The Treaties of Versailles Settlement (AQA GCSE History): Revision Note
Exam code: 8145
The Versailles Settlement - Timeline & Summary
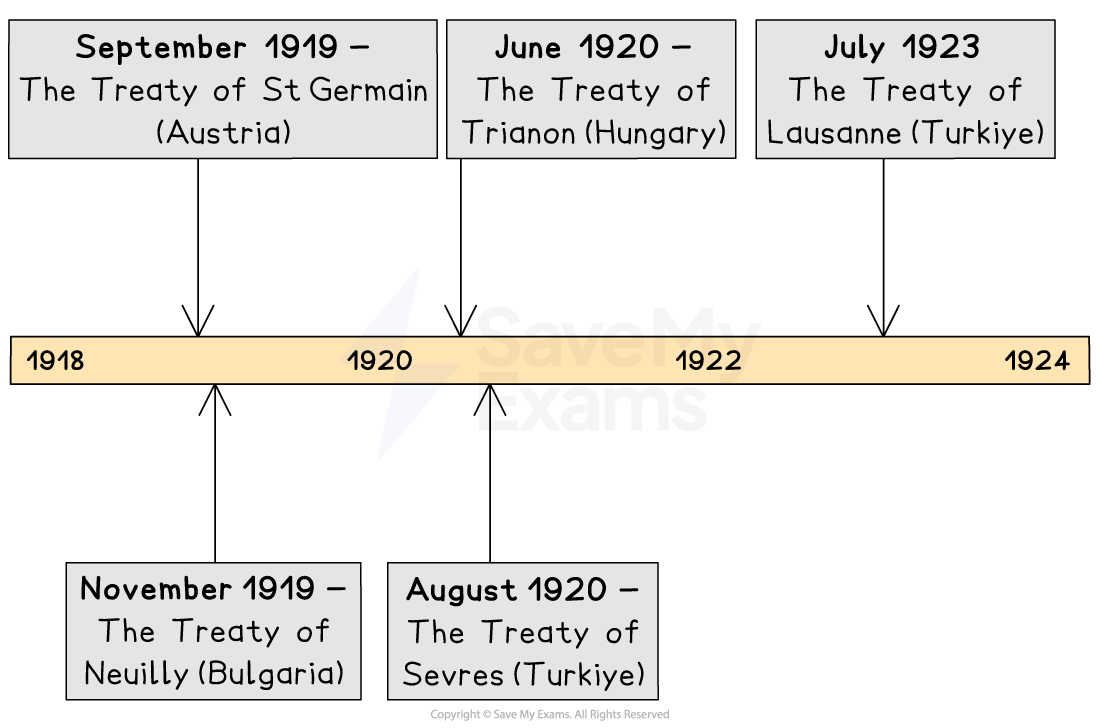
The Versailles Settlement was not just one treaty. It was a series of peace agreements made after the First World War. Besides the Treaty of Versailles with Germany, there were four other important treaties with different ‘defeated’ countries.
The Treaty of St Germain was signed with Austria in 1919. This treaty broke up the Austro-Hungarian Empire, creating new countries like Czechoslovakia and Yugoslavia. Austria had to give up large areas of land to these new countries and Italy and Poland. Anschluss with Germany was forbidden. The treaty aimed to weaken Austria and prevent it from becoming a threat again.
The Treaty of Neuilly was signed with Bulgaria in 1919. Bulgaria had to give up land to Greece, Romania, and Yugoslavia. Like the other treaties, it also reduced Bulgaria's military power.
The Treaty of Trianon was signed with Hungary in 1920, which lost a significant amount of its territory to neighbouring countries like Romania, Czechoslovakia and Yugoslavia. This left Hungary much smaller and weaker.
The Treaty of Sevres was signed with the Ottoman Empire in 1920. The treaty created new countries in the Middle East like Iraq and Syria, which were put under British and French control. Türkiye also lost land to Greece and Italy. This treaty caused much anger in Türkiye which eventually resulted in a new peace settlement, the Treaty of Lausanne, in 1923.
