Resistant Bacteria (AQA GCSE Combined Science: Trilogy): Revision Note
Exam code: 8464
Did this video help you?
Mutations & Bacterial Evolution
The theory of evolution by natural selection is now widely accepted and many sources of data are now available to support the theory of evolution
One very clear piece of evidence for evolution is antibiotic resistance in bacteria
An antibiotic is a chemical that can kill or inhibit the growth and reproduction of bacteria
Antibiotics are extremely useful to humans as some bacteria are pathogenic and can cause life-threatening disease
Bacteria reproduce, on average, every 20 minutes and therefore evolution occurs in a much shorter time span
Like all other organisms, within a population, there will be variation caused by mutations
A chance mutation might cause some bacteria to become resistant to an antibiotic (eg penicillin)
When the population is treated with this antibiotic, the resistant bacteria do not die
This means they can continue to reproduce with less competition from non-resistant bacteria, which are now dead
Therefore the genes for antibiotic resistance are passed on with a much greater frequency to the next generation
Over time the whole population of bacteria becomes antibiotic-resistant because the bacteria are best suited to their environment
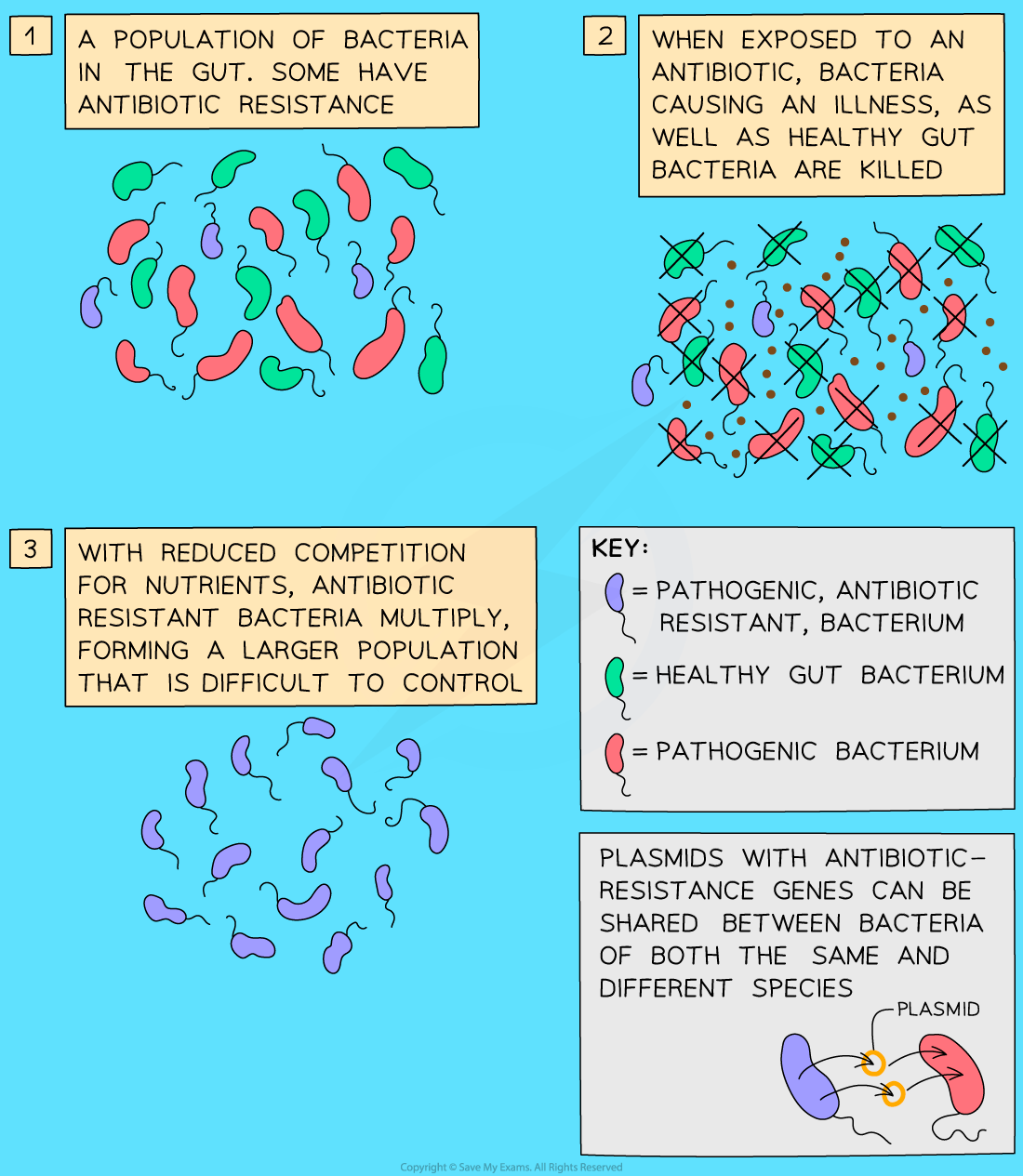
Development of antibiotic resistance in bacteria
This is an example of natural selection that humans have helped to develop due to overuse of antibiotics in situations where they were not really necessary, for example:
For the treatment of non-serious infections
Routine treatment to animals in agriculture
Failure to finish the prescribed course of antibiotics
MRSA
Increases in the population of antibiotic-resistant bacteria cause infections and diseases which are harder to control as it is difficult to find antibiotics that certain strains of bacteria are not resistant to
An example of this is MRSA, a very dangerous bacterial strain that is resistant to most antibiotics
If someone gets infected with MRSA they cannot be treated easily
Antibiotic Development
The increase we are currently seeing in antibiotic resistance is encouraging drug companies to develop new antibiotics that are effective against these new resistant strains, such as MRSA
However, the number of new antibiotics discovered has slowed significantly
Developing new antibiotics is also a very costly process
Some scientists are worried we may not be able to keep up with the demand for new antibiotics, as more and more antibiotic-resistant strains evolve

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?