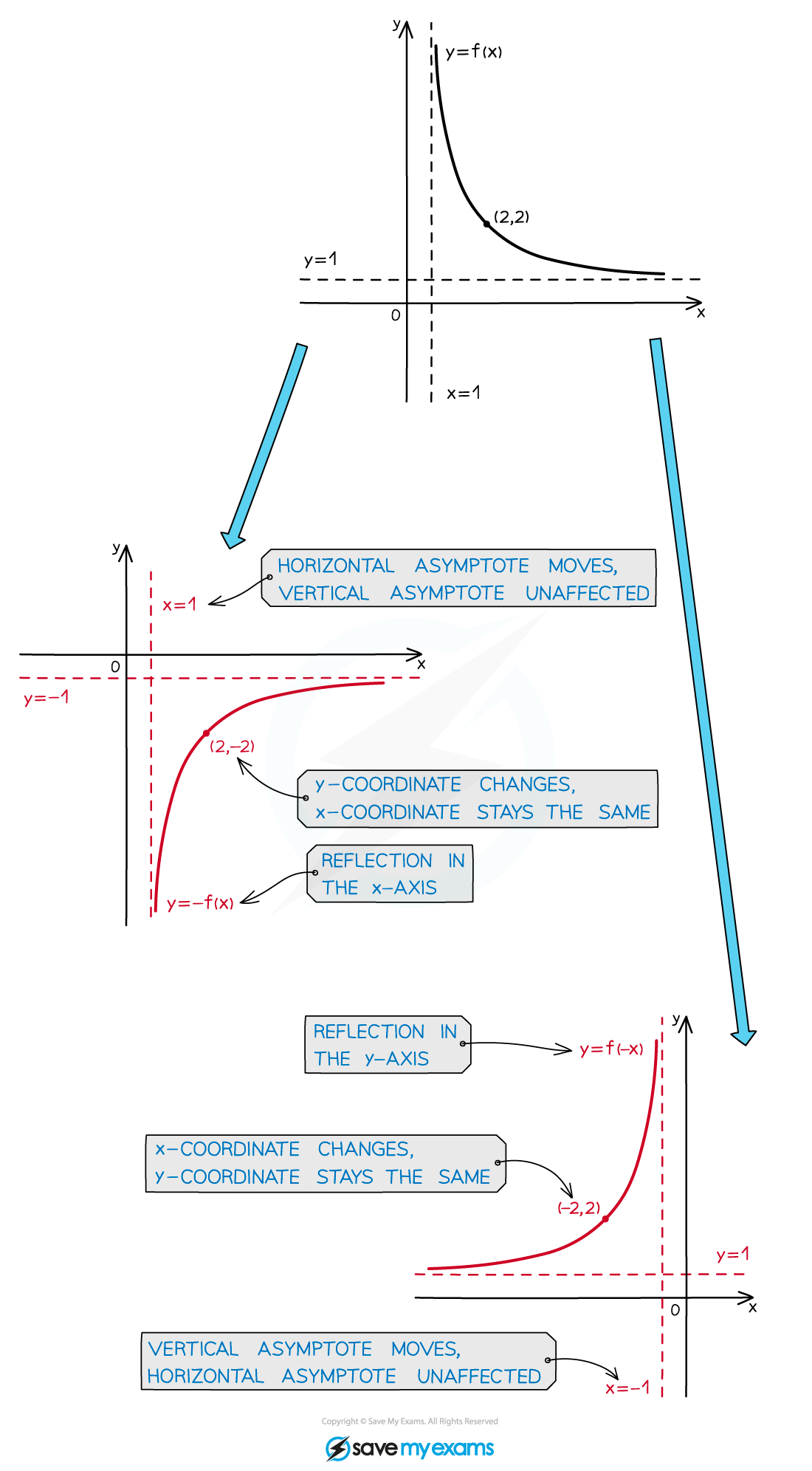
What happens to asymptotes when a graph is reflected?
Any asymptotes of
are also reflected
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When reflecting graphs in the exam, reflect any key points on the graph first, then join them up with a smooth curve.
How does a reflection affect the equation of the graph?
When a graph is reflected, you can change its equation algebraically
There is no need to sketch the graph
Reflecting in the
-axis puts a
in front of the whole equation
For example,
becomes
This simplifies to
Reflecting in the
-axis replaces any
with
in the equation
For example,
becomes
This simplifies to
How do I apply a combined reflection?