The Versailles Settlement was designed to create new borders, reduce the power of the Central Powers and promote peace. However, the treaties caused a lot of dissatisfaction and instability, which contributed to future conflicts.

The Treaty of St Germain
Date | Format | Terms | Impacts |
|---|---|---|---|
September 1919 | The Allies' dictated peace treaty with Austria | Ending of the Austro-Hungarian Empire Loss of land to Hungary, Czechoslovakia and Yugoslavia Anschluss with Germany forbidden Austria limited to 30,000 troops Reparations Accept blame for starting the First World War Recognition of the League of Nations | Land given to Czechoslovakia housed most of Austria’s industry Austria experienced a financial crisis in 1921 Austria never paid reparations The small states created from the old Austro-Hungarian empire caused conflict and instability in Eastern and Central Europe |
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Some students struggle to remember the differences between the four other treaties in the Versailles Settlement. In your revision, create a similarities and differences concept map or Venn diagram. This will make it easier for you to compare the treaties and recognise their unique terms and features.
The Treaty of Neuilly
Date | Format | Terms | Impacts |
|---|---|---|---|
November 1919 | The Allies' dictated peace treaty with Bulgaria | Loss of land to Yugoslavia, Greece and Romania Recognise the existence of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes Bulgaria limited to 20,000 troops Reparations set at £100 million Accept blame for starting the First World War Recognition of the League of Nations | Loss of access to the Aegean Sea The Allies cancelled 75% of Bulgaria’s reparation bill Bulgaria continued to claim their right to Macedonia Continued unrest in the Balkans |
The Treaty of Trianon
Date | Format | Terms | Impacts |
|---|---|---|---|
June 1920 | The Allies’ dictated peace treaty with Hungary | Ending of the Austro-Hungarian Empire
| The collapse of its economy, which resulted in not paying reparations
|
The Treaty of Sevres
Date | Format | Terms | Impacts |
|---|---|---|---|
August 1920 | The Allies' dictated peace treaty with Ottoman Türkiye | Ending of the Ottoman Empire Britain and France to take control of land in the Middle East Loss of control of the Dardanelles Strait, an important waterway Türkiye limited to 50,000 troops Allied control of Türkiye’s tax system and budget Reparations Accept blame for starting the First World War Recognition of the League of Nations | The people of Türkiye threatened to overthrow the government The Allies negotiated a new treaty with Türkiye in 1923 called the Treaty of Lausanne The new treaty gave Türkiye land back in Europe. They gained back control of the Dardanelles Strait. Türkiye no longer had reparations or restrictions on the army |
Worked Example
“The Treaty of Versailles was the harshest treaty in the Versailles Settlement”
How far do you agree with this statement?
[16 marks]
Partial answer:
Overall, I strongly believe that the Treaty of Versailles was the harshest treaty in the Versailles Settlement. Whilst the treaties of St Germain, Neuilly, Trianon and Sevres had similar clauses to Versailles such as reparations and war guilt clauses, most of their terms had been reversed in the 1920s. The Allies allowed the reversal of these terms due to the economic struggles of each ‘defeated’ country. However, despite Germany facing a severe depression, the Allies refused to cancel their reparation bill. This created so much anger in Germany against the Allies and the Treaty of Versailles. This ultimately contributed towards the rise of Hitler and the start of the Second World War. Therefore, the Treaty of Versailles had longer, harsher consequences on Germany than the other treaties in the Versailles Settlement.
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The example above is a conclusion to this question. You may notice that it examines the long-term impacts of the Treaty of Versailles and the significance of this event. This means that the conclusion is justified with evidence.
To complete this answer, you should add two or three well-explained PEEL paragraphs that explain how the Treaty of Versailles compared to the other treaties in the Versailles Settlement. You could use evidence from any of the four other treaties and have a sustained judgement throughout.
For further guidance on this question, you can read this revision note on how to answer the 16-mark “How far do you agree” question.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?