Arranging the Elements (AQA GCSE Chemistry) : Revision Note
How the elements are ordered
There are over 100 chemical elements which have been isolated and identified
Elements are arranged on the periodic table in order of increasing atomic number
Each element has one proton more than the element preceding it
This is done so that elements end up in columns with other elements which have similar properties
The table is arranged in vertical columns called groups and in rows called periods
Period: These are the horizontal rows that show the number of shells of electrons an atom has and are numbered from 1 - 7
E.g. elements in Period 2 have two electron shells, elements in Period 3 have three electron shells
Group: These are the vertical columns that show how many outer electrons each atom has and are numbered from 1 – 7, with a final group called Group 0 (instead of Group 8)
E.g. Group 4 elements have atoms with 4 electrons in the outermost shell, Group 6 elements have atoms with 6 electrons in the outermost shell and so on
The Periodic Table
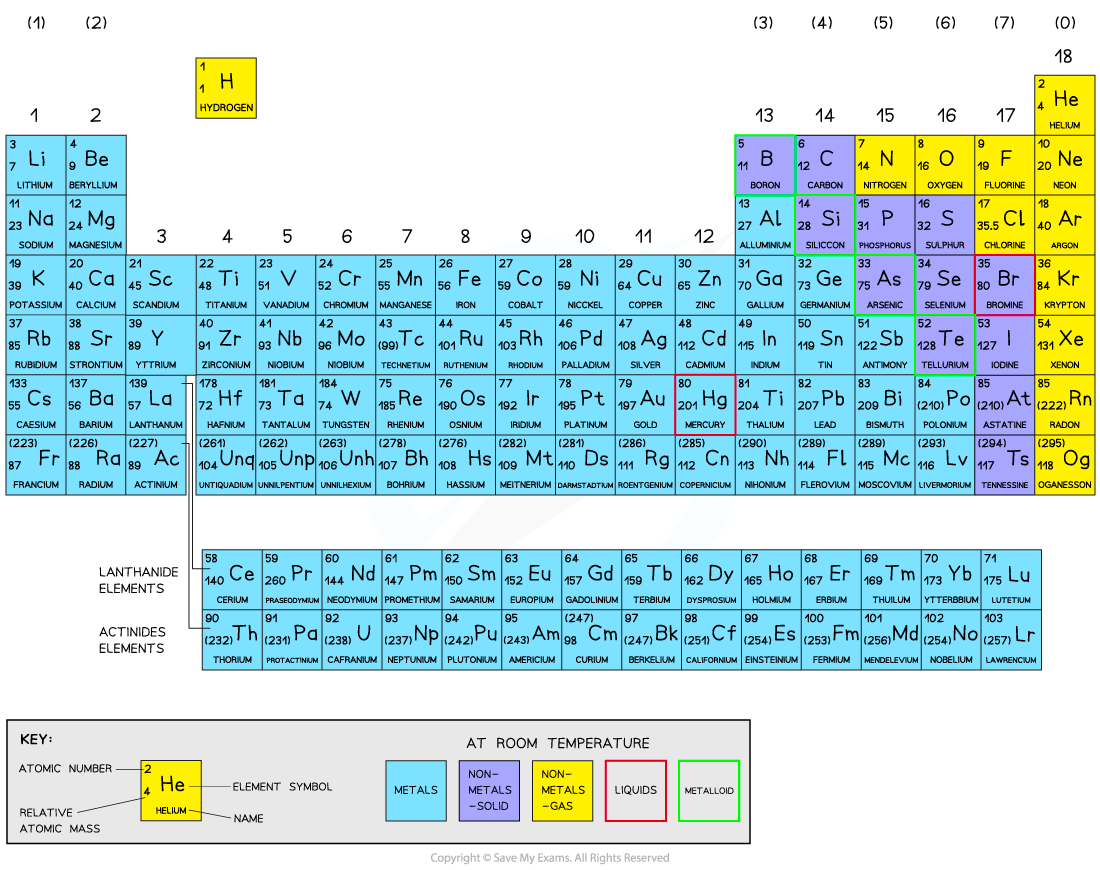
The Periodic Table of the Elements
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The atomic number is unique to each element and could be considered as an element's “fingerprint”.
The number of electrons changes during chemical reactions, but the atomic number does not change.
Predicting reactions
The group number of an element which is given on the Periodic Table indicates the number of electrons in the outer shell (valence electrons)
This rule holds true for all elements except helium; although is in Group 0, it has only one shell, the first and innermost shell, which holds only 2 electrons
We can use the group number to predict how elements will react as the number of valence shell electrons in an element influences how the element reacts.
Therefore, elements in the same group react similarly
By observing the reaction of one element from a group, you can predict how the other elements in that group will react
By reacting two or more elements from the same group and observing what happens in those reactions you can make predictions about reactivity and establish trends in reactivity in that group
For example, lithium, sodium and potassium are in Group 1 and can all react with elements in Group 7 to form an ionic compound
The Group 1 metals become more reactive as you move down the group while the Group 7 halides show a decrease in reactivity moving down the group
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The word “periodic” is used in the name of the Periodic Table as similar properties appear in elements placed at regular intervals throughout the table.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