The graph of
is a combined reflection in both the
and
axes
It does not matter which order you apply these in
For example, reflect about the
-axis then about the
-axis
Worked Example
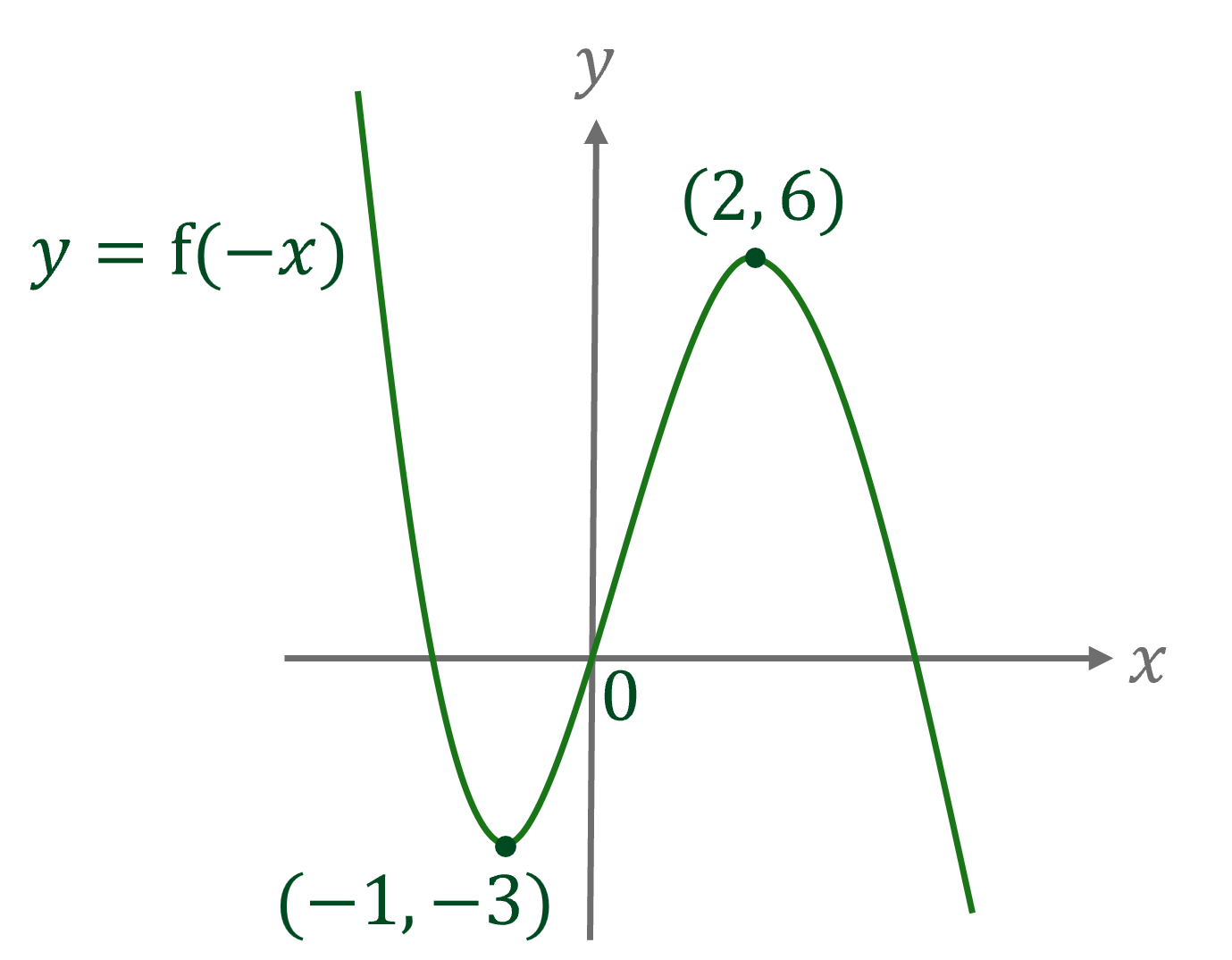
The diagram below shows the graph of .
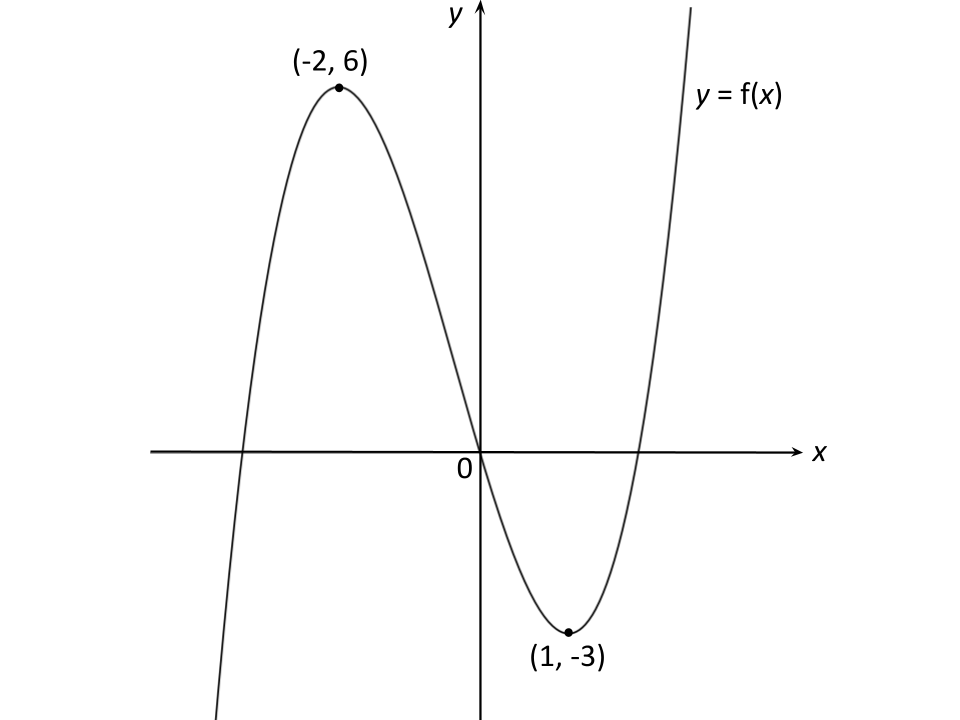
Sketch the graph of .
The transformation is a reflection in the
-axis
Reflect the points (-2, 6) and (1, -3) in the -axis to get (2, 6) and (-1, -3)
Sketch these points and join with a smooth curve through the origin

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?

