The Periodic Table (WJEC GCSE Chemistry): Revision Note
Exam code: 3410
The Periodic Table
There are over 100 chemical elements which have been isolated and identified
Elements are arranged on the periodic table in order of increasing atomic number
Each element has one proton more than the element preceding it
This is done so that elements end up in columns with other elements which have similar properties
The table is arranged in vertical columns called groups and in rows called periods
Period: These are the horizontal rows that show the number of shells of electrons an atom has and are numbered from 1 - 7
E.g. elements in Period 2 have two electron shells, elements in Period 3 have three electron shells
Group: These are the vertical columns that show how many outer electrons each atom has and are numbered from 1 – 7, with a final group called Group 0 (instead of Group 8)
E.g. Group 4 elements have atoms with 4 electrons in the outermost shell, Group 6 elements have atoms with 6 electrons in the outermost shell and so on
The Periodic Table
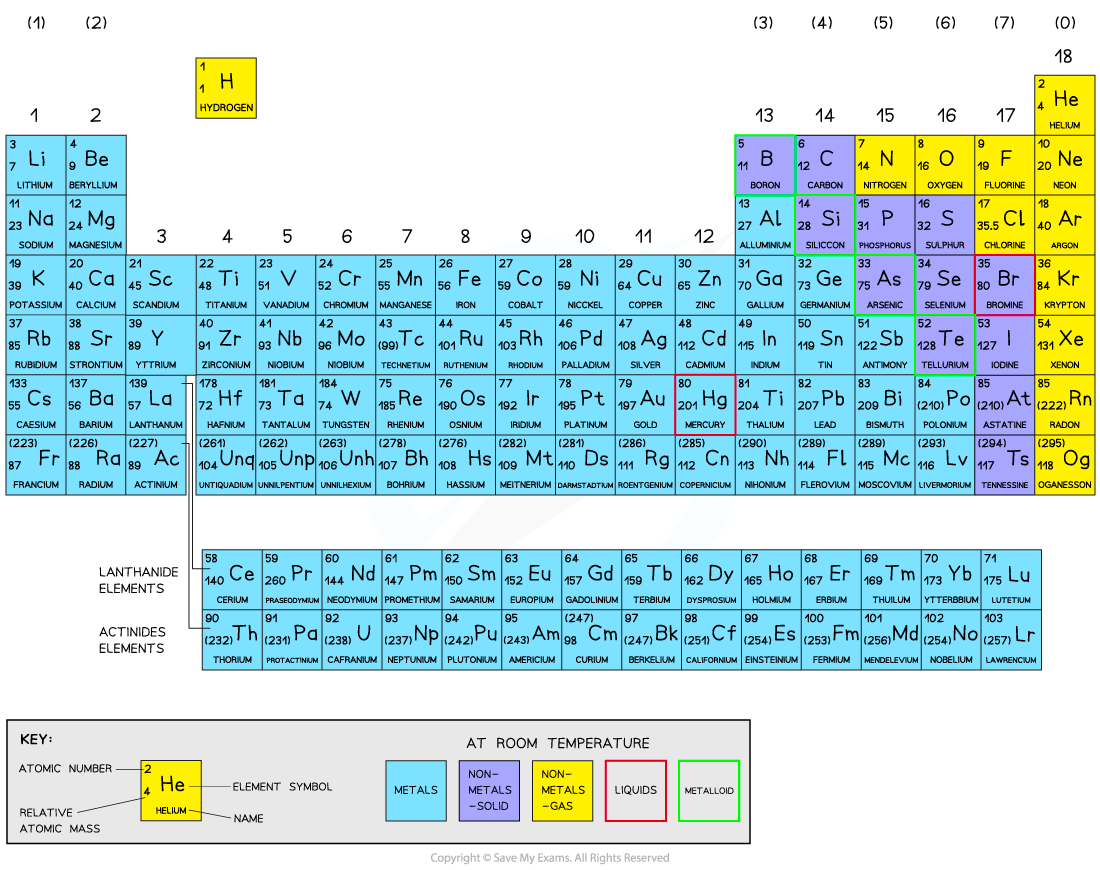
The Periodic Table is arranged in groups (columns) and periods (rows)
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The atomic number is unique to each element and could be considered as an element's “fingerprint”.
The number of electrons changes during chemical reactions, but the atomic number does not change.
Metals in the Periodic Table
The elements can be divided into two broad types: metals and non-metals
Atoms of different elements which do not have a full outer shell of electrons, can try to achieve a full outer shell by gaining or losing electrons in chemical reactions
Elements that react by losing electrons to form positive ions are metals
Metals are located on the left and centre of the Periodic Table
Elements that do not form positive ions are non-metals; this includes elements that react by gaining electrons to form negative ions and Group 0 elements
Non-metals are located on the right hand side of the Periodic Table
Most of the elements are metals and a small number of elements display properties of both types
These elements are called metalloids or semi-metals
The metallic character of the elements decreases as you move across a period on the periodic table, from left to right, and it increases as you move down a group
This trend occurs due to atoms more readily accepting electrons to fill their valence shells
The Periodic Table showing the location of metals and non-metals

The metallic character diminishes moving left to right across the Periodic Table
Examiner Tips and Tricks
In an exam, it is a good idea to draw a 'stair line' on the Periodic Table to separate the metals and non-metals.
This should start above aluminium and continue as if drawing a staircase down the Periodic Table.
This can be seen in the Periodic Table above- the metals are on the left, and the non-metals on the right.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?