Risks & Uncertainty (AQA GCSE Business) : Revision Note
Key Business Risks
Business uncertainty is when a business cannot predict what is going to happen or directly influence it
All businesses face uncertainty
Uncertainty cannot be prepared for because it is unknown and cannot be measured
Factors that typically cause uncertainty include:
Environmental factors such as the Japanese Tsunami in March 2011
Economic changes such as Covid lockdowns, Brexit or collapses in the banking system
The entry of new competitors
Changes in local and national legislation (laws)
Changes in the political party governing the country
Risk can be measured, allowing business owners to make informed decisions before taking action
E.g. Awareness of increased demand for music on vinyl, extensive market research and a strong business plan convinced entrepreneurs Joel Magill and Will Greenham to set up Smugglers Records in the small seaside town of Deal
Diagram: Risk versus Uncertainty
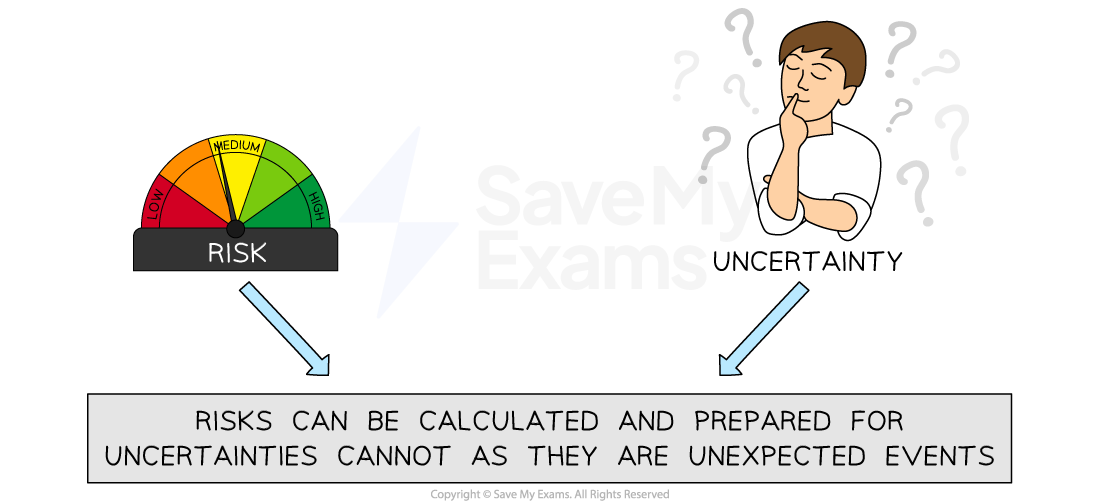
Whilst risk can be calculated and planned-for, uncertainty does not allow for preparation as it is based on the unexpected
Business risks can be classified as internal risks or external risks
Internal risks arise from inside of a business, over which the business often has a significant level of control
External risks are those outside of the business over which the business is likely to have less control
Examples of Internal and External Business Risks
Internal | External |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Business owners have varying levels of risk they are willing to accept
Risk-averse entrepreneurs may prefer to start small and achieve slow growth
Some entrepreneurs may prefer to share risks with others in a partnership or protect their personal assets by forming a private limited company
Successful entrepreneurs can manage risk and quickly respond to uncertainty in the business environment
An Example of Entrepreneurial Response to Uncertainty
|
|---|
|
Minimising Risks
Although some level of risk is to be expected, businesses can reduce the level of risk they face by taking a range of actions
Diagram: Ways to Reduce risk

Businesses can reduce risk by investing in training, careful business planning, using experts and carrying out research
Invest in training
Providing employees with the necessary skills, techniques and information can have a significant impact on risk reduction, as they will know how to respond when facing risks
E.g. Public relations training can improve communication with the media, whilst IT training can help workers understand how to protect the security of systems with which they work
Diversification
Developing new products and targeting different markets helps a business diversify into different markets and reduces the risk of overall failure
If a key market is affected by an unexpected event, resources can be focused on a different market, allowing business objectives to be met
Carry out research
Market research helps businesses find out what customers want, reducing the risk of developing products that fail to meet their needs
Business planning
Business planning involves detailed forecasting of what is likely to happen in the future
It can help businesses make appropriate decisions and prepare resources in anticipation of external events that could affect business success
Use experts
Taking on board the advice of business consultants and experts can aid business planning with a deeper understanding of risks
E.g. Finance consultants can improve understanding of economic factors that could impact a business, and help managers make appropriate decisions to avoid the worst impacts
Take out insurance
Businesses can purchase insurance policies that provide some protection against the most common risks, such as fire, floods and theft
Financial compensation can fund business recovery from these kinds of risks
Examiner Tips and Tricks
It is important to remember that risks cannot be eliminated, and uncertainty cannot be measured. Look for evidence in the case study that might indicate how well-prepared a business is to deal with the unexpected. A well-prepared business is more likely to recover quickly from setbacks, whilst a poorly-prepared business may struggle to survive.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?

