Tangents & Normals (AQA GCSE Further Maths): Revision Note
Exam code: 8365
Finding a tangent
Using the derivative to find a tangent
At any point on a curve, the tangent is the line that touches the point and has the same gradient as the curve at that point
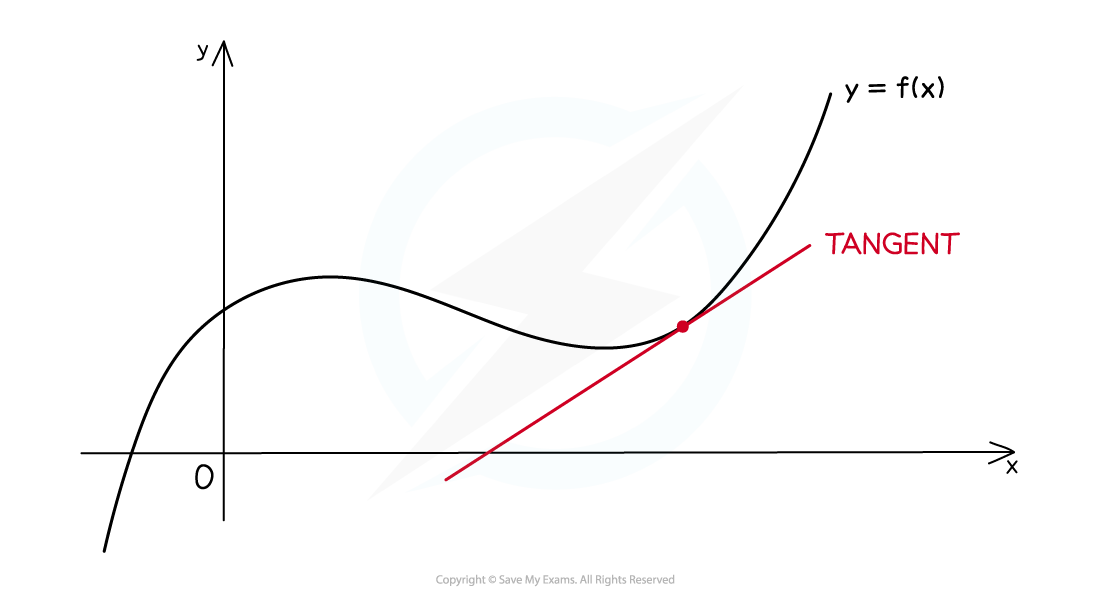
When given a curve, you can find the equation of the tangent to the curve at the point
by:
Finding the derivative (gradient) of the curve at point
This is also the gradient of the tangent line
You can find this by differentiating the equation of the curve, and substituting in
Substituting the value of the gradient
into the equation of the tangent, in the form
To find the full equation of the tangent, substitute in the point
as
and
and solve to find
You could alternatively use the form
for the equation of a line where
is the point
and
is still the gradient
Sometimes, you may not be told the full coordinate; just the
-value
In this case, substitute the
-value into the equation of the curve (not the derivative) to find the full coordinate, and then follow the method above
Examiner Tips and Tricks
A good sketch of the curve and the tangent at a point can help you spot if the tangent will have a positive or negative gradient; helping you to check your answer
Worked Example
Work out the equation of the tangent to the curve at the point where
.
Write your answer in the form .
Find the derivative of the curve.
To find the gradient of the curve at the point where substitute
into the derivative of the curve.
This is the same as the gradient of the tangent to the curve at the point where , so the equation of the line is in the form
To find the value of we will need to know the full coordinate at the point where
We can find this by substituting
into the equation for the curve (be careful to substitute it into the original equation and not your differentiated version).
Simplify to find the value of and hence, the full coordinate.
Substitute and
into the equation of the line.
Solve this equation to find
Write out the equation of the tangent to the curve in the form given in the question.
