Working with Suppliers (Edexcel GCSE Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 1BS0
Interpretation of bar gate stock graphs
A Bar Gate Stock Control diagram illustrates the flow of stock (inventory) into and out of a business over time
Example Bar Gate Stock Graph
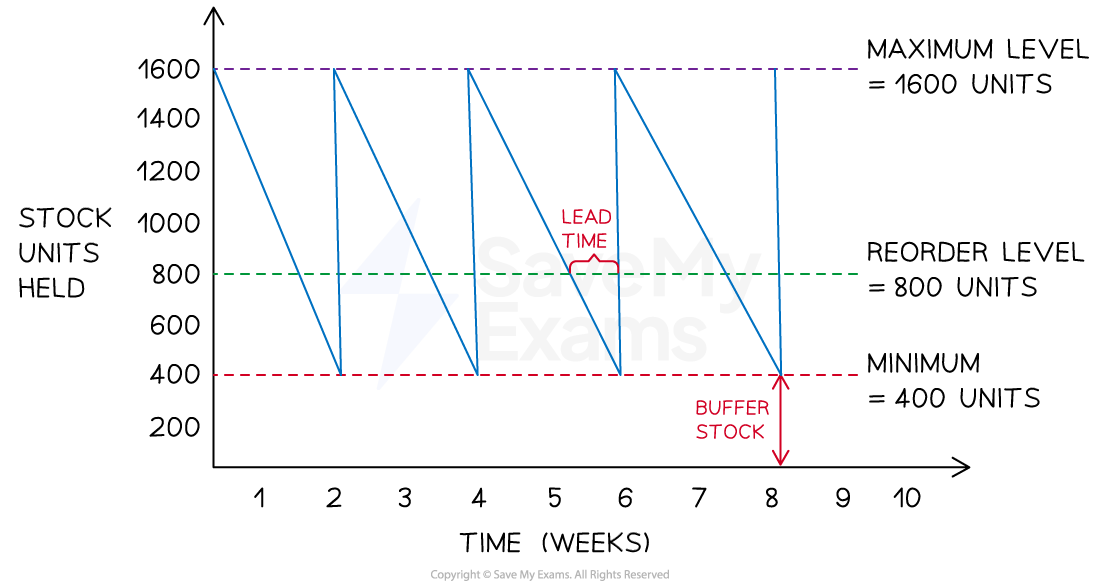
Diagram analysis
The maximum stock level is the maximum amount of stock a business is able to hold in normal circumstances (1600)
The reorder level is the level at which a business places a new order with its supplier (800)
The minimum stock level is also known as the buffer stock level and is the lowest level to which a business is willing to allow stock levels to fall (400)
The lead time is the length of time from the point of stock being ordered from the supplier to it being delivered (1 week)
The stock level line shows how stock levels change over the given time period
As stock is used up, a downwards slope is plotted
When an order is delivered by a supplier, the stock level line shoots upwards
Worked Example
The diagram below shows stock movements of kitchen shelving units sold by TamFix Ltd.
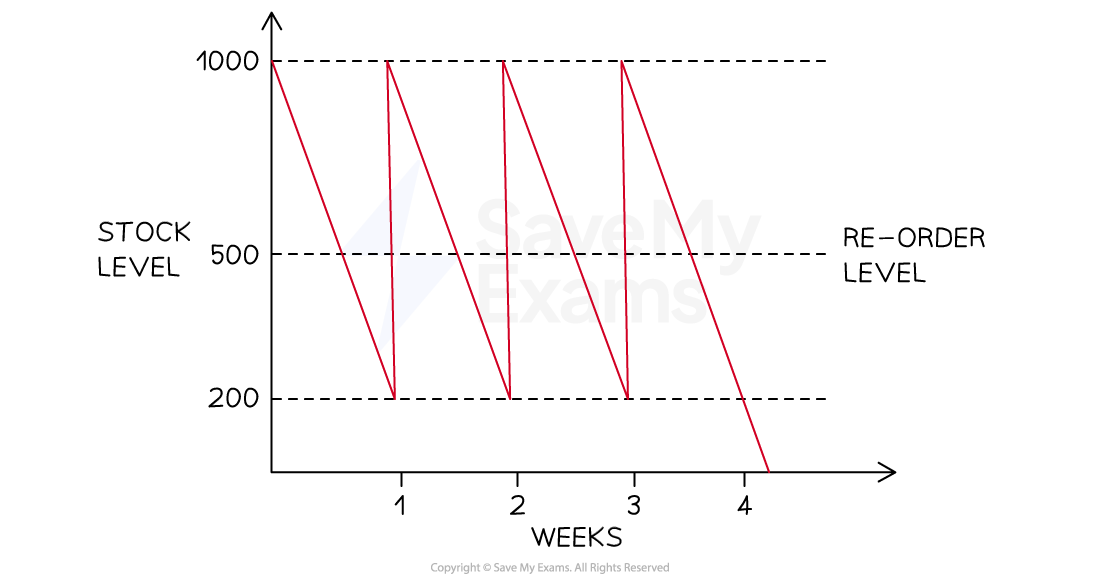
Identify the following points:
the minimum stock level
the re-order level
the re-order quantity
the lead time for kitchen shelving units
(4)
Step 1: Identify the minimum stock level
The minimum stock level is identified by the bottom-most dotted line. In this case it shows that the minimum stock level is 200 units (1)
Step 2: Identify the reorder level
The reorder level is clearly identified on the diagram. In this case, it shows that the reorder level is 500 units (1)
Step 3: Identify the reorder quantity
The reorder quantity is the difference between the maximum stock level (shown by the topmost dotted line) and the minimum stock level
