Ionic Compounds (AQA GCSE Chemistry) : Revision Note
Did this video help you?
Giant ionic lattice
The lattices formed by ionic compounds consist of a regular arrangement of alternating positive and negative ions in which the ions are tightly packed together
Strong electrostatic forces of attraction are present between oppositely charged ions, holding the lattice together
Electrostatic forces are strong, acting in all directions - they form the basis of ionic bonding
As a result of so many electrostatic forces existing in this lattice structure, ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points
Giant ionic lattice of sodium chloride

The 3D ball & stick model is one way of representing the lattice structure of sodium chloride
The lattice arrangement exists in three dimensions which allows solid ionic compounds to form regular shapes
Solid ionic crystals contain huge numbers of ions and so are referred to as giant ionic lattices
Ions are incredibly small - a single grain of sodium chloride contains trillions of sodium and chloride ions - so models are used to represent the structure of the ionic compound
3D space-filling model of a giant ionic lattice
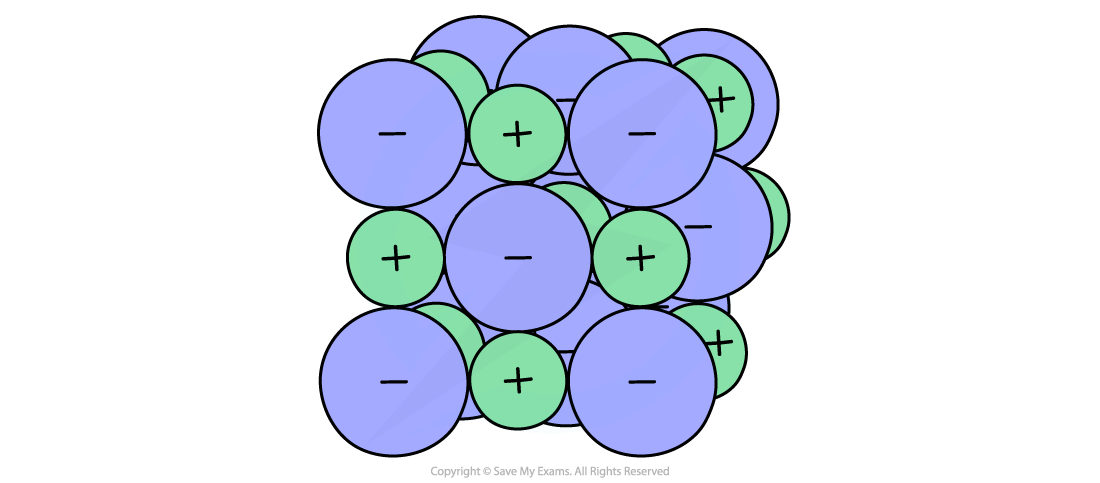
A 3D space-filling model showing an ionic lattice structure of oppositely charged ions
Representing Ionic Compounds
3D ball and stick model
3D drawings and models depict the arrangement of ions in space, showing the repeating pattern of ions throughout giant ionic lattice structures (whereas 2D models only show the arrangement of ions in one layer)
The 3D ball and stick model shows the arrangement of oppositely charged ions but represents ionic bonds as sticks between ions; in reality an ionic bond is an electrostatic force of attraction that acts in all directions around an ion
Another limitation of the 3D ball and stick model is that it incorrectly depicts space existing between individual ions whereas the 3D space-filling model is more accurate (there is not much space between separate ions)
It is difficult to represent the relative sizes of the ions in relation to each other correctly in any model
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remember that in ionic lattice structures, positively charged and negatively charged ions are arranged in an alternating pattern.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
