Calculating the Particles (OCR GCSE Chemistry A (Gateway)): Revision Note
Exam code: J248
Defining Terminology
Atomic Number
The atomic number (or proton number) is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
The symbol for this number is Z
It is also the number of electrons present in an atom and determines the position of the element on the Periodic Table
The proton number is unique to each element, so no two elements have the same number of protons
Electrons can be lost, gained, or shared during chemical processes but the proton number of an atom does not change in a chemical reaction
Mass Number
The mass number (or nucleon number) is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom
The symbol for this number is A
The mass number minus the proton number gives you the number of neutrons of an atom
Note that protons and neutrons can collectively be called nucleons
The atomic number and mass number for every element is on the Periodic Table

Diagram showing the notation used on the Periodic Table
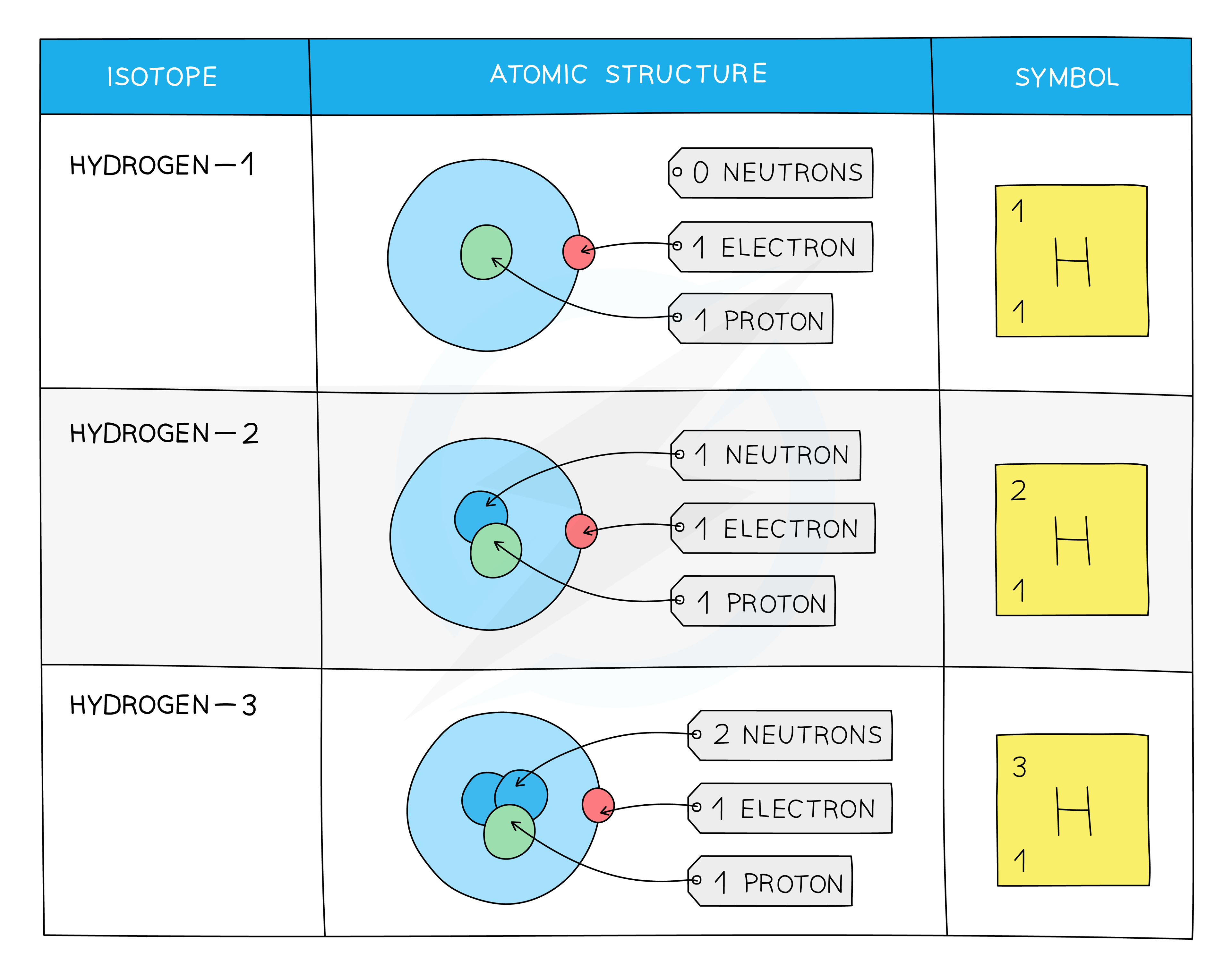
Isotopes
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that contain the same number of protons and electrons but a different number of neutrons
The symbol for an isotope is the chemical symbol (or word) followed by a dash and then the mass number
So, C-14 is the isotope of carbon which contains 6 protons and 6 electrons, but the 14 signifies that it has 8 neutrons (14 - 6 = 8)
It can also be written as 14C
Isotopes display the same chemical characteristics
This is because they have the same number of electrons in their outer shells, and this is what determines their chemistry
The difference between isotopes is the neutrons which are neutral particles within the nucleus and add mass only
The Atomic Structure and Symbols of the Three Isotopes of Hydrogen
Ions
An ion is an atom or group of atoms that has an electrical charge, either positive and negative
Atoms have an equal number of protons and electrons and so do not have an overall charge
Atoms with incomplete outer electron shells are unstable
By either gaining or losing electrons, atoms can obtain full outer electron shells and become stable
When this happens, atoms have an unequal number of protons and electrons and so have an overall charge.
This is how atoms become ions
An atom that loses electrons has more protons than electrons and so has a positive overall charge
This is called a positive ion or cation
An atom that gains electrons has more electrons than protons and so has a negative overall charge
This is called a negative ion or anion
Calculating the Numbers
Protons
The atomic number is equal to the number of protons (p) in an atom
Since atoms are neutral, then it is also the same as the number of electrons (e)
The mass number is the number of protons plus neutrons
The number of neutrons (n) can thus be calculated by subtracting the atomic number from the mass number
For example, beryllium has an atomic number of 4, therefore it has 4 protons and 4 electrons
The mass number of beryllium is 9, so it has 9 - 4 = 5 neutrons
The PEN numbers for beryllium are thus: p = 4 e = 4 n = (9 - 4 =) 5