(1)
Step 4: Identify the lead time for kitchen shelving units
The lead time is the difference in time between an order for stock being placed and its delivery
In this case, assuming a five-day working week, the lead time for shelving units is two days (1)
Efficient procurement of raw materials
Efficient procurement of raw materials is crucial for ensuring the success of any manufacturing process
There are several factors that can influence the efficiency of raw material procurement
Important factors in procurement
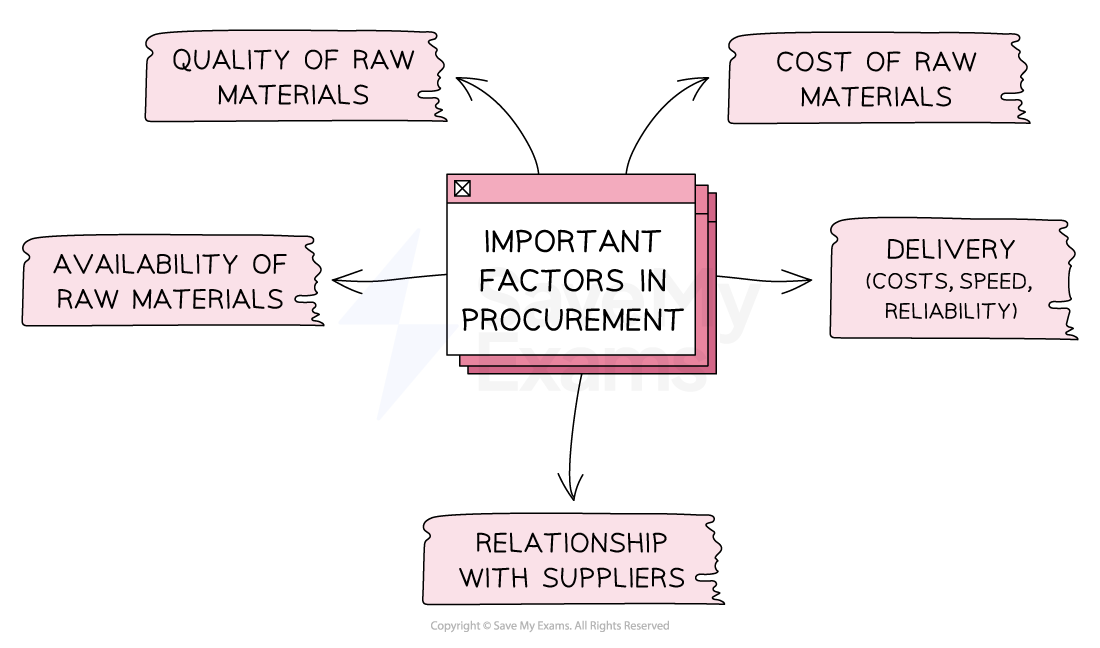
Businesses need to carefully consider these factors when sourcing raw materials to ensure that they can efficiently produce high-quality products at a reasonable cost
Factors that influence the sourcing of raw materials
Factor | Explanation | Example |
|---|---|---|
Quality |
|
|
Delivery |
|
|
Availability |
|
|
Costs |
|
|
Trust |
|
|
Just in time stock management
Just in Time (JIT) stock management is a process in which raw materials are not stored onsite but ordered as required and delivered by suppliers 'just in time' to be used
Careful coordination is required ensure that raw materials and components are delivered by suppliers at the moment that they are to be used
Advantages and disadvantages of just in time stock management
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When answering questions on procurement, consider any case study material provided.
For example, a more reliable supplier could possibly be more expensive, raising business costs. However, this would reduce the negative impact on branding and customer satisfaction as the business would be able to improve availability of their product and reduce the likelihood of stock costs.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?