Structured Query Language (SQL) (AQA GCSE Computer Science): Revision Note
Exam code: 8525
Retrieving Data Using SQL
What is SQL?
SQL (Structured Query Language) is a programming language used to interact with a DBMS.
The use of SQL allows a user to:
Select data (flat file)
Select data (relational)
Order data
Insert data
Update data
Delete records
Selecting data commands (flat file)
Command | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
SELECT | Retrieves data from a database table | SELECT * FROM users; SELECT name, age |
FROM | Specifies the tables to retrieve data from | SELECT name, age FROM users; |
WHERE | Filters the data based on a specified condition | SELECT * FROM users |
AND | Combines multiple conditions in a WHERE clause | SELECT * FROM users |
OR | Retrieves data when at least one of the conditions is true | SELECT * FROM users |
WILDCARDS | '*' and '%' symbols are used for searching and matching data | SELECT * FROM users; SELECT * FROM users WHERE name LIKE 'J%'; |
Nested SELECT | A select within another select statement (nested). A mini select within the main one | SELECT * FROM users WHERE age > (SELECT AVG(age) FROM users); (retrieves users with an age greater than the average age) |
ORDER BY | How data is organised (sorted) when it is retrieved | SELECT Forename, Lastname FROM Students (retrieves only the forename and lastname of all students from the students table who have a studentID of less than 10 and displays in ascending order by lastname and forename) |
Examples
Select all the fields from the Customers table
Command:

Output:
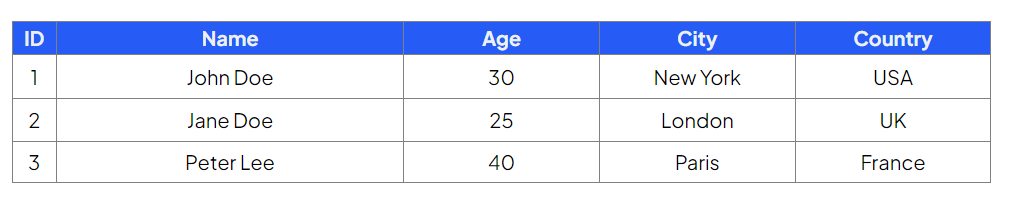
Select the ID, name & age of customers who are older than 25
Command:

Output:

Select the name and country of customers who are from a country that begins with 'U'
Command:

Output:

Select all fields of customers who are from 'London' or 'Paris'
Command:

Output:
Nested select
Table: Employees
ID | Name | Salary | Department | City |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Fynn Roberts | 45000 | HR | London |
2 | Zarmeen Azra | 52000 | Sales | Manchester |
3 | Ella Stanley | 39500 | Marketing | Birmingham |
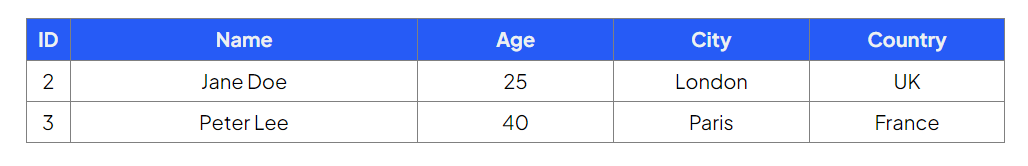
Select all fields for employees whose salary is bigger than the average salary of all employees
Command:

Output:
ID | Name | Salary | Department | City |
|---|---|---|---|---|
2 | Zarmeen Azra | 52000 | Sales | Manchester |
Selecting data commands (relational)
Command | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
JOIN | Combines data from two or more tables based on a related column | SELECT users.name, orders.order_id FROM users |
Example
Table: Employees
EmployID | Name | Salary | City |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | Fynn Roberts | 45000 | London |
2 | Zarmeen Azra | 52000 | Manchester |
3 | Ella Stanley | 39500 | Birmingham |
Table: Departments
DepartID | EmployID | Department | Manager | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | 1 | HR | Sally Jones | [email protected] (opens in a new tab) |
2 | 2 | Sales | Peter Evans | [email protected] (opens in a new tab) |
3 | 3 | Marketing | Stuart Davies | [email protected] (opens in a new tab) |
Select the name, manager and email address of employees in the sales department
Command:

Output:

