Interpreting Chromatograms (Edexcel GCSE Chemistry)
Revision Note
Did this video help you?
Interpreting Chromatograms
Identifying Mixtures
Pure substances will produce only one spot on the chromatogram
If two or more substances are the same, they will produce identical chromatograms
If the substance is a mixture, it will separate on the paper to show all the different components as separate spots
An impure substance therefore will produce a chromatogram with more than one spot

Diagram showing the analysis of a mixture and pure substances using chromatography
Rf Values
These values are used to identify the components of mixtures
Rf stands for retention factor
The Rf value of a particular compound is always the same but it is dependent, however, on the solvent used
If the solvent is changed then the value changes
Calculating the Rf value allows chemists to identify unknown substances because it can be compared with Rf values of known substances under the same conditions
These values are known as reference values
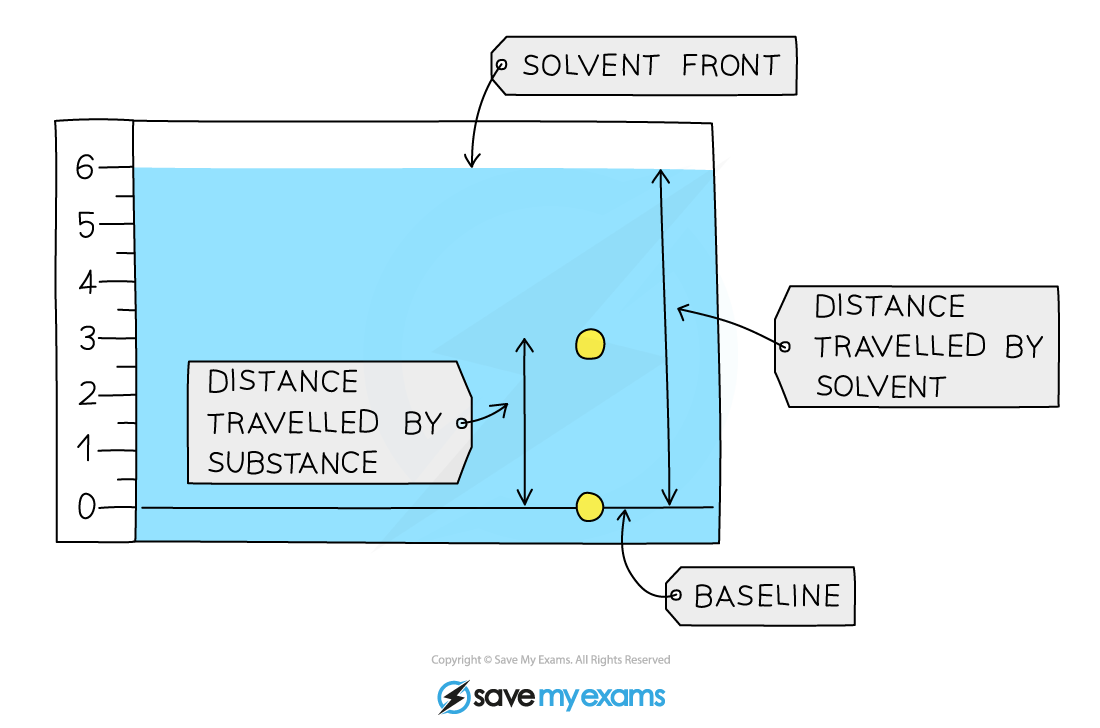
Calculation
The Retention factor is found using the following calculation:
Rf = distance travelled by substance ÷ distance travelled by solvent
The Rf value will always lie between 0 and 1; the closer it is to 1, the more soluble is that component in the solvent
The Rf value is a ratio and therefore has no units
Using Rf values to identify components of a mixture
Examiner Tips and Tricks
For the Rf calculations, both distances are measured from the baseline.
Did this video help you?

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?