The Nature of Globalisation (OCR GCSE Business): Revision Note
Exam code: J204
What is globalisation?
Globalisation is the economic integration of different countries through:
Increased freedom of movement of people
More cross-border trade of goods and services
Freer transfer of capital and finance
Globalisation has several impacts on domestic businesses that increasingly need to compete with global brands
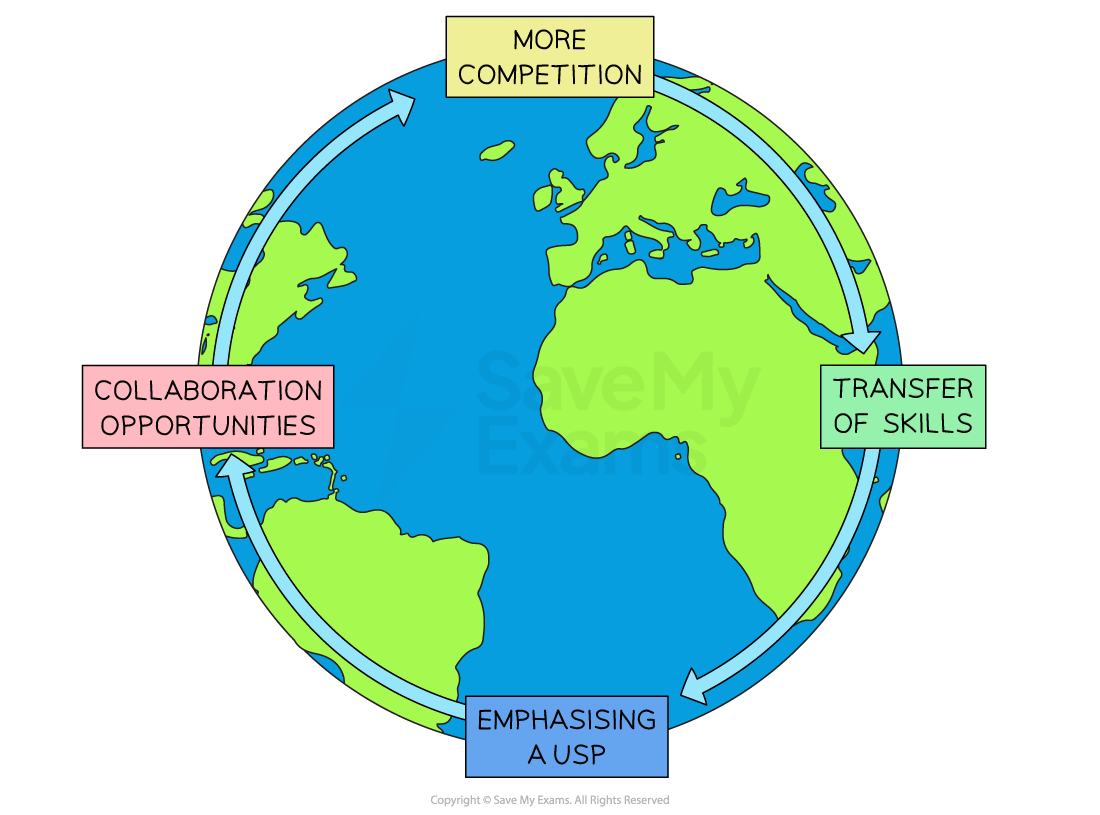
Domestic businesses face increased competition as a result of globalisation
This incentivises them to improve efficiency in order to remain competitive against global brands
Some domestic businesses may drastically cut staffing or require higher levels of productivity from workers
The transfer of skills between global and domestic businesses can be mutually beneficial
Domestic workers can gain skills and knowledge from an international competitor
Global businesses will gain local knowledge, market insight and experience from domestic workers
Domestic businesses can compete by developing or emphasising a persuasive unique selling point (perhaps the fact they are local)
Both domestic and global businesses can benefit from close collaboration through joint ventures or strategic alliances
Imports and exports
Businesses that trade internationally import and export goods and services
Imports are goods and services bought by people and businesses in one country from another country
Imports result in money leaving the country, which generates extra revenue for foreign businesses
In 2022, the UK’s biggest import was cars, valued at approximately £34 billion
Exports are goods and services sold by domestic businesses to people or businesses in other countries
Exports generate extra sales revenue for businesses selling their goods abroad
In 2023, 56% of UK's exports were made up of services, including financial, education, legal and financial services, worth approximately £470 billion
Key reasons for globalisation
Reason | Explanation |
|---|---|
Advances in communication technology |
|
Trade liberalisation |
|
Transportation improvements |
|
Political and economic reforms |
|
Cultural awareness |
|
Examiner Tips and Tricks
This topic contains a large number of key terms that you need to revise carefully so that you can use them correctly and with confidence in your explanations. You will not usually achieve marks for definitions.
The implications of Brexit
Brexit refers to the UK's decision to end its membership of the European Union (EU) in 2016
Following several years of negotiation, the UK ceased to be a member of the trading bloc on January 1st 2021
Post-Brexit agreements with the EU include:
Tariff-free trade of most goods and services will continue
Most product regulations and standards will remain in alignment
A level playing field between UK and EU businesses
Neither the EU nor the UK government can change regulations to give businesses an unfair advantage over competitors in other countries
UK citizens' freedom of movement is restricted, with visa requirements for those wishing to work in most parts of the EU
EU workers are also restricted from working in the UK
There is significant disagreement about the long-term impact of Brexit on the UK economy
A range of short-term benefits and drawbacks of Brexit have been reported
An evaluation of Brexit
Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?