Chromatography (AQA GCSE Chemistry) : Revision Note
Did this video help you?
Chromatography
What is chromatography used for?
Chromatography is used to separate substances and provide information to help identify them
The components have different solubilities in a given solvent (e.g. different coloured inks that have been mixed to make black ink) and different adhesion to the supporting medium - usually paper
A pencil line is drawn on chromatography paper and spots of the sample are placed on it
Pencil is used for this as ink would run into the chromatogram along with the sample
The paper is then lowered into the solvent container, making sure that the pencil line sits above the level of the solvent so the samples don’t wash into the solvent container
The solvent travels up the paper by capillary action, taking some of the coloured substances with it
Different substances have different solubilities so will travel at different rates, causing the substances to spread apart
Those substances with higher solubility will travel further than the others
Chromatography diagram

The pigments in ink can be analysed using paper chromatography
The mobile and stationary phase
All chromatography techniques use two phases called the mobile phase and the stationary phase
In paper chromatography:
The mobile phase is the solvent in which the sample molecules can move, which in paper chromatography is liquid e.g. water or ethanol
The stationary phase in paper chromatography is the actual chromatography paper itself
The substances which are more soluble in the solvent will travel further up the paper because they spend more time in the mobile phase and are thus carried further up the paper than the less soluble components
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Paper chromatography is the name given to the overall separation technique while a chromatogram is the name given to the visual output of a chromatography run. This is the piece of chromatography paper with the visibly separated components after the run has finished.
Distinguishing pure & impure substances
Pure substances will produce only one spot on the chromatogram
If two or more substances are the same, they will produce identical chromatograms
If the substance is a mixture, it will separate on the paper to show all the different components as separate spots
An impure substance therefore will produce a chromatogram with more than one spot
Chromatogram

Diagram showing the analysis of a mixture and pure substances using chromatography
Rf value
Calculating Rf values
These values are used to identify the components of mixtures
The Rf value of a particular compound is always the same but it is dependent, however, on the solvent used
If the solvent is changed then the value changes
Calculating the Rf value allows chemists to identify unknown substances because it can be compared with Rf values of known substances under the same conditions
These values are known as reference values
Retention factor, Rf, is calculated by the equation:
The Rf value is a ratio and therefore has no units and will be less that 1
Calculating Rf value
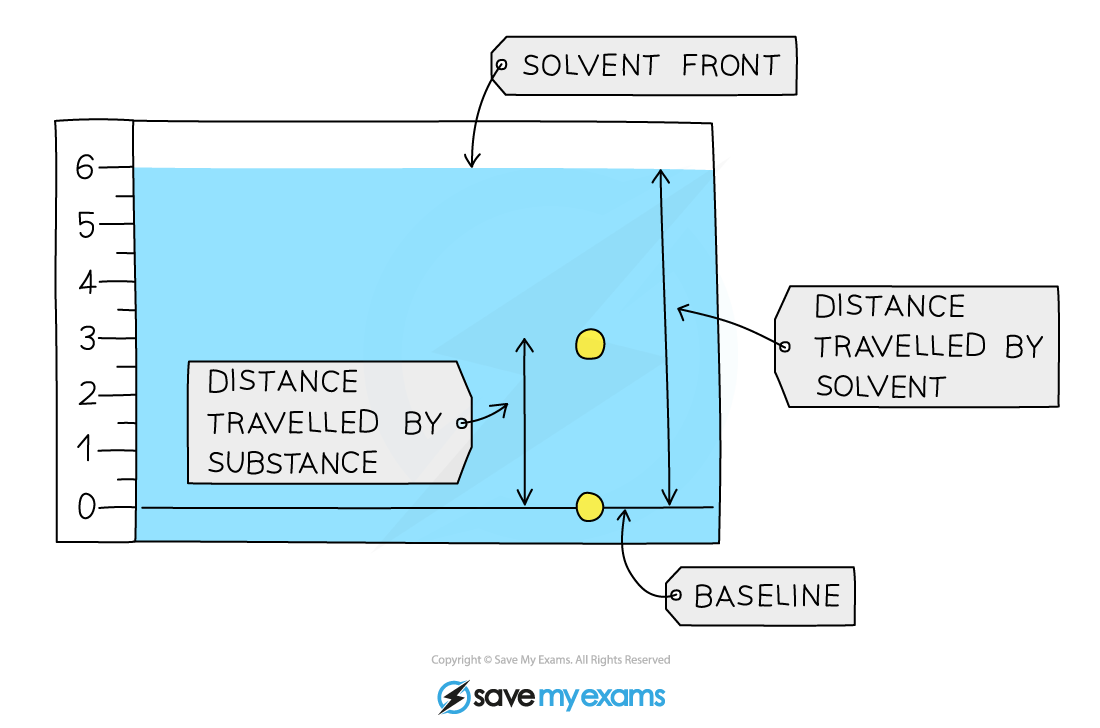
Using Rf values to identify components of a mixture
The Rf value of the substances in the chromatogram above can be calculated by:
Examiner Tips and Tricks
For the Rf calculations, both distances are measured from the baseline.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?


