Separating Mixtures (WJEC GCSE Chemistry): Revision Note
Exam code: 3410
Separating Mixtures
A mixture is a combination of two or more substances that are not chemically joined together
These substances can be elements and / or compounds
Examples of mixtures

Mixtures can be just elements, just compounds or elements and compounds, but the substances must not be chemically joined together
This means that mixtures can be easily separated by physical processes such as:
Filtration
Evaporation
Distillation
Chromatography
The physical process that is used for separation depends on the substances being separated
All processes rely on a difference of some sort between the substances being separated
This is usually in a physical property such as boiling point, solubility, magnetism
Filtration
Filtration is used to separate an insoluble solid from a mixture of the solid and a liquid / solution
For example, sand from a mixture of sand and water
Method
A filter paper is placed in a filter funnel above a beaker
The mixture of insoluble solid and liquid is poured into the filter funnel
The filter paper will only allow liquid particles and soluble solids to pass
The liquid that passes through into the beaker is called the filtrate
Insoluble solids do not pass through the filter paper and are left behind as a residue
The filtration process

For a mixture of sand and water, the insoluble sand would be left as the residue and the water would be the filtrate
Evaporation
This method is used to separate a dissolved solid from a solution
A simple application of this is to heat a solution to boiling, remove the heat and leave the solvent to evaporate
A more common application of this is sometimes called crystallisation
This is when the solid is more soluble in hot solvent than in cold, e.g. copper sulphate from a solution of copper(II) sulphate
The solution is heated, allowing the solvent to evaporate and leaving a saturated solution behind
You can test if the solution is saturated by dipping a clean, dry, cold glass rod into the solution
If the solution is saturated, crystals will form on the glass rod when it is removed and allowed to cool
The saturated solution is allowed to cool slowly
Solids will come out of the solution as the solubility decreases
This will be seen as crystals growing
The crystals are collected by filtration
They are then washed with distilled water to remove any impurities
Finally, they are allowed to dry
Common places to dry crystals are between sheets of filter paper or in a drying oven
The process of evaporation / crystallisation

The solution is slowly heated to remove around half of the liquid. The remaining liquid will evaporate slowly
Distillation
Simple Distillation
Distillation is used to separate a liquid and soluble solid from a solution (e.g. water from a solution of saltwater) or a pure liquid from a mixture of liquids
The solution is heated and pure water evaporates producing a vapour which rises through the neck of the round-bottomed flask
The vapour passes through the condenser, where it cools and condenses, turning into pure water which is collected in a beaker
After all the water is evaporated from the solution, only the solid solute will be left behind
Simple distillation apparatus

Diagram showing the distillation of a mixture of salt and water
Simple distillation can be used to separate the products of fermentation, such as alcohol and water
However, fractional distillation is a more effective separation technique, commonly used when the boiling points of the liquids are close and/or a higher degree of purity is required, such as crude oil
Chromatography
This technique is used to separate substances that have different solubilities in a given solvent (e.g. different coloured inks that have been mixed to make black ink)
A pencil line is drawn on chromatography paper and spots of the sample are placed on it
Pencil is used for this as ink would run into the chromatogram along with the samples
The paper is then lowered into the solvent container
The pencil line must sit above the level of the solvent so the samples don´t wash into the solvent container
The solvent travels up the paper by capillary action, taking some of the coloured substances with it
Different substances have different solubilities so will travel at different rates
This causes the substances to separate
Those substances with higher solubility will travel further than the others
This will show the different components of the ink / dye
The process of chromatography

The diagram shows how to complete a chromatography experiment and gives a basic analysis of the results
Chromatographic data analysis
If two or more substances are the same, they will produce identical chromatograms
It is common practice to include a known compound as a reference spot
This can help match up to an unknown spot or set of spots in order to identify it
If the substance is a mixture, it will separate on the paper to show all the different components as separate spots
An impure substance will show up with more than one spot, a pure substance should only show up with one spot
Rf values
These values are used to identify the components of mixtures
The Rf value of a particular compound is always the same
Calculating the Rf value allows chemists to identify unknown substances because it can be compared with the Rf values of known substances under the same conditions
Calculation
The formula to calculate the retention factor is:
Retention factor, Rf =
The Rf value is a ratio and therefore has no units
Analysing a chromatogram
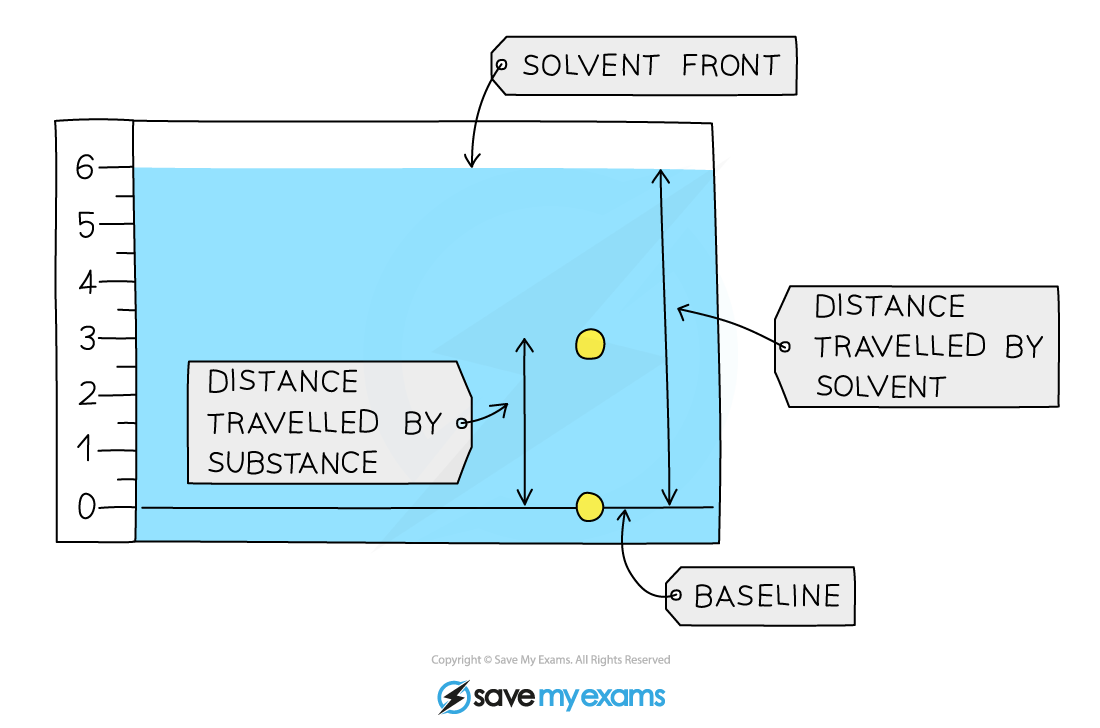
The key pieces of information from a chromatogram for calculating the Rf value are the distance travelled by the substance and the distance travelled by the solvent
The Rf value of the substance in the chromatogram above can be calculated by:
Rf =

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?