Merge Sort (AQA GCSE Computer Science): Revision Note
Exam code: 8525
What is a sorting algorithm?
Sorting algorithms are precise step-by-step instructions that a computer can follow to efficiently sort data in massive datasets
Two common sorting algorithms are:
Bubble sort
Merge sort
Merge Sort
What is a merge sort?
A merge sort is a sorting algorithm that uses the 'divide and conquer' strategy of dividing a dataset into smaller sub-datasets and merging them back together in the correct order
How do you perform a merge sort?
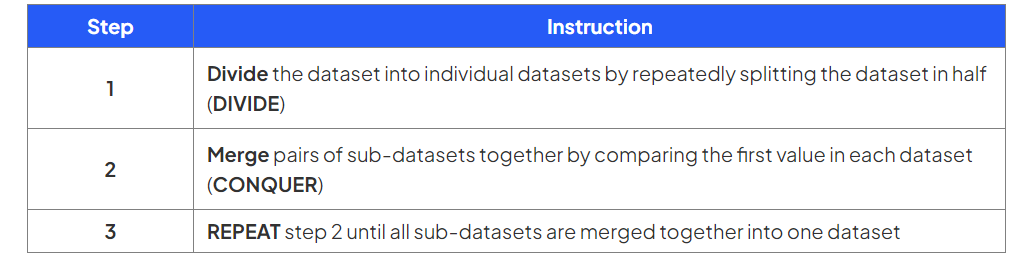
Example
Perform a merge sort on the following dataset
![Table showing the merge sort algorithm. The dataset [7, 4, 1, 2, 6, 3, 8, 5] is repeatedly divided, then merged back together by comparing values, resulting in a sorted array.](https://cdn.savemyexams.com/cdn-cgi/image/f=auto,width=3840/https://cdn.savemyexams.com/uploads/2024/08/51116_answer-mergesort.png)
Examiner Tips and Tricks
In the exam, the divide stage could already be done for you and you would only need to demonstrate the conquer stage!
A Merge Sort in Python
# List of numbers to perform merge sort on
numbers = [7, 4, 1, 2, 6, 3, 8, 5]
# Merge function to merge two sorted lists
def merge(left, right):
merged = []
left_index, right_index = 0, 0
# Merge the two sorted lists
while left_index < len(left) and right_index < len(right):
if left[left_index] < right[right_index]:
merged.append(left[left_index])
left_index += 1
else:
merged.append(right[right_index])
right_index += 1
# Append remaining elements from left or right sublist if there are any remaining elements in the left sublist
while left_index < len(left):
merged.append(left[left_index])
left_index += 1
# If there are any remaining elements in the right sublist
while right_index < len(right):
merged.append(right[right_index])
right_index += 1
return merged
# Merge sort implementation without using a separate function
def merge_sort(arr):
# Checks to see if the list has 1 or 0 elements, it's already sorted
if len(arr) <= 1:
return arr
# Split the list into two halves
mid = len(arr) // 2
left_half = merge_sort(arr[:mid]) # Split and recursively sort left half
right_half = merge_sort(arr[mid:]) # Split and recursively sort right half
# Merge the sorted halves
return merge(left_half, right_half)
# Perform merge sort
sorted_numbers = merge_sort(numbers)
print("Sorted numbers:", sorted_numbers)

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?