Simplifying Surds (AQA GCSE Further Maths) : Revision Note
Did this video help you?
Surds & Exact Values
What is a surd?
A surd is the square root of a non-square integer
Using surds lets you leave answers in exact form
e.g.
rather than

How do I calculate with surds?
Multiplying surds
You can multiply numbers under square roots together
eg.
Dividing surds
You can divide numbers under square roots
eg.
Factorising surds
You can factorise numbers under square roots
eg.
Adding or subtracting surds is very like adding or subtracting letters in algebra – you can only add or subtract multiples of “like” surds
eg.
Be very careful here, you can not add or subtract numbers under square roots
Think about
It is not equal to
Examiner Tips and Tricks
If you are working on an exam question and your calculator gives you an answer as a surd, leave the value as a surd throughout the rest of your calculations to make sure you do not lose accuracy throughout your questions
Simplifying Surds
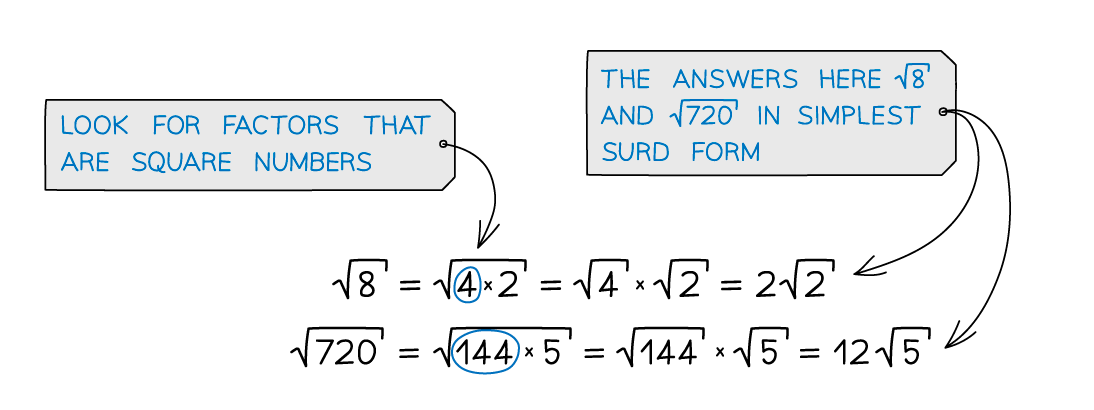
How do I simplify surds?
To simplify a surd, separate out a square factor and square root it
Look for the greatest square number that is a factor of the number you are simplifying
eg.
You can collect like terms with surds like you do with letters in algebra
Understanding how to simplify surds can help reduce expressions and collect like terms
e.g. simplify
by simplifying each part separately
An important skill is multiplying double brackets containing surds
This can be done in the same way as multiplying out double brackets algebraically and simplifying
The property
can be used to simplify the expression, once expanded
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When simplifying surds, use the fact that the one, non square factor will be the same in each part to help you find the correct, highest square factor
Worked Example
Write in the form
where
and
are integers and
has no square factors.
Simplify both surds separately by finding the highest square number that is a factor of each of them
9 is a factor of 54, so
4 is a factor of 24, so
Simplify the whole expression by collecting the like terms

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?

