The Warsaw Pact, 1955 (AQA GCSE History) : Revision Note
The Warsaw Pact, 1955 - Summary
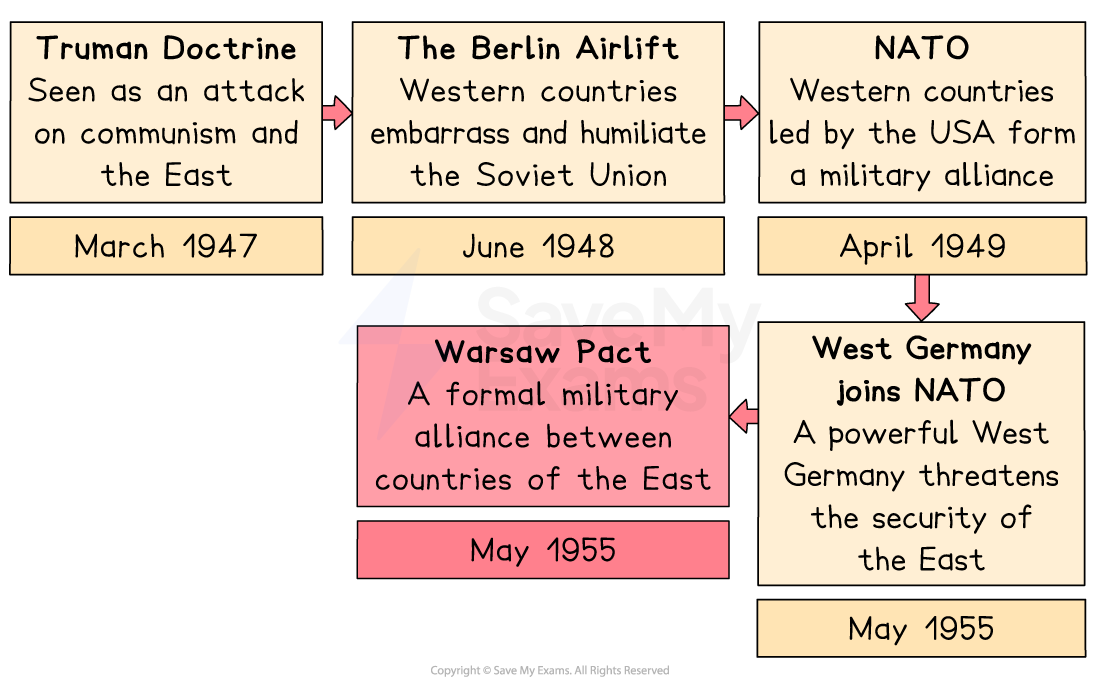
Tensions between the two 'Superpowers' of the USA and the Soviet Union had increased following the creation of Cominform in 1947 and Comecon in 1949. These organisations had convinced President Truman that the Soviet Union was seeking to spread communism in Europe.
After the Soviet Union blocked access to Berlin during the Berlin Crisis, the Western powers formed the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO) in 1949 to make sure that they could counter any potential Soviet invasion of Western Europe.
After the introduction of the Federal Republic of Germany (West Germany) into NATO in May 1955, Stalin quickly moved to create a similar military alliance made up of countries of the 'Eastern Bloc'. This became known as the Warsaw Pact.
Europe was now not only divided by ideological differences but also by two rival military forces prepared for conflict.
What was the Warsaw Pact?
The Warsaw Pact was created in May 1955 in response to the German Federal Republic (West Germany) joining NATO:
The Soviet Union were worried about a strong West Germany being part of a military alliance with the USA
The Warsaw Pact was a military alliance based on 'Collective Security'
If one member was attacked, all members would defend it
The Warsaw Pact was under the command of the Soviet Union
Reasons for the Warsaw Pact
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Some students confuse the Warsaw Pact with NATO. They are both military alliances. However, NATOcombined the military force of the West whereas the Warsaw Pact was a military agreement within Eastern Europe.
Aims and membership of the Warsaw Pact

The Impact of the Warsaw Pact
The Warsaw Pact confirmed the separation of Europe into two groups:
Western, capitalist countries that were members of NATO
Eastern, communist countries that were members of the Warsaw Pact
The creation of the Warsaw Pact was a military decision by the Soviet Union
As of August 1949, the Soviet Union had achieved parity with the USA with both countries having atomic weapons
The presence of two military alliances in Europe increased the likelihood of war and led to both groups increasing their military power
How did the Warsaw Pact affect US-Soviet relations?

Worked Example
‘The creation of the Warsaw Pact was the most important response by the USSR to the actions of the West between 1949 and 1955.’
How far do you agree with this statement?
[16 marks + 4 SPaG]
Partial answer
Overall, the creation of the Warsaw Pact was an important response by the USSR, but it was not the most important. The Berlin Blockade was a more significant response because it was an immediate and aggressive attempt to force the West out of Berlin. While the Warsaw Pact formalised the divide between East and West, it was a reaction to NATO and did not directly increase tension in the same way. The Berlin Blockade had greater short-term consequences, including the Berlin Airlift and the first major crisis of the Cold War, which increased tensions.
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Conclusions are usually where most of your judgement marks will be awarded. Students often rush their conclusions so they are not as developed as they could be
All great conclusions have these three elements:
Judgement – Start with your opinion. Try to include the words from the question. Consider second-order concepts like short- and long-term consequences, change and continuity and significance
Counter – Give an example from the other side of the argument to show your awareness of this
Support – Explain why, after considering all the evidence, you have reached your judgement. Use your best piece of evidence to show your opinion
For further guidance on this question, you can read this revision note on how to answer the 16-mark “How far do you agree” question.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?