Finding a normal
Using the derivative to find a normal
At any point on a curve, the normal is the line that goes through the point and is perpendicular to the tangent at that point
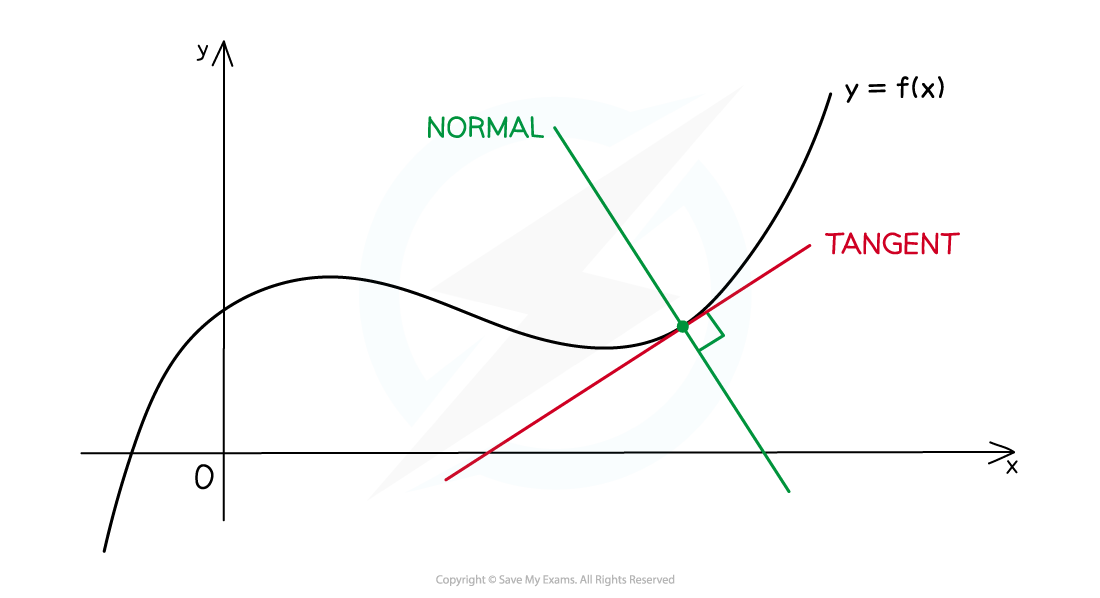
The process for finding a normal to a curve is the same as finding a tangent to a curve, but with one extra step
When given a curve, you can find the equation of the normal to the curve at the point
by:
Finding the derivative (gradient) of the curve at point
This is also the gradient of the tangent line
You can find this by differentiating the equation of the curve, and substituting in
EXTRA STEP: Find the negative reciprocal of the gradient
This will be the gradient of the normal
The negative reciprocal of
is
e.g. If the gradient of the tangent is
, the gradient of the normal will be
Substituting the value of the gradient of the normal
into the equation of the normal, in the form
To find the full equation of the normal, substitute in the point
as
and
and solve to find
You could alternatively use the form
for the equation of a line where
is the point
and
is still the gradient
Sometimes, you may not be told the full coordinate; just the
-value
In this case, substitute the
-value into the equation of the curve (not the derivative) to find the full coordinate, and then follow the method above
Examiner Tips and Tricks
It sounds obvious, but read the question carefully to see if you need to find a normal or a tangent! (and check again at the end!)
It is a very common mistake, especially under exam pressure
Worked Example
Work out the equation of the normal to the curve at the point where
.
Give your answer in the form where
,
, and
are integers.
Find the derivative of the curve, you will need to rewrite the equation of the curve using index form first.
To find the gradient of the curve at the point where substitute
into the derivative of the curve.
This is the same as the gradient of the tangent to the curve at the point where , to find the gradient of the normal to the curve at the point where
find the negative reciprocal of
So the equation of the normal is in the form
To find the value of we will need to know the full coordinate at the point where
We can find this by substituting
into the equation for the curve (be careful to substitute it into the original equation and not your differentiated version).
Substitute and
into the equation of the normal.
Solve this equation to find
Write out the equation of the normal to the curve in the form and then rearrange to the form given in the question.
Multiply each term by 4.
Subtract from both sides.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?