The symbol key for beryllium as represented on the periodic table
Worked Example
Determine the number of protons of the following ions and atoms:
Mg2+ ion
Carbon atom
An unknown atom of element X with mass number 63 and 34 neutrons
Answer
Answer 1: The atomic number of a magnesium atom is 12, therefore the number of protons in the magnesium atom is 12
Therefore, the number of protons in a Mg2+ ion is also 12 - the number of protons does not change when an ion is formed
Answer 2: The atomic number of a carbon atom is 6 suggesting that a carbon atom has 6 protons in its nucleus
Answer 3: Use the formula to calculate the number of protons
Number of protons = mass number - number of neutrons
Number of protons = 63 - 34
Number of protons = 29
Neutrons
The mass and atomic numbers can be used to find the number of neutrons in ions and atoms:
Number of neutrons = mass number (A) - atomic number (Z)
Worked Example
Determine the number of neutrons in the following ions and atoms:
Mg2+ ion
Carbon atom
An unknown atom of element X with mass number 63 and 34 neutrons
Answer
Answer 1: The atomic number of a magnesium atom is 12 and its mass number is 24
Number of neutrons = mass number (A) - atomic number (Z)
Number of neutrons = 24 - 12
Number of neutrons = 12
The Mg2+ ion has 12 neutrons in its nucleus
Answer 2: The atomic number of a carbon atom is 6 and its mass number is 12
Number of neutrons = mass number (A) - atomic number (Z)
Number of neutrons = 12 - 6
Number of neutrons = 6
The carbon atom has 6 neutrons in its nucleus
Answer 3: The atomic number of an element X atom is 29 and its mass number is 63
Number of neutrons = mass number (A) - atomic number (Z)
Number of neutrons = 63 - 29
Number of neutrons = 34
The neutral atom of element X has 34 neutrons in its nucleus
Electrons
An atom is neutral and therefore has the same number of protons and electrons
Ions have a different number of electrons to the number of protons, depending on their charge
A positively charged ion has lost electrons and therefore has fewer electrons than protons
A negatively charged ion has gained electrons and therefore has more electrons than protons
Worked Example
Determine the number of electrons in the following ions and atoms:
Mg2+ ion
Carbon atom
An unknown atom of element X with mass number 63 and 34 neutrons
Answer
Answer 1: The atomic number of a magnesium atom is 12 suggesting that the number of protons in the neutral magnesium atom is 12
However, the 2+ charge in Mg2+ ion suggests it has lost two electrons. It only has 10 electrons left now
Answer 2: The atomic number of a carbon atom is 6 suggesting that the neutral carbon atom has 6 electrons orbiting around the nucleus
Answer 3: The number of protons of element X can be calculated by:
Number of protons = mass number - number of neutrons
Number of protons = 63 - 34
Number of protons = 29
The neutral atom of element X therefore also has 29 electrons

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?
