Sales Revenue & Costs (Edexcel GCSE Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 1BS0
Sales revenue
Sales Revenue is the value of the units sold by a business
E.g the revenue earned by Apple Music from sales of music downloads
Sales revenue is a key business performance measure and must be calculated to identify profit
Sales revenue is calculated using the formula
When a firm sells one product, it is easy to calculate the sales revenue
The more products a firm sells, the harder it is to calculate the sales revenue
Computer systems make it easier to track sales revenue when multiple products are sold by the business
Worked Example
Moped Maestro's has made the following forecasts for the costs and sales of its mopeds for 2022
| Forecast |
Total number of moped sales | 3000 |
Total revenue | £2 200 000 |
Variable cost per moped | £450 |
Fixed costs | £180 000 |
Using the information in the Table, calculate the selling price per bike. You are advised to show your workings.
(2)
Step 1: Insert the appropriate figures into the sales revenue formula
(1 )
Step 2: Rearrange the formula and solve for ?
(1 )
Examiner Tips and Tricks
In Paper 1, you may be asked to conduct a simple sales revenue calculation where you use the formula as is. Alternatively, you may be asked to calculate the percentage change in sales revenue between two years or to rearrange the formula to calculate any component (as in the example above).
To calculate any percentage change use the formula
Costs
Businesses incur a range of costs
Examples include purchasing raw materials, paying staff salaries and wages and paying utility bills such as electricity
These costs can be classified as follows:
Fixed costs
Variable costs
Total costs
Fixed costs
Fixed costs (FC) are costs that do not change as the level of output changes
These have to be paid whether the output is zero or 5000
Examples include rent, management salaries, insurance and bank loan repayments

Fixed costs can be plotted on a graph as a horizontal line
The fixed costs for this firm are $4,000 at all levels of output
Variable costs
Variable costs (VC) are costs that change directly with the output
These increase as output increases and vice versa
Examples include raw material costs and wages of workers directly involved in the production

Variable costs are plotted on a graph as an upwards sloping line, starting at 0
Total costs
The total cost is the sum of the variable and fixed costs
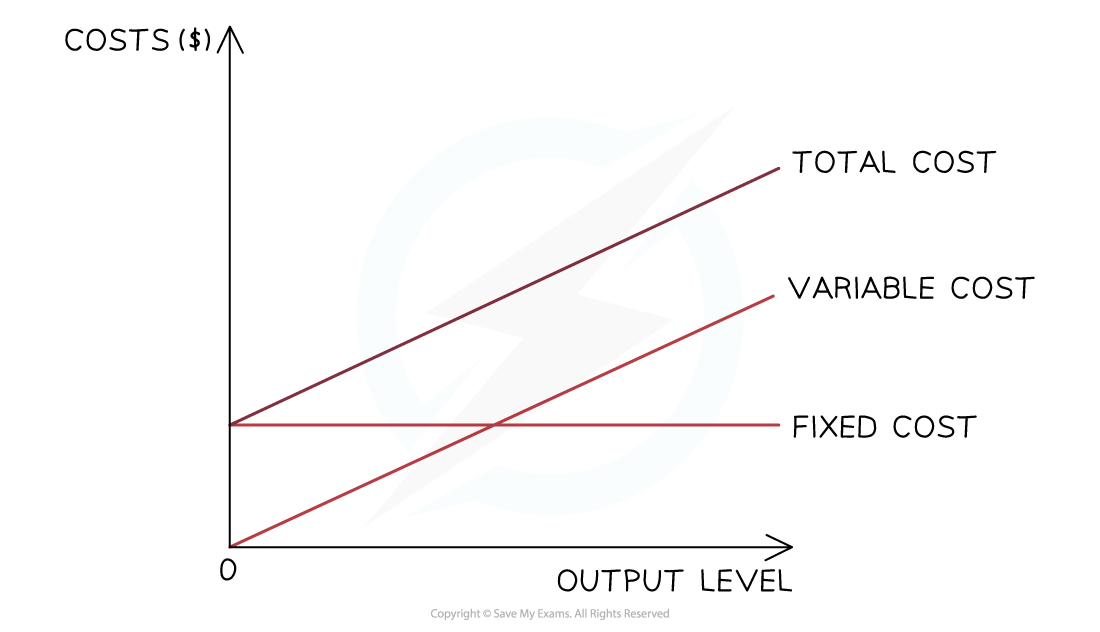
The total costs cannot be 0, as all firms have some level of fixed costs
Total costs are plotted on a graph as an upwards sloping line, parallel to the variable costs, starting at the level of fixed costs
Cost calculations
Cost formulas
Cost | Formula |
|---|---|
Total costs (TC) | |
Total variable cost (TVC) |
Applying formulas where VC = £60
Output (Q) | FC | TVC = | TC = |
|---|---|---|---|
0 | 200 | - | 200 |
1 | 200 | 60 | 260 |
2 | 200 | 120 | 320 |
3 | 200 | 180 | 380 |
Worked Example
Rosebud Aromas manufactures luxury scented candles. The production of each candle incurs the following costs
Item | £ per Candle |
Wax | 0.14 |
Perfume oil | 0.72 |
Loan repayment | 100 |
Glass jar | 1.46 |
Outer Packaging | 0.33 |
Calculate the variable cost in £ for each candle. (2)
Step 1: Identify the variable costs in the list
Loan repayment is classified as a fixed cost so should not be included in the calculation
Step 2: Total the variable costs listed
(2)
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Take care when calculating variable costs per unit, as it is likely that one or more fixed costs will be included in the list as seen above.
If you are asked to calculate the total variable costs, follow the above process and multiply the answer by the number of units produced/sold.
Reducing costs
An important way to improve profit is to reduce costs
Fixed costs may be reduced by relocating to cheaper business premises, reducing salaries for workers, spending less on promotional activities or seeking lower-priced utilities providers
Variable costs may be reduced by sourcing cheaper materials, buying raw materials and components in bulk or outsourcing distribution and packaging to a third party business
For example, many businesses sell their products via platforms such as Amazon which manages the packaging and shipping of items, usually at a cost much lower than that an independent business can achieve
Businesses must consider carefully the impacts of reducing costs on customer service, quality and speed of delivery
For example, paying lower salaries to staff may mean that employees have fewer customer service skills or experience
Cheaper raw materials and components may lead to worsening quality

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?