Inserting Data Using SQL
Command | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
INSERT | Adds new data to a database table | INSERT INTO users (name, age) |
UPDATE | Edit data in a database table | UPDATE users |
Example
Table: Employees
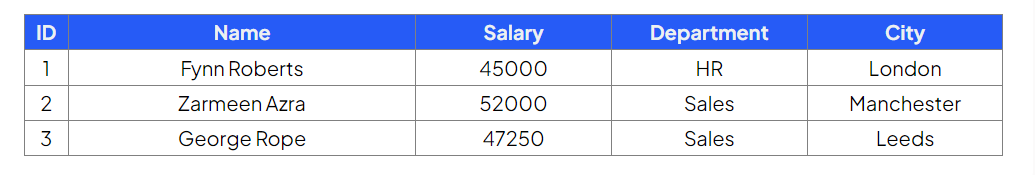
Insert a new employee into the Employees table with the 'Name', 'Salary', 'Department' and 'City' fields
Command:

Output:
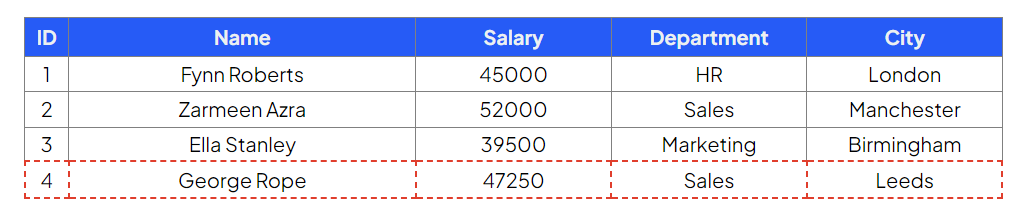
Table: Employees
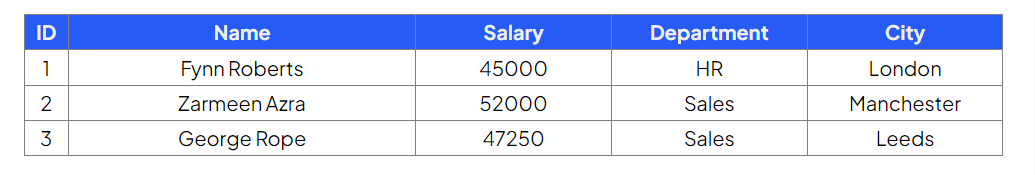
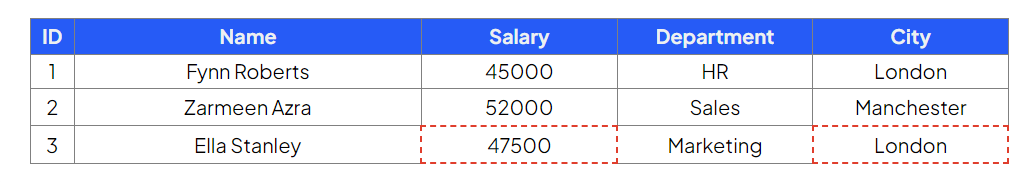
Update employee ID 3 to a salary of 47500 and city to London
Command:

Output
Deleting Data Using SQL
Command | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
DELETE | Removes data from a database table | DELETE FROM users DELETE FROM users |
Example
Table: Employees
ID | Name | Salary | Department | City |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Fynn Roberts | 45000 | HR | London |
2 | Zarmeen Azra | 52000 | Sales | Manchester |
3 | Ella Stanley | 39500 | Marketing | Birmingham |
4 | George Rope | 47250 | Sales | Leeds |
Delete all records from the Employees table whose department is 'Marketing'
Command:
DELETE FROM Employees |
Output:
ID | Name | Salary | Department | City |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Fynn Roberts | 45000 | HR | London |
2 | Zarmeen Azra | 52000 | Sales | Manchester |
3 | George Rope | 47250 | Sales | Leeds |
Worked Example
A database stores information about songs on a music streaming service. One of the tables called Song has the fields Title, Artist, Genre and Length
A band called RandomBits removes their permission for their songs to be streamed. The company removes all the songs belonging to RandomBits from their service.
Write an SQL statement that will remove all songs by RandomBits from the table Song [2]
Answer
DELETE FROM Song [1]
WHERE Artist = “RandomBits” [1]

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?