The Atmosphere (WJEC GCSE Chemistry) : Revision Note
The Early Atmosphere
Theories on the development of Earth’s atmosphere have altered and developed over time as instrumental analysis has improved
It is difficult to gather evidence about the early atmosphere because it happened 4.6 billion years ago
The surface of the early Earth was molten for millions of years with no atmosphere
As cooling slowly occurred, the molten surface began to slowly solidify into land masses
Volcanoes formed on the land masses
One theory of how the early atmosphere formed suggests that the volcanoes released gases from the Earth’s interior through violent eruptions
These eruptions released large amounts of carbon dioxide and water vapour, as well as nitrogen, hydrogen, and other gases which may have included small proportions of ammonia and methane
How volcanoes affected the atmosphere

Volcanoes spewed out water, carbon dioxide and other gases from the Earth's interior
Earth’s gravity prevented these gases from escaping into outer space and they formed the early atmosphere
Analysis of the minerals in the Earth's crust enables scientists to deduce the gases present billions of years ago
It is thought that the Earth's early atmosphere was similar to that of Venus or Mars today, consisting mainly of carbon dioxide and water vapour
There was little or no oxygen present
The Present Atmosphere
The Earth's atmosphere has changed over time
While the surface of the Earth was still very hot the large quantities of water vapour remained in the gaseous state
When conditions cooled sufficiently, the water vapour later condensed and fell to the surface of the Earth, forming the oceans
How carbon dioxide levels decreased
Carbon dioxide is a water soluble gas (it is the gas used in fizzy drinks) and dissolves readily
When the water vapour in Earth’s early atmosphere condensed large amounts of CO2 dissolved in the oceans
Carbonates were precipitated during this process which later formed sediments on the seabed
As marine life began to evolve sea creatures began to appear which used up the carbonates to form shells and skeletons
Limestone and chalk are formed from these shells and skeletons
Green plants and algae began to evolve and absorbed considerable amounts of carbon dioxide during photosynthesis
Photosynthesis word equation

Carbon dioxide is used during photosynthesis
Animals fed on the plants which transferred carbon to their tissues including bones and shells
When these organisms died, their remains formed sedimentary rocks
Some of the living organisms were buried under layers of mud when they died
Over millions of years, the heat and pressure turned the dead organisms into fossil fuels, such as crude oil, natural gas and coal
The formation of sedimentary rock and fossil fuels 'locked up' the carbon from carbon dioxide in the early atmosphere
This is how the large amounts of carbon dioxide in the early atmosphere were reduced
How oxygen levels increased
Primitive plants and algae began photosynthesising which used up carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and released oxygen
Algae first evolved around 2.7 billion years ago and during the next billion years or so small green plants began to appear
As more and more plants began to appear the levels of oxygen began to increase which allowed for more complex life forms to evolve
Photosynthesis symbol equation

Oxygen is produced during photosynthesis
Over billions of years, photosynthesis caused the amount of oxygen in the atmosphere to increase and the amount of carbon dioxide to decrease
This trend continued until around 200 million years ago when the composition of the atmosphere reached similar characteristics as today
Changes in atmospheric nitrogen
In the early atmosphere, most of the nitrogen was in the form of ammonia released from volcanoes
In sunlight, ammonia decomposed by reacting with oxygen to form nitrogen and water
Decomposition of ammonia

The decomposition of ammonia by sunlight reduced the level of ammonia and increased the level of nitrogen in the atmosphere
The present composition of the atmosphere
The present composition of gases in the atmosphere has not changed much in 200 million years
About four-fifths of the air is nitrogen and one-fifth is oxygen
The remaining gases include carbon dioxide, water vapour and trace quantities of the noble gases
Pie chart of the current atmosphere
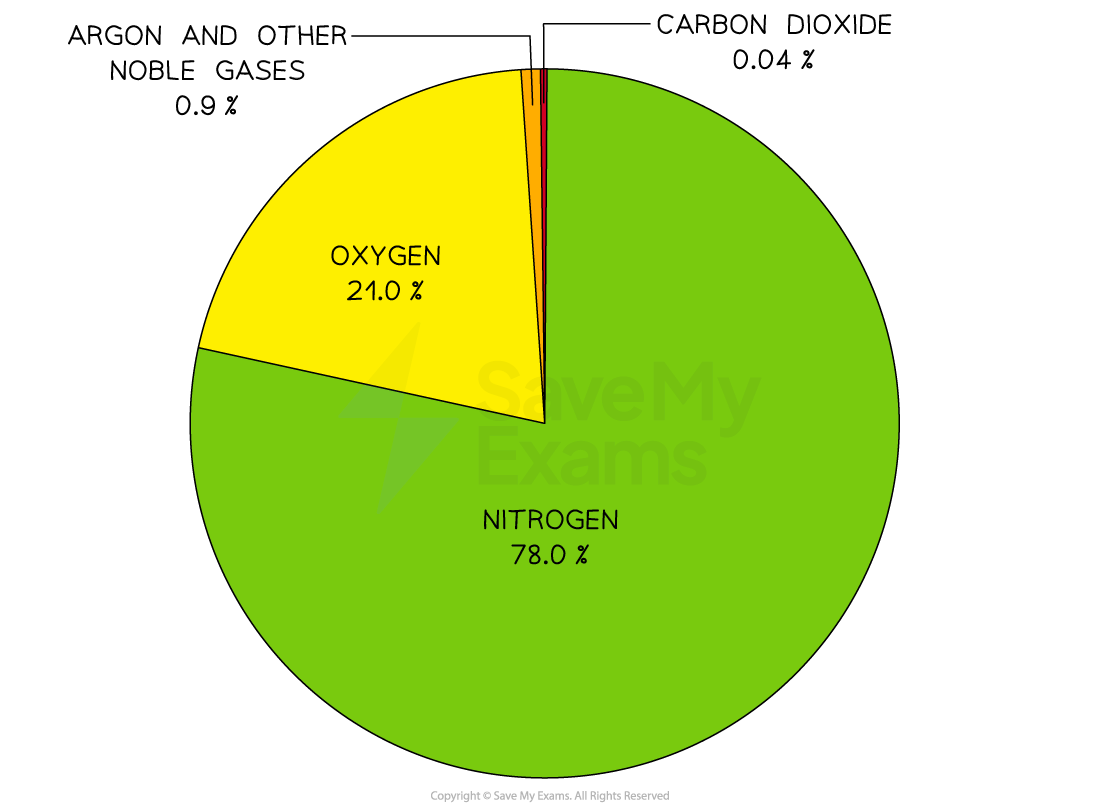
The two main gases in the air are nitrogen and oxygen
Some useful gases in the air, such as nitrogen, oxygen, neon and argon, can be extracted and used
Fractional distillation is used to separate these gases because they have different boiling points
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You need to know that the different gases in the air are separated by fractional distillation but you do not need to know the details of how this happens
Respiration, Combustion & Photosynthesis
Levels of O2 of CO2 in the atmosphere
The following processes are involved in the maintenance of oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere because they use oxygen and release carbon dioxide
Combustion of fossil fuels, e.g. methane:
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
Respiration: the production of energy in living things, represented by the equation:
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O
Photosynthesis uses carbon dioxide and water to produce glucose and oxygen in the presence of chlorophyll and light:
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Carbon dioxide dissolves in the water in seas and oceans and is removed by shellfish for making their calcium carbonate shells
Maintaining the level of carbon dioxide
Carbon as carbonate, carbon dioxide or organic carbon compounds is present in the sea, the air and under the Earth
There is a continuous cycle of these compounds between these sources called the carbon cycle
There is a constant amount of carbon compounds in the sea, atmosphere and under the Earth
As long as these are balanced, the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere remains constant
In the atmosphere, the main source of carbon is carbon dioxide
Scientists are worried that increased combustion of fossil fuels will increase the amount of atmospheric carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide that was used to form fossil fuels or carbonate rocks is described as 'locked in'
Therefore, the combustion of fossil fuels is releasing carbon from millions of years ago which is disturbing the current equilibrium
This will lead to increased global warming and unbalance the carbon cycle
Carbon cycle diagram

The carbon cycle shows the movement of carbon through the Earth

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?
