Trigonometric Identities (AQA GCSE Further Maths): Revision Note
Exam code: 8365
Trigonometric identities
What is a trigonometric identity?
Trigonometric identities (trig identity) are statements that are true for all values (of
or
)
They are used to help simplify trigonometric equations before solving them
Sometimes you may see identities written with the symbol ≡
This means 'identical to'
What trigonometric identities do I need to know?
There are two trig identities you need to know and use
This is the identity for tan θ
You may see this referred to as the Pythagorean identity
Note that the notation
is the same as
Similar for
Both identities are given on the formulae sheet
Where do the trigonometric identities come from?
You do not need to know the proof for these identities
However it is a good idea to know where they come from
The identity for
can be seen by diving
by
using their definitions from SOHCAHTOA
The Pythagorean identity can be seen by considering a right-triangle with a hypotenuse of 1
Then using Pythagoras' theorem (
, where
is the hypotenuse)
From SOHCAHTOA,
and
And so
How are the trigonometric identities used?
Most commonly trig identities are used to rewrite an equation
Rearrangements of the Pythagorean identity are very useful for rewriting equations
This allows us to write equations in terms of sine or cosine only (making them easier to solve)
Examiner Tips and Tricks
If you are asked to show that one expression is identical (≡) to another, look for anything that has gone missing!
e.g. if
is in the original expression but not the 'answer' it must have been replaced by
Worked Example
Show that the equation can be written in the form
, where
,
and
are integers to be found.
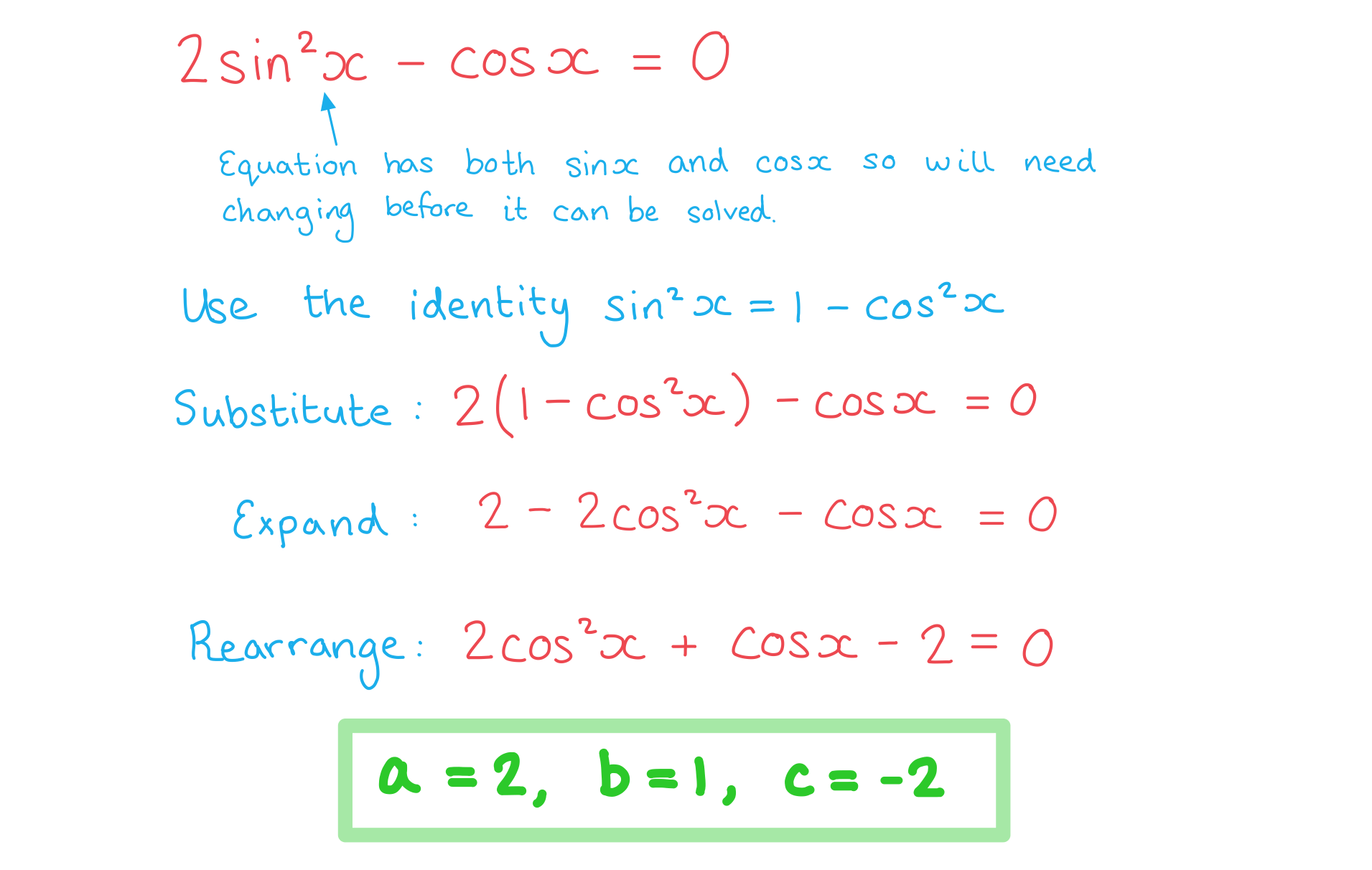

